Genetic variants predicting warfarin sensitivity
A warfarin-sensitive technology, applied in the field of warfarin, can solve the problems of unexplainable diversity, unexplainable warfarin dose diversity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0126] Example 1. Among the selected Chinese patients with warfarin sensitivity or resistance CYP2C9 and VKORC1 DNA sequence variants
[0127] The average maintenance dose of warfarin for Chinese is 3.3mg / day [8,9]. We therefore considered warfarin-sensitive patients receiving maintenance doses ≤1.5 mg / day (see 1, 11 patients) and warfarin-resistant patients receiving maintenance doses ≥6 mg / day (see Table 1, 5 patients, see Materials and Methods, supra). Sequencing of the coding region, exon-intron junctions, and promoter regions of the CYP2C9 gene revealed three sequence variants in 4 of 11 warfarin-sensitive patients. The variations are: 1075A>C (I359L is CYP2C9*3), 895A>G (T299A) and 1145C>T (P382L). CYP2C9*3 was detected in 3 patients (see Table 1, subjects 1, 3, 5). In addition to CYP2C9*3, subject 5 also had 895A>G (T299A) changes, as mentioned above [7]. A novel exonic mutation 1145C>T (P382L) was detected in a fourth patient (individual 6). As shown in Table ...
Embodiment 2
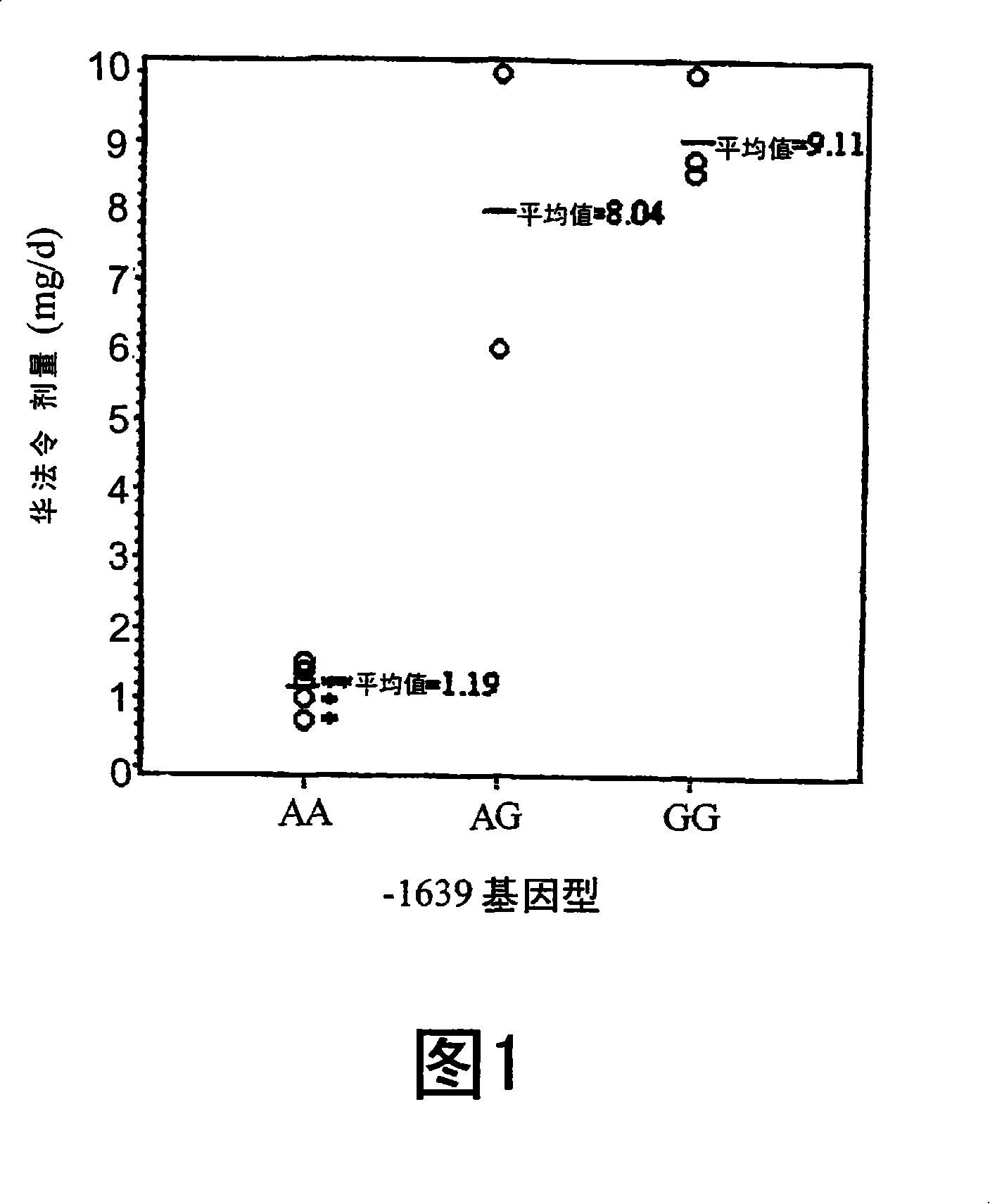
[0133] Example 2. VKORC1-1639G>A among random Chinese patients receiving warfarin polymorphism
[0134] To further investigate whether the -1639G>A polymorphism was associated with interindividual differences in warfarin dose, we genotyped 104 patients receiving warfarin regardless of dose using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. The AA and AG / GG groups did not differ in terms of age, sex and INR (see Table 2). Only two patients were found to be homozygous for GG and were included in the AG population for statistical analysis. We analyzed the data without considering the presence of other confounding variables, such as diet or other medications. As shown in Table 2, the AA group had significantly lower dose requirements (2.61 mg / day) compared to the AG / GG group (3.81 mg / day). This difference was significant between the AA and AG / GG populations whether using the T-test (p<0.0001) or the Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test (p=0.0002).
[0135] Table 2. Mean doses of patients randomly se...
Embodiment 3
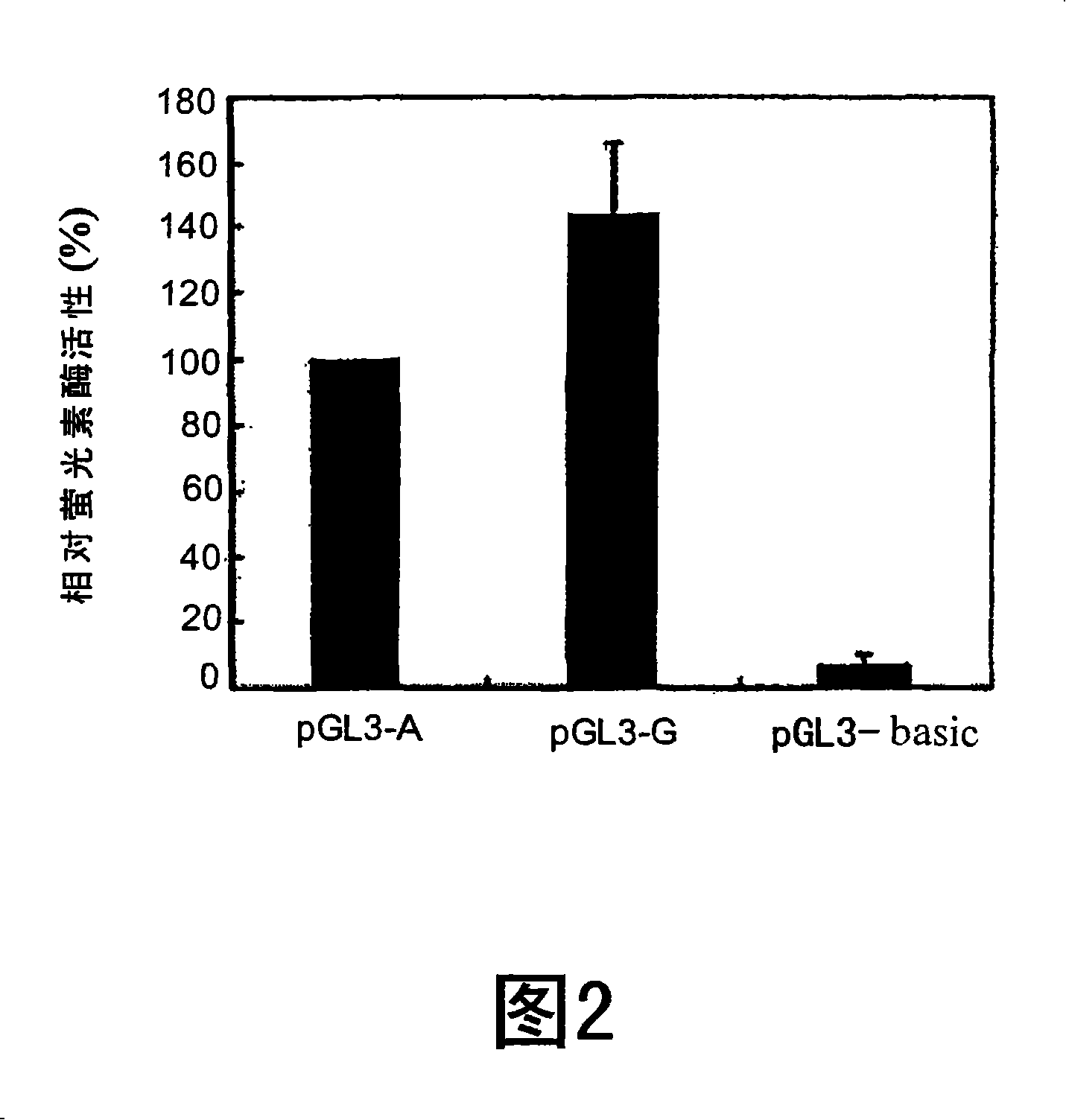
[0138] Example 3, VKORC1-1639 G>A polymorphism of Chinese and Caucasians and Genotype frequency of CYP2C9 variants
[0139] The Chinese population is known to have much lower maintenance doses of warfarin than Caucasians. To test whether frequency differences in VKORC1-1639 genotypes could explain interethnic differences in warfarin dosing, 95 normal Han Chinese subjects and 92 normal Caucasian subjects were genotyped. In the Caucasian population, AA homozygosity had the lowest frequency, while AG and GG genotypes accounted for the majority of the population (14.2%, 46.7%, and 39.1%, respectively) (see Table 3). On the contrary, in the Chinese population, homozygous AA accounted for the majority (82.1%) of the population, and the rest were AG heterozygous (17.9%). No GG homozygotes were found in randomly selected populations. This proportion was similar to that of 104 warfarin-treated patients, of which 79.8% were homozygous for AA, 18.3% were heterozygous for AG, and on...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com