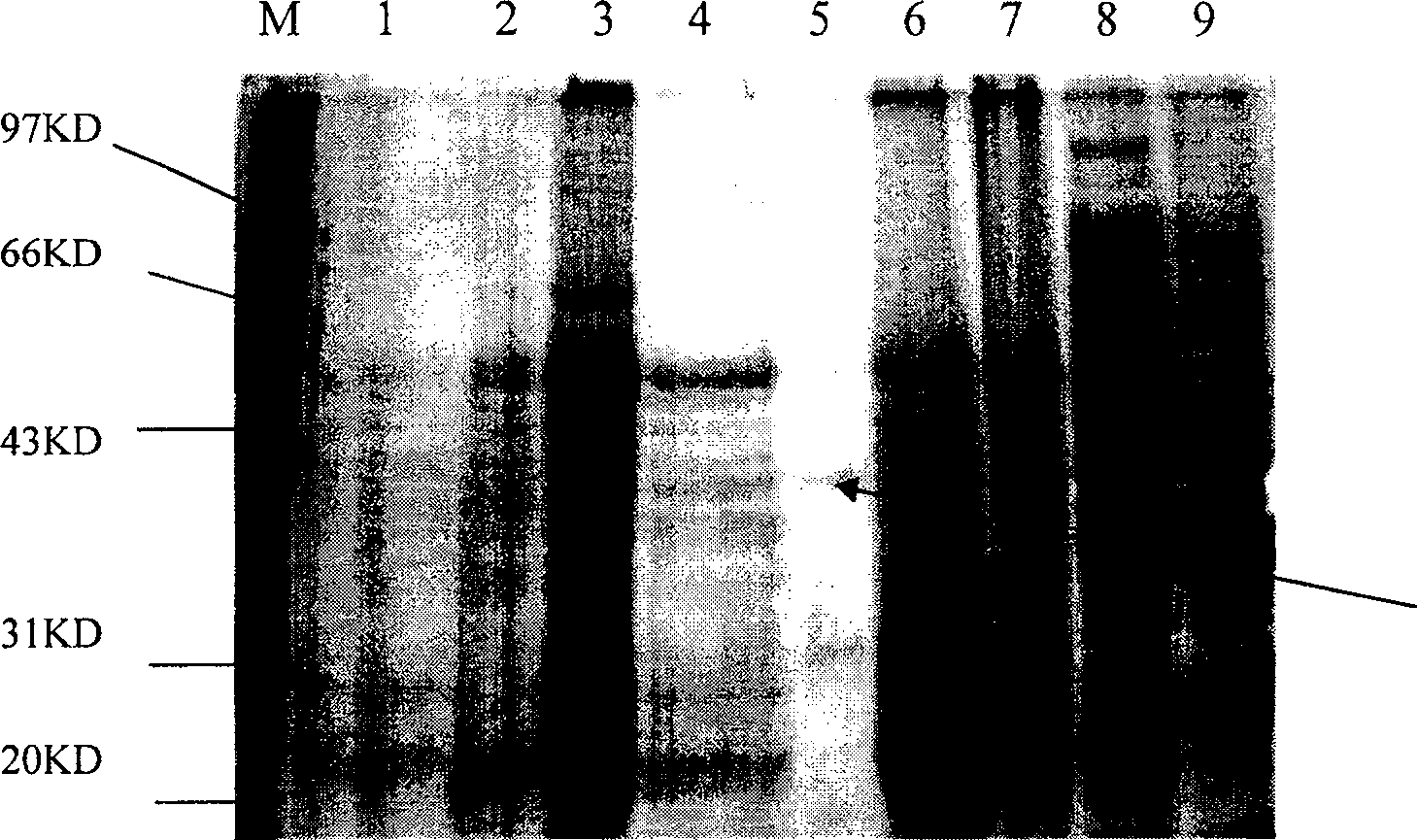Ethyl chrysanthemate esterase and coding gene and specific engineering baterium for expression and uses of the enzyme
A technology of ethyl chrysanthemum acid esterase and coding gene, which is applied in the direction of genetic engineering, microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem of low enzyme activity of ethyl chrysanthemum acid esterase, and achieve high practicability And the effects of generalizability, easy industrialization, and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Embodiment 1, the cloning of ethyl chrysanthemum acid esterase gene ECE1
[0041] 1. PCR amplification of ethyl chrysanthemic acid esterase gene
[0042] According to the nucleotide sequence (GenBank number: L22516) of the disclosed ethyl chrysanthemic acid esterase gene, primers are designed, and the primer sequences are as follows:
[0043] ECE-UP (upstream primer): 5'-GAGCT CCATGG ATGCACAGACGATTGCC-3';
[0044] ECE-Down (downstream primer): 5'-GAAGACTCCTACTGAGCCAGTTCGG-3'
[0045] Wherein, the upstream primer introduces the restriction endonuclease NcoI recognition sequence (underlined base), and changes the start codon "GTG" of the chrysanthemum acid ethyl esterase gene to "ATG". Using the genomic DNA of Arthrobacter globiformis as a template, under the guidance of primer ECE-UP and primer ECE-Down, PCR amplified ethyl chrysanthemum acid esterase gene. The PCR reaction system is: 1 μl of Arthrobacter annulus bacteria solution treated with ultrasonic treatment f...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Embodiment 2, the construction of special-purpose expression engineering bacteria for ECE1
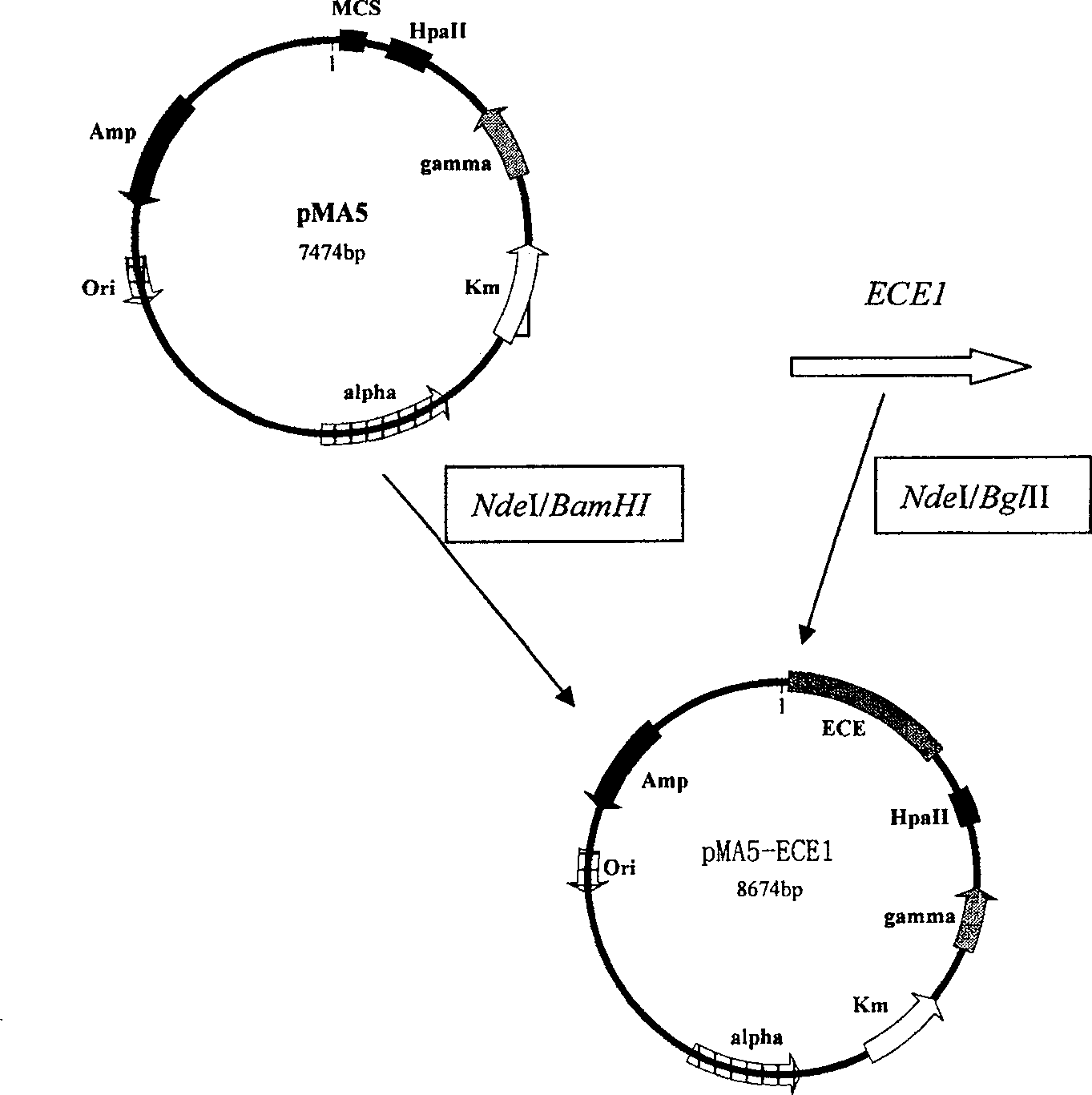
[0053] 1. Construction of the special expression vector pMA5-ECE1 for ECE1
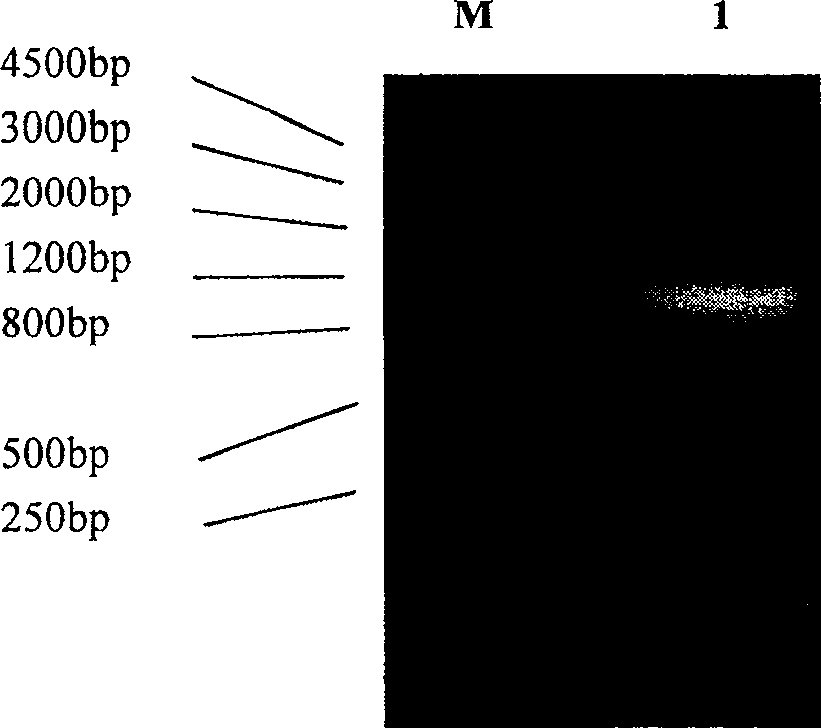
[0054] Such as figure 2 As shown, the construction method of the special expression vector pMA5-ECE1 for ECE1 is as follows: Precipitate with absolute ethanol and recover the ECE1 amplified by PCR in Example 1, cut it with restriction endonucleases NdeI and BglII, and combine with T 4 DNA ligase ligation, the ligation product was transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α, and the transformant was selected to extract the plasmid after screening, and the restriction endonuclease NdeI and XbaI were used for enzyme digestion and identification, and the 1100bp fragment obtained by enzyme digestion was a positive clone, and then positive The cloned plasmid was further identified by PCR. The primers used were primer 1 and primer 2 in Example 1, and the PCR product was sequenced. The sequencing results showed t...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Embodiment 3, ECE1 expression in Bacillus subtilis and the mensuration of enzyme activity
[0058] 1. Expression of ECE1 in Bacillus subtilis
[0059]Common Bacillus subtilis medium formula: 2-3% yeast extract, 1-2% peptone, 0.1-0.2% K per 1000mL water 2 HPO 4 .3H 2 O, 0.1% KH 2 PO 4 , 1% NaCl.
[0060] Inoculate the BsMA5-ECE1 special-purpose expression engineered bacterium BsMA5-ECE1 constructed in Example 2 in common Bacillus subtilis culture medium, and continuously culture it at 37°C for 120 hours to transform Bacillus subtilis DB1342 with pMA5 empty vector and Escherichia coli transformed with ECE1 BL21(DE3)plys (cloning ECE1 into the vector pET26 (Navagen Company) to obtain an Escherichia coli expression vector containing ECE1, named pET26-ECE1, and then transforming pET26-ECE1 into Escherichia coli BL21(DE3)plys, obtained by screening Positive clone transformant, the fermentation culture condition is 12h under 37 ℃.) as the control. On the third day, samp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com