Self-adaptive space-time filter for human vision system model
A human visual system, spatiotemporal filtering technology, applied in the field of video processing, can solve the problems of gross error of perceived contrast, no consideration of time factor, no consideration of nonlinearity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
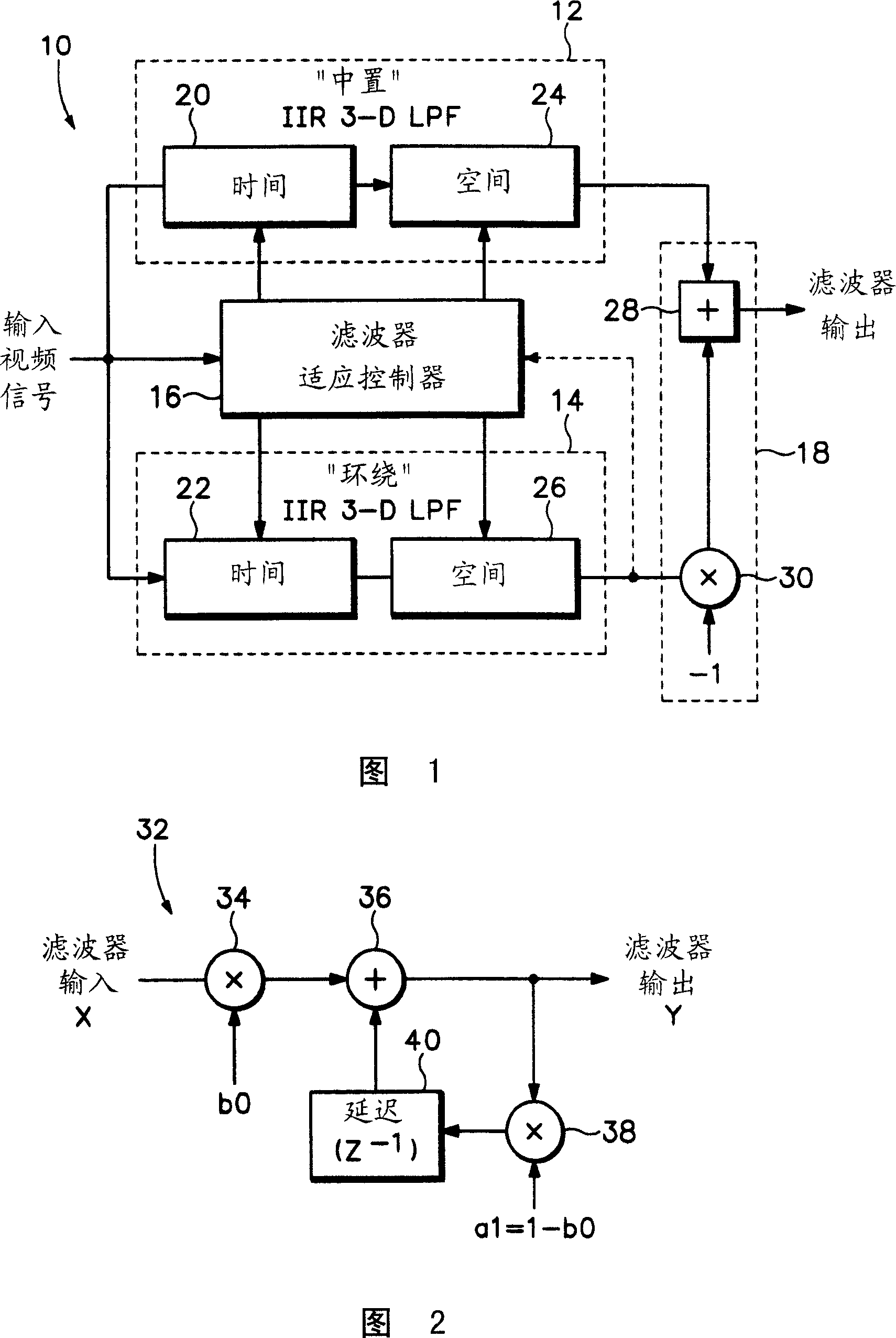
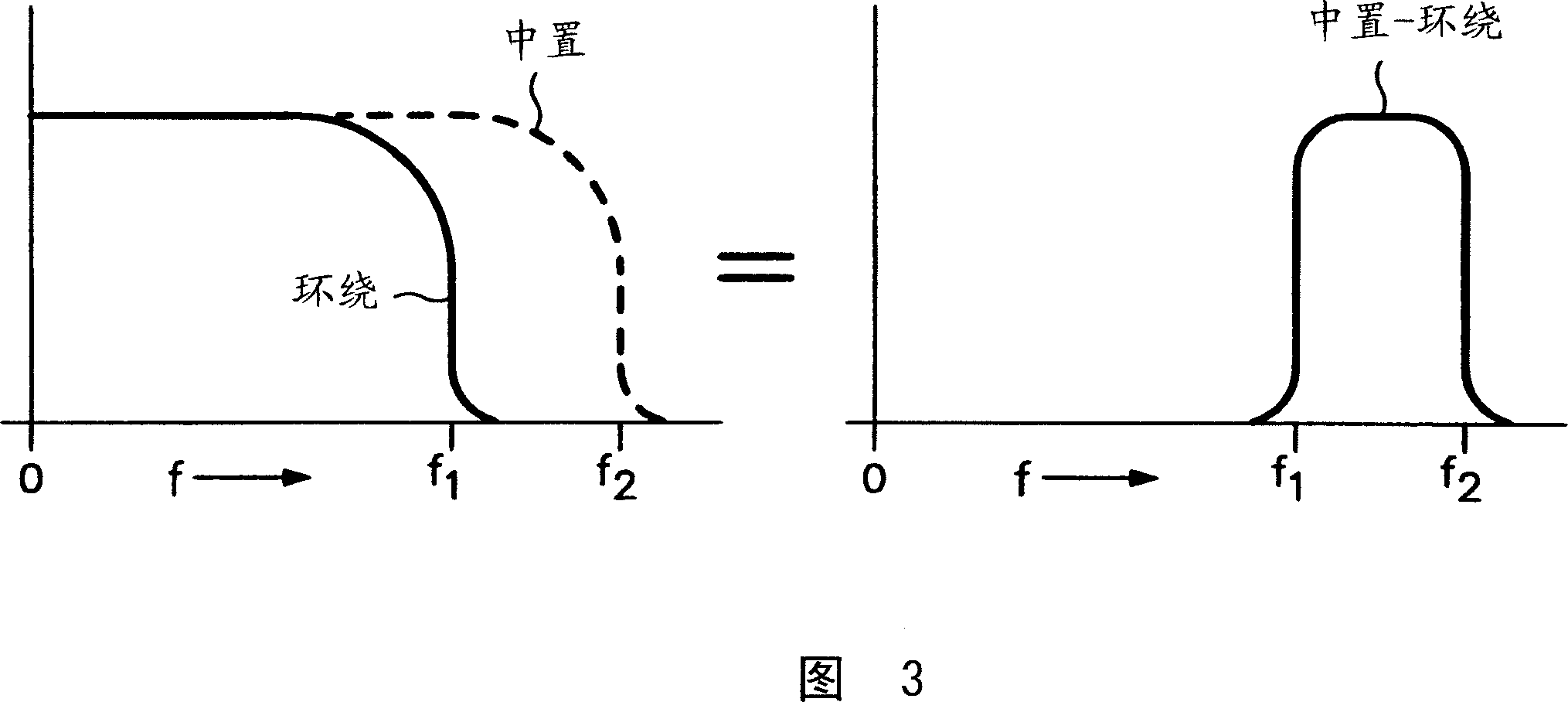
[0013] Referring now to the adaptive three-dimensional (3-D) filter 10 shown in FIG. 1 , it passes the principal of the accuracy of the HVS model with the equivalent non-HVS model, as according to the weighted SNR as described by T. Hamada et al. Algorithm (Picture Quality Assessment System by Three-Layered Bottom-Up NoiseWeighting Considering Human Visual Perception, SMPTE journal, January 1999, pgs20-26), combined with improvements to existing filters for the Human Visual System (HVS) model . The filter 10 has a pair of adaptive 3-D filters 12, 14, "center" and "surround" filters, which receive coefficients from a filter adaptation controller 16 as a coefficient generator. The input video signal is input to filters 12 , 14 and filter adaptive controller 16 . Outputs of the filters 12 , 14 are input to a differential circuit 18 . The output of the center filter 12 or the surround filter 14 is also input to a filter adaptive controller 16 . A filter adaptive controller 16 g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com