What are the Implications of 5G UC for Enhanced Global Trade Agreements?
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
5G UC Background and Objectives
5G Ultra-Capacity (UC) represents a significant leap in mobile network technology, offering unprecedented speeds, low latency, and massive connectivity. This advanced iteration of 5G technology has emerged as a critical enabler for enhanced global trade agreements, promising to revolutionize international commerce and economic cooperation.
The evolution of mobile networks from 1G to 5G has been marked by exponential improvements in data transmission speeds and network capacity. 5G UC, in particular, leverages high-band spectrum to deliver peak data rates of up to 20 Gbps, a substantial increase from its predecessors. This technological advancement aims to support a wide array of applications crucial for global trade, including real-time data exchange, remote operations, and seamless cross-border transactions.
The primary objective of 5G UC in the context of global trade agreements is to facilitate faster, more efficient, and more secure international business operations. By providing ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), 5G UC enables near-instantaneous data transfer across vast distances, potentially transforming supply chain management, customs procedures, and financial transactions on a global scale.
Another key goal of 5G UC is to enhance the capabilities of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in international trade. With its ability to support up to 1 million connected devices per square kilometer, 5G UC can enable sophisticated tracking and monitoring systems for goods in transit, improving transparency and reducing the risk of fraud or loss in cross-border trade.
The technology also aims to bridge the digital divide between developed and developing nations, potentially leading to more inclusive global trade agreements. By providing high-speed connectivity to remote areas, 5G UC could open up new markets and opportunities for businesses worldwide, fostering economic growth and international cooperation.
Furthermore, 5G UC technology seeks to address security concerns in global trade by offering enhanced encryption and network slicing capabilities. These features aim to protect sensitive trade data and ensure the integrity of cross-border transactions, building trust among trading partners and facilitating smoother negotiations of international agreements.
As we examine the implications of 5G UC for enhanced global trade agreements, it is crucial to consider both the technological advancements and the broader economic and geopolitical context. The deployment of 5G UC infrastructure is expected to be a key factor in shaping future trade policies, potentially influencing everything from intellectual property rights to data sovereignty regulations.
The evolution of mobile networks from 1G to 5G has been marked by exponential improvements in data transmission speeds and network capacity. 5G UC, in particular, leverages high-band spectrum to deliver peak data rates of up to 20 Gbps, a substantial increase from its predecessors. This technological advancement aims to support a wide array of applications crucial for global trade, including real-time data exchange, remote operations, and seamless cross-border transactions.
The primary objective of 5G UC in the context of global trade agreements is to facilitate faster, more efficient, and more secure international business operations. By providing ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC), 5G UC enables near-instantaneous data transfer across vast distances, potentially transforming supply chain management, customs procedures, and financial transactions on a global scale.
Another key goal of 5G UC is to enhance the capabilities of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in international trade. With its ability to support up to 1 million connected devices per square kilometer, 5G UC can enable sophisticated tracking and monitoring systems for goods in transit, improving transparency and reducing the risk of fraud or loss in cross-border trade.
The technology also aims to bridge the digital divide between developed and developing nations, potentially leading to more inclusive global trade agreements. By providing high-speed connectivity to remote areas, 5G UC could open up new markets and opportunities for businesses worldwide, fostering economic growth and international cooperation.
Furthermore, 5G UC technology seeks to address security concerns in global trade by offering enhanced encryption and network slicing capabilities. These features aim to protect sensitive trade data and ensure the integrity of cross-border transactions, building trust among trading partners and facilitating smoother negotiations of international agreements.
As we examine the implications of 5G UC for enhanced global trade agreements, it is crucial to consider both the technological advancements and the broader economic and geopolitical context. The deployment of 5G UC infrastructure is expected to be a key factor in shaping future trade policies, potentially influencing everything from intellectual property rights to data sovereignty regulations.
Global Trade Market Analysis
The global trade market has experienced significant transformations in recent years, driven by technological advancements and changing economic landscapes. The introduction of 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) technology is poised to further revolutionize international commerce, offering unprecedented opportunities for enhanced trade agreements and market expansion.
5G UC's impact on global trade is multifaceted, affecting various sectors and facilitating new forms of economic cooperation. The technology's ultra-high-speed connectivity and low latency enable real-time data exchange, which is crucial for seamless cross-border transactions and supply chain management. This enhanced communication infrastructure supports more efficient logistics, inventory tracking, and just-in-time manufacturing processes, potentially reducing trade barriers and operational costs.
The adoption of 5G UC in global trade is expected to accelerate the growth of e-commerce and digital marketplaces. With faster and more reliable internet connections, businesses can expand their reach to international customers, offering immersive shopping experiences through augmented and virtual reality technologies. This expansion of digital trade platforms may lead to the development of new trade agreements focused on data flow, digital services, and intellectual property rights in the digital realm.
Furthermore, 5G UC technology is set to revolutionize customs and border control processes. Advanced IoT sensors and AI-powered systems can streamline cargo inspections, reduce processing times, and enhance security measures. These improvements could lead to the negotiation of new trade agreements that emphasize the use of smart border technologies and harmonized digital documentation standards.
The financial sector stands to benefit significantly from 5G UC, potentially reshaping international financial transactions and trade financing. The technology enables faster and more secure cross-border payments, real-time currency exchanges, and innovative blockchain-based trade finance solutions. As a result, new trade agreements may emerge that focus on digital financial services, cryptocurrency regulations, and cross-border fintech collaborations.
5G UC also has the potential to transform agriculture and food trade. Precision farming techniques enabled by 5G networks can increase crop yields and quality, while improved traceability systems can enhance food safety standards. This may lead to the development of trade agreements that address agricultural technology sharing, sustainable farming practices, and food security measures on a global scale.
In the manufacturing sector, 5G UC facilitates the implementation of Industry 4.0 concepts, such as smart factories and autonomous production lines. This advancement in manufacturing capabilities could reshape global supply chains and lead to new trade agreements focused on advanced manufacturing cooperation, technology transfer, and standards for smart industrial systems.
5G UC's impact on global trade is multifaceted, affecting various sectors and facilitating new forms of economic cooperation. The technology's ultra-high-speed connectivity and low latency enable real-time data exchange, which is crucial for seamless cross-border transactions and supply chain management. This enhanced communication infrastructure supports more efficient logistics, inventory tracking, and just-in-time manufacturing processes, potentially reducing trade barriers and operational costs.
The adoption of 5G UC in global trade is expected to accelerate the growth of e-commerce and digital marketplaces. With faster and more reliable internet connections, businesses can expand their reach to international customers, offering immersive shopping experiences through augmented and virtual reality technologies. This expansion of digital trade platforms may lead to the development of new trade agreements focused on data flow, digital services, and intellectual property rights in the digital realm.
Furthermore, 5G UC technology is set to revolutionize customs and border control processes. Advanced IoT sensors and AI-powered systems can streamline cargo inspections, reduce processing times, and enhance security measures. These improvements could lead to the negotiation of new trade agreements that emphasize the use of smart border technologies and harmonized digital documentation standards.
The financial sector stands to benefit significantly from 5G UC, potentially reshaping international financial transactions and trade financing. The technology enables faster and more secure cross-border payments, real-time currency exchanges, and innovative blockchain-based trade finance solutions. As a result, new trade agreements may emerge that focus on digital financial services, cryptocurrency regulations, and cross-border fintech collaborations.
5G UC also has the potential to transform agriculture and food trade. Precision farming techniques enabled by 5G networks can increase crop yields and quality, while improved traceability systems can enhance food safety standards. This may lead to the development of trade agreements that address agricultural technology sharing, sustainable farming practices, and food security measures on a global scale.
In the manufacturing sector, 5G UC facilitates the implementation of Industry 4.0 concepts, such as smart factories and autonomous production lines. This advancement in manufacturing capabilities could reshape global supply chains and lead to new trade agreements focused on advanced manufacturing cooperation, technology transfer, and standards for smart industrial systems.
5G UC Challenges and Opportunities
The deployment of 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) networks presents both significant challenges and opportunities for enhanced global trade agreements. One of the primary challenges lies in the substantial infrastructure investments required to implement 5G UC technology on a global scale. This includes the need for extensive fiber optic networks, small cell deployments, and spectrum allocation, which can be particularly challenging for developing nations with limited resources.
Interoperability and standardization pose another significant hurdle. As different countries and regions adopt varying 5G UC standards and technologies, ensuring seamless cross-border connectivity and data exchange becomes crucial for facilitating global trade. This challenge is further compounded by cybersecurity concerns, as the increased connectivity and data flow associated with 5G UC networks create new vulnerabilities that need to be addressed through robust security protocols and international cooperation.
Regulatory challenges also emerge, as nations grapple with issues such as data sovereignty, privacy protection, and fair competition in the digital economy. Harmonizing these regulations across different jurisdictions is essential for creating a conducive environment for global trade agreements in the 5G UC era.
Despite these challenges, 5G UC technology offers unprecedented opportunities for enhancing global trade. The ultra-low latency and high bandwidth capabilities of 5G UC networks can revolutionize supply chain management, enabling real-time tracking, monitoring, and optimization of goods movement across borders. This can lead to significant improvements in logistics efficiency and reduced trade costs.
Furthermore, 5G UC can facilitate the growth of digital trade by enabling new services and business models. Advanced technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) can be leveraged for remote collaboration, virtual product demonstrations, and immersive e-commerce experiences, potentially transforming international business interactions and negotiations.
The technology also has the potential to bridge the digital divide between developed and developing nations. By providing high-speed connectivity to previously underserved areas, 5G UC can create new opportunities for businesses in emerging markets to participate in global trade on a more equal footing.
Lastly, 5G UC can enhance the implementation and enforcement of trade agreements through improved data analytics and real-time monitoring capabilities. This can lead to more transparent and efficient customs processes, reduced trade barriers, and better compliance with international trade regulations.
Interoperability and standardization pose another significant hurdle. As different countries and regions adopt varying 5G UC standards and technologies, ensuring seamless cross-border connectivity and data exchange becomes crucial for facilitating global trade. This challenge is further compounded by cybersecurity concerns, as the increased connectivity and data flow associated with 5G UC networks create new vulnerabilities that need to be addressed through robust security protocols and international cooperation.
Regulatory challenges also emerge, as nations grapple with issues such as data sovereignty, privacy protection, and fair competition in the digital economy. Harmonizing these regulations across different jurisdictions is essential for creating a conducive environment for global trade agreements in the 5G UC era.
Despite these challenges, 5G UC technology offers unprecedented opportunities for enhancing global trade. The ultra-low latency and high bandwidth capabilities of 5G UC networks can revolutionize supply chain management, enabling real-time tracking, monitoring, and optimization of goods movement across borders. This can lead to significant improvements in logistics efficiency and reduced trade costs.
Furthermore, 5G UC can facilitate the growth of digital trade by enabling new services and business models. Advanced technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) can be leveraged for remote collaboration, virtual product demonstrations, and immersive e-commerce experiences, potentially transforming international business interactions and negotiations.
The technology also has the potential to bridge the digital divide between developed and developing nations. By providing high-speed connectivity to previously underserved areas, 5G UC can create new opportunities for businesses in emerging markets to participate in global trade on a more equal footing.
Lastly, 5G UC can enhance the implementation and enforcement of trade agreements through improved data analytics and real-time monitoring capabilities. This can lead to more transparent and efficient customs processes, reduced trade barriers, and better compliance with international trade regulations.
Current 5G UC Trade Solutions
01 5G Ultra-Capacity Network Architecture
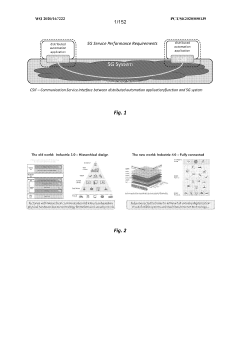
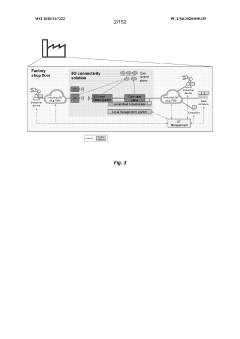
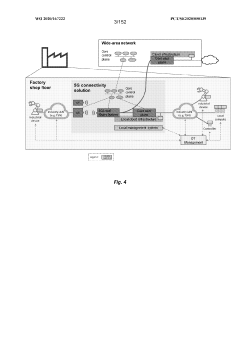
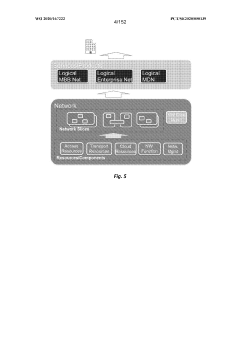
5G UC refers to an advanced network architecture that utilizes mid-band and high-band spectrum to deliver enhanced capacity, speed, and coverage. This technology enables higher data rates, lower latency, and improved network performance compared to standard 5G networks.- 5G Ultra-Capacity Network Architecture: 5G UC refers to an advanced network architecture that enables ultra-high capacity and low latency in 5G networks. It utilizes a combination of mid-band and high-band spectrum to deliver enhanced performance, including faster data speeds and improved network responsiveness. This architecture supports a wide range of applications, from enhanced mobile broadband to mission-critical communications.
- Spectrum Management for 5G UC: Efficient spectrum management is crucial for 5G UC networks. This involves techniques for dynamic spectrum allocation, carrier aggregation, and spectrum sharing to maximize the use of available frequency bands. Advanced algorithms and AI-based solutions are employed to optimize spectrum utilization and enhance network capacity.
- Massive MIMO and Beamforming in 5G UC: 5G UC leverages massive MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) technology and advanced beamforming techniques to improve spectral efficiency and network coverage. These technologies enable the creation of focused beams of data, enhancing signal quality and reducing interference in dense urban environments.
- Edge Computing Integration with 5G UC: The integration of edge computing with 5G UC networks enables processing of data closer to the source, reducing latency and improving overall network performance. This combination supports real-time applications, IoT devices, and services requiring ultra-low latency, such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation.
- Network Slicing in 5G UC: Network slicing is a key feature of 5G UC, allowing the creation of multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure. This enables operators to tailor network resources to specific use cases and service requirements, optimizing performance for different applications and ensuring efficient resource allocation.
02 Spectrum Utilization in 5G UC
5G Ultra-Capacity networks leverage a combination of mid-band (typically 2.5 GHz to 6 GHz) and high-band (mmWave) spectrum to maximize capacity and throughput. This approach allows for efficient use of available spectrum resources and supports a wide range of 5G applications and services.Expand Specific Solutions03 5G UC Network Optimization Techniques
Various optimization techniques are employed in 5G UC networks to enhance performance and efficiency. These may include advanced beamforming, massive MIMO, carrier aggregation, and dynamic spectrum sharing, which collectively contribute to improved network capacity and user experience.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of 5G UC with Existing Infrastructure
5G Ultra-Capacity networks are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing 4G LTE and early 5G infrastructure. This integration allows for efficient resource allocation, improved coverage, and smoother transitions between different network technologies, ensuring a consistent user experience.Expand Specific Solutions05 5G UC Device and Equipment Innovations
The development of 5G UC networks has driven innovations in device and equipment design. This includes advanced antenna systems, improved power management techniques, and enhanced signal processing capabilities to fully leverage the benefits of Ultra-Capacity networks and support high-bandwidth applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key 5G UC Industry Players
The 5G UC (Ultra Capacity) technology landscape is in a rapid growth phase, with significant market potential and increasing technological maturity. The competitive landscape is characterized by intense rivalry among major players such as Ericsson, Qualcomm, Samsung, and Huawei, who are driving innovation and infrastructure development. These companies are investing heavily in R&D to enhance 5G capabilities, focusing on improving network speed, capacity, and reliability. The market is expected to expand substantially as 5G UC technology becomes more widely adopted, potentially revolutionizing global trade through enhanced connectivity and data transfer capabilities. As the technology matures, we can anticipate increased collaboration between telecom providers, equipment manufacturers, and software developers to create comprehensive solutions that leverage 5G UC for international trade facilitation.
Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
Technical Solution: Ericsson's 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) technology focuses on enhancing global trade agreements through improved connectivity and network capabilities. Their solution integrates advanced spectrum utilization techniques, massive MIMO, and network slicing to provide tailored services for different trade sectors[1]. Ericsson's 5G UC enables ultra-low latency communication, which is crucial for real-time logistics tracking and smart customs operations[3]. The company has also developed AI-powered predictive analytics tools that can optimize supply chain management and facilitate smoother cross-border transactions[5].
Strengths: Global presence, extensive 5G infrastructure experience, and strong R&D capabilities. Weaknesses: High implementation costs and potential geopolitical challenges in certain markets.
QUALCOMM, Inc.
Technical Solution: Qualcomm's approach to 5G UC for enhanced global trade agreements centers on their advanced chipset solutions and modems. Their Snapdragon X65 5G Modem-RF System supports mmWave and sub-6 GHz bands, enabling high-speed, low-latency connections crucial for international trade operations[2]. Qualcomm's technology facilitates seamless IoT integration in global supply chains, allowing for real-time tracking and management of goods across borders[4]. Their 5G UC solutions also incorporate advanced security features, such as enhanced encryption and network slicing, to protect sensitive trade data and ensure compliance with international regulations[6].
Strengths: Leading position in 5G chipset technology, strong patent portfolio. Weaknesses: Dependence on smartphone market, potential regulatory challenges in some countries.
Core 5G UC Trade Innovations
Industrial automation with 5g and beyond
PatentWO2020167222A2
Innovation
- The integration of 5G wireless networks with Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) techniques, including methods for establishing TSN data streams, configuring data packets, and managing radio resources, to provide deterministic and reliable communication services within industrial environments.
Base station, terminal, and communication method
PatentPendingUS20250151034A1
Innovation
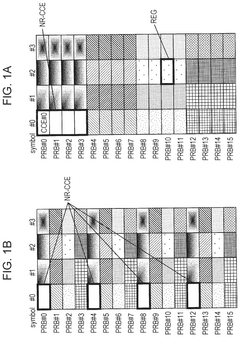
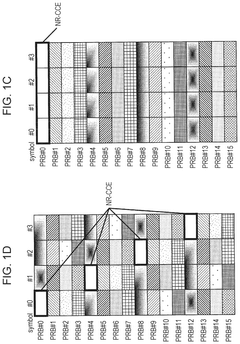
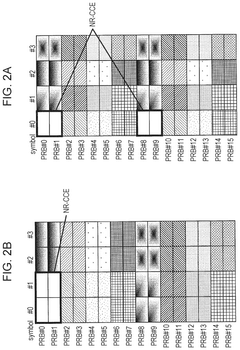
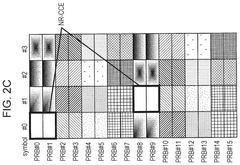
- The solution involves allocating downlink control signals to a control channel region constituted by a plurality of CCEs, where the number of resource element groups (REGs) per CCE is a power of 2, and the bundling size indicating the number of REGs included in the REGs that constitute the CCE and arranged in adjacent resource blocks is also a power of 2.
Regulatory Framework for 5G UC
The regulatory framework for 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) is a critical aspect of its implementation and impact on global trade agreements. As 5G UC technology continues to evolve and expand, governments and international organizations are working to establish comprehensive regulations to ensure its safe and effective deployment.
One of the primary concerns in the regulatory landscape is spectrum allocation. Regulatory bodies are tasked with managing the limited radio frequency spectrum to accommodate 5G UC networks while avoiding interference with existing services. This process involves coordinating with multiple stakeholders, including telecommunications companies, satellite operators, and other spectrum users.
Security and privacy regulations play a crucial role in the 5G UC framework. As the technology enables more connected devices and facilitates the transfer of sensitive data, regulators are implementing stringent measures to protect user information and prevent cyber attacks. These regulations often include requirements for end-to-end encryption, data localization, and regular security audits.
Interoperability standards are another key component of the regulatory framework. To ensure seamless global connectivity and support international trade, regulatory bodies are working to harmonize technical specifications across different regions. This includes efforts to align frequency bands, network protocols, and equipment standards.
Environmental regulations are also being developed to address the potential impact of 5G UC infrastructure. These include guidelines for energy efficiency, electromagnetic radiation exposure limits, and the responsible deployment of small cell networks in urban areas.
Cross-border data flow regulations are particularly relevant to global trade agreements. Regulators are working to balance the need for free data exchange with national security concerns and data privacy requirements. This involves establishing clear rules for data localization, cross-border data transfers, and international data sharing agreements.
The regulatory framework also addresses competition and market access issues. Antitrust regulations are being adapted to prevent monopolistic practices in the 5G UC ecosystem, while also encouraging innovation and investment. This includes measures to promote fair spectrum allocation, network sharing agreements, and open access to essential infrastructure.
As 5G UC technology continues to advance, regulatory bodies are adopting flexible approaches to keep pace with innovation. This includes the use of regulatory sandboxes, which allow for controlled testing of new technologies and business models in real-world environments, helping to inform future regulatory decisions.
One of the primary concerns in the regulatory landscape is spectrum allocation. Regulatory bodies are tasked with managing the limited radio frequency spectrum to accommodate 5G UC networks while avoiding interference with existing services. This process involves coordinating with multiple stakeholders, including telecommunications companies, satellite operators, and other spectrum users.
Security and privacy regulations play a crucial role in the 5G UC framework. As the technology enables more connected devices and facilitates the transfer of sensitive data, regulators are implementing stringent measures to protect user information and prevent cyber attacks. These regulations often include requirements for end-to-end encryption, data localization, and regular security audits.
Interoperability standards are another key component of the regulatory framework. To ensure seamless global connectivity and support international trade, regulatory bodies are working to harmonize technical specifications across different regions. This includes efforts to align frequency bands, network protocols, and equipment standards.
Environmental regulations are also being developed to address the potential impact of 5G UC infrastructure. These include guidelines for energy efficiency, electromagnetic radiation exposure limits, and the responsible deployment of small cell networks in urban areas.
Cross-border data flow regulations are particularly relevant to global trade agreements. Regulators are working to balance the need for free data exchange with national security concerns and data privacy requirements. This involves establishing clear rules for data localization, cross-border data transfers, and international data sharing agreements.
The regulatory framework also addresses competition and market access issues. Antitrust regulations are being adapted to prevent monopolistic practices in the 5G UC ecosystem, while also encouraging innovation and investment. This includes measures to promote fair spectrum allocation, network sharing agreements, and open access to essential infrastructure.
As 5G UC technology continues to advance, regulatory bodies are adopting flexible approaches to keep pace with innovation. This includes the use of regulatory sandboxes, which allow for controlled testing of new technologies and business models in real-world environments, helping to inform future regulatory decisions.
Economic Impact of 5G UC Trade
The economic impact of 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) on global trade agreements is expected to be substantial and far-reaching. As 5G UC technology continues to evolve and expand, it is poised to revolutionize international trade by enhancing connectivity, reducing latency, and increasing data transfer speeds. These advancements will likely lead to more efficient supply chains, improved logistics, and streamlined cross-border transactions.
One of the primary economic benefits of 5G UC in global trade is the potential for increased productivity and cost reduction. With faster and more reliable communication networks, businesses can optimize their operations, automate processes, and make real-time decisions based on accurate data. This enhanced efficiency is likely to result in lower operational costs and improved competitiveness in the global marketplace.
The implementation of 5G UC technology is also expected to facilitate the growth of digital trade and e-commerce. As online transactions become more seamless and secure, businesses of all sizes will have greater opportunities to participate in international markets. This democratization of global trade could lead to increased economic growth and job creation across various sectors and regions.
Furthermore, 5G UC has the potential to transform traditional industries through the adoption of advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and augmented reality (AR). These innovations can enable new business models, products, and services, fostering innovation and driving economic growth on a global scale.
The enhanced connectivity provided by 5G UC is likely to promote greater collaboration and knowledge sharing among businesses and research institutions worldwide. This increased exchange of ideas and expertise could accelerate technological advancements and scientific breakthroughs, leading to new economic opportunities and solutions to global challenges.
However, the economic impact of 5G UC on global trade agreements also presents challenges that need to be addressed. Issues such as data privacy, cybersecurity, and the digital divide between developed and developing nations must be carefully considered in future trade negotiations. Policymakers and industry leaders will need to work together to ensure that the benefits of 5G UC are distributed equitably and that potential risks are mitigated.
In conclusion, the economic implications of 5G UC for enhanced global trade agreements are significant and multifaceted. As this technology continues to mature and expand, it has the potential to reshape the global economic landscape, creating new opportunities for growth, innovation, and collaboration across borders. To fully realize these benefits, stakeholders must work together to develop comprehensive and forward-thinking trade agreements that address both the opportunities and challenges presented by 5G UC technology.
One of the primary economic benefits of 5G UC in global trade is the potential for increased productivity and cost reduction. With faster and more reliable communication networks, businesses can optimize their operations, automate processes, and make real-time decisions based on accurate data. This enhanced efficiency is likely to result in lower operational costs and improved competitiveness in the global marketplace.
The implementation of 5G UC technology is also expected to facilitate the growth of digital trade and e-commerce. As online transactions become more seamless and secure, businesses of all sizes will have greater opportunities to participate in international markets. This democratization of global trade could lead to increased economic growth and job creation across various sectors and regions.
Furthermore, 5G UC has the potential to transform traditional industries through the adoption of advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and augmented reality (AR). These innovations can enable new business models, products, and services, fostering innovation and driving economic growth on a global scale.
The enhanced connectivity provided by 5G UC is likely to promote greater collaboration and knowledge sharing among businesses and research institutions worldwide. This increased exchange of ideas and expertise could accelerate technological advancements and scientific breakthroughs, leading to new economic opportunities and solutions to global challenges.
However, the economic impact of 5G UC on global trade agreements also presents challenges that need to be addressed. Issues such as data privacy, cybersecurity, and the digital divide between developed and developing nations must be carefully considered in future trade negotiations. Policymakers and industry leaders will need to work together to ensure that the benefits of 5G UC are distributed equitably and that potential risks are mitigated.
In conclusion, the economic implications of 5G UC for enhanced global trade agreements are significant and multifaceted. As this technology continues to mature and expand, it has the potential to reshape the global economic landscape, creating new opportunities for growth, innovation, and collaboration across borders. To fully realize these benefits, stakeholders must work together to develop comprehensive and forward-thinking trade agreements that address both the opportunities and challenges presented by 5G UC technology.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!