What are the Implications of 5G UC for Enhanced National Security?
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
5G UC Background and Objectives
5G Ultra-Capacity (UC) represents a significant leap in wireless communication technology, offering enhanced capabilities that have profound implications for national security. The evolution of 5G UC stems from the need for faster, more reliable, and secure communication networks to support critical infrastructure and defense systems.
The primary objective of 5G UC in the context of national security is to provide a robust, high-capacity network that can handle the increasing demands of data-intensive applications and services crucial for defense and intelligence operations. This technology aims to enable real-time data processing, seamless communication between various security agencies, and enhanced situational awareness across multiple domains.
5G UC builds upon the foundation of previous generations of wireless technology, incorporating advanced features such as massive MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output), beamforming, and network slicing. These innovations allow for more efficient spectrum utilization, improved coverage, and the ability to prioritize critical communications during emergencies or high-stress situations.
The development of 5G UC has been driven by the growing need for secure and resilient communication networks that can withstand cyber threats and potential disruptions. As nations increasingly rely on digital infrastructure for their defense and security operations, the importance of a reliable and high-performance network becomes paramount.
One of the key goals of 5G UC in enhancing national security is to facilitate the rapid deployment of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) in defense applications. These technologies require ultra-low latency and high bandwidth, which 5G UC is designed to provide.
Furthermore, 5G UC aims to support the integration of various communication systems used by different branches of the military and intelligence agencies. This interoperability is crucial for coordinated responses to national security threats and for maintaining a strategic advantage in an increasingly complex global security landscape.
The implementation of 5G UC also addresses the need for improved communication in remote and challenging environments, which is essential for border security, disaster response, and military operations. The technology's ability to maintain connectivity in adverse conditions and its potential for rapid deployment make it a valuable asset in national security infrastructure.
As nations race to develop and deploy 5G UC networks, the technology has become a focal point in geopolitical discussions and strategic planning. The objectives extend beyond mere technological advancement, encompassing economic competitiveness, cybersecurity, and the ability to maintain technological sovereignty in critical communication infrastructure.
The primary objective of 5G UC in the context of national security is to provide a robust, high-capacity network that can handle the increasing demands of data-intensive applications and services crucial for defense and intelligence operations. This technology aims to enable real-time data processing, seamless communication between various security agencies, and enhanced situational awareness across multiple domains.
5G UC builds upon the foundation of previous generations of wireless technology, incorporating advanced features such as massive MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output), beamforming, and network slicing. These innovations allow for more efficient spectrum utilization, improved coverage, and the ability to prioritize critical communications during emergencies or high-stress situations.
The development of 5G UC has been driven by the growing need for secure and resilient communication networks that can withstand cyber threats and potential disruptions. As nations increasingly rely on digital infrastructure for their defense and security operations, the importance of a reliable and high-performance network becomes paramount.
One of the key goals of 5G UC in enhancing national security is to facilitate the rapid deployment of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT) in defense applications. These technologies require ultra-low latency and high bandwidth, which 5G UC is designed to provide.
Furthermore, 5G UC aims to support the integration of various communication systems used by different branches of the military and intelligence agencies. This interoperability is crucial for coordinated responses to national security threats and for maintaining a strategic advantage in an increasingly complex global security landscape.
The implementation of 5G UC also addresses the need for improved communication in remote and challenging environments, which is essential for border security, disaster response, and military operations. The technology's ability to maintain connectivity in adverse conditions and its potential for rapid deployment make it a valuable asset in national security infrastructure.
As nations race to develop and deploy 5G UC networks, the technology has become a focal point in geopolitical discussions and strategic planning. The objectives extend beyond mere technological advancement, encompassing economic competitiveness, cybersecurity, and the ability to maintain technological sovereignty in critical communication infrastructure.
National Security Market Analysis
The national security market for 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) technology is experiencing rapid growth and transformation. As governments and defense organizations worldwide recognize the critical role of advanced telecommunications in safeguarding national interests, the demand for 5G UC solutions tailored to security applications is surging. This market segment is expected to expand significantly over the next decade, driven by the need for enhanced communication capabilities, real-time data processing, and secure network infrastructure.
The primary drivers of this market include the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, the growing importance of intelligence gathering and analysis, and the need for robust command and control systems. 5G UC technology offers unprecedented speed, low latency, and massive connectivity, making it an ideal platform for developing next-generation security applications. These applications range from advanced surveillance systems and secure communication networks to AI-powered threat detection and response mechanisms.
Defense agencies and intelligence services are particularly interested in leveraging 5G UC capabilities to enhance their operational effectiveness. The technology enables seamless integration of various sensors, drones, and autonomous systems, facilitating real-time situational awareness and decision-making. Additionally, 5G UC's ability to support edge computing and network slicing allows for the creation of dedicated, secure communication channels for critical national security operations.
The market for 5G UC in national security is also being shaped by geopolitical factors. As nations compete for technological supremacy, investments in 5G infrastructure and related security applications are becoming a strategic priority. This has led to increased government funding and public-private partnerships aimed at developing indigenous 5G capabilities and securing supply chains against potential vulnerabilities.
Key market segments within the national security domain include border security, critical infrastructure protection, emergency response systems, and military communications. Each of these segments presents unique opportunities for 5G UC implementation, with solutions ranging from high-bandwidth video surveillance networks to ultra-reliable, low-latency communication systems for tactical operations.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces several challenges. Concerns over network security, potential backdoors, and the geopolitical implications of 5G technology adoption are influencing procurement decisions and market dynamics. Additionally, the need for interoperability with existing systems and the high costs associated with 5G infrastructure deployment are factors that may impact market growth.
As the market evolves, we anticipate a trend towards more specialized 5G UC solutions tailored to specific national security applications. This includes the development of hardened, military-grade 5G equipment, advanced encryption technologies, and integrated platforms that combine 5G connectivity with other emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and quantum computing.
The primary drivers of this market include the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, the growing importance of intelligence gathering and analysis, and the need for robust command and control systems. 5G UC technology offers unprecedented speed, low latency, and massive connectivity, making it an ideal platform for developing next-generation security applications. These applications range from advanced surveillance systems and secure communication networks to AI-powered threat detection and response mechanisms.
Defense agencies and intelligence services are particularly interested in leveraging 5G UC capabilities to enhance their operational effectiveness. The technology enables seamless integration of various sensors, drones, and autonomous systems, facilitating real-time situational awareness and decision-making. Additionally, 5G UC's ability to support edge computing and network slicing allows for the creation of dedicated, secure communication channels for critical national security operations.
The market for 5G UC in national security is also being shaped by geopolitical factors. As nations compete for technological supremacy, investments in 5G infrastructure and related security applications are becoming a strategic priority. This has led to increased government funding and public-private partnerships aimed at developing indigenous 5G capabilities and securing supply chains against potential vulnerabilities.
Key market segments within the national security domain include border security, critical infrastructure protection, emergency response systems, and military communications. Each of these segments presents unique opportunities for 5G UC implementation, with solutions ranging from high-bandwidth video surveillance networks to ultra-reliable, low-latency communication systems for tactical operations.
Despite the promising outlook, the market faces several challenges. Concerns over network security, potential backdoors, and the geopolitical implications of 5G technology adoption are influencing procurement decisions and market dynamics. Additionally, the need for interoperability with existing systems and the high costs associated with 5G infrastructure deployment are factors that may impact market growth.
As the market evolves, we anticipate a trend towards more specialized 5G UC solutions tailored to specific national security applications. This includes the development of hardened, military-grade 5G equipment, advanced encryption technologies, and integrated platforms that combine 5G connectivity with other emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and quantum computing.
5G UC Challenges and Limitations
While 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) technology offers significant advancements for national security, it also presents several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed. One of the primary concerns is the increased vulnerability to cyber attacks due to the expanded network surface area. As 5G UC networks become more complex and interconnected, they provide more potential entry points for malicious actors, making it challenging to secure all aspects of the network effectively.
Another limitation is the potential for increased electromagnetic interference. The higher frequency bands used in 5G UC can be more susceptible to interference from various sources, which could impact the reliability and performance of critical national security communications. This issue becomes particularly significant in densely populated urban areas or locations with high electromagnetic activity.
The deployment of 5G UC infrastructure also faces physical security challenges. The need for a higher density of small cell sites and antennas increases the number of potential targets for physical attacks or sabotage. Protecting these numerous distributed network elements becomes a logistical and resource-intensive task for national security agencies.
Interoperability issues present another significant challenge. As different countries and regions adopt varying 5G UC standards and technologies, ensuring seamless communication and data exchange between allied nations' security systems becomes more complex. This lack of standardization could hinder international cooperation in security operations and intelligence sharing.
The reliance on foreign-made 5G UC equipment and software raises concerns about supply chain security. Many countries lack domestic manufacturers for all components of 5G UC networks, necessitating the use of foreign-sourced technology. This dependency introduces potential vulnerabilities and risks of backdoors or hidden malware in critical national security infrastructure.
Furthermore, the rapid pace of 5G UC technology evolution poses challenges for national security agencies in terms of keeping their systems and personnel up-to-date. Continuous training, equipment upgrades, and policy adjustments are required to effectively leverage the latest 5G UC capabilities while mitigating emerging threats.
Lastly, the increased data transmission capabilities of 5G UC networks, while beneficial, also create challenges in data management and analysis. The sheer volume of data generated and transmitted through these networks can overwhelm existing security monitoring and analysis systems, making it difficult to identify and respond to threats in real-time. This necessitates the development of more advanced AI and machine learning-based security solutions to keep pace with the data influx.
Another limitation is the potential for increased electromagnetic interference. The higher frequency bands used in 5G UC can be more susceptible to interference from various sources, which could impact the reliability and performance of critical national security communications. This issue becomes particularly significant in densely populated urban areas or locations with high electromagnetic activity.
The deployment of 5G UC infrastructure also faces physical security challenges. The need for a higher density of small cell sites and antennas increases the number of potential targets for physical attacks or sabotage. Protecting these numerous distributed network elements becomes a logistical and resource-intensive task for national security agencies.
Interoperability issues present another significant challenge. As different countries and regions adopt varying 5G UC standards and technologies, ensuring seamless communication and data exchange between allied nations' security systems becomes more complex. This lack of standardization could hinder international cooperation in security operations and intelligence sharing.
The reliance on foreign-made 5G UC equipment and software raises concerns about supply chain security. Many countries lack domestic manufacturers for all components of 5G UC networks, necessitating the use of foreign-sourced technology. This dependency introduces potential vulnerabilities and risks of backdoors or hidden malware in critical national security infrastructure.
Furthermore, the rapid pace of 5G UC technology evolution poses challenges for national security agencies in terms of keeping their systems and personnel up-to-date. Continuous training, equipment upgrades, and policy adjustments are required to effectively leverage the latest 5G UC capabilities while mitigating emerging threats.
Lastly, the increased data transmission capabilities of 5G UC networks, while beneficial, also create challenges in data management and analysis. The sheer volume of data generated and transmitted through these networks can overwhelm existing security monitoring and analysis systems, making it difficult to identify and respond to threats in real-time. This necessitates the development of more advanced AI and machine learning-based security solutions to keep pace with the data influx.
Current 5G UC Security Solutions
01 Enhanced security protocols for 5G Ultra-Capacity networks
Implementation of advanced encryption and authentication mechanisms specifically designed for 5G UC networks to protect against cyber threats and unauthorized access. These protocols ensure secure communication channels and data integrity in high-capacity networks.- Enhanced security protocols for 5G Ultra-Capacity networks: Implementation of advanced encryption and authentication mechanisms specifically designed for 5G UC networks to protect against cyber threats and unauthorized access. These protocols ensure secure communication channels and data integrity in high-capacity environments.
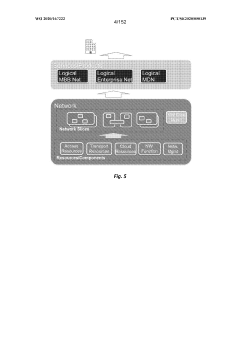
- Network slicing for national security applications: Utilization of network slicing technology in 5G UC to create isolated, secure virtual networks for critical national security operations. This allows for dedicated resources and customized security measures for sensitive communications and data transmission.
- AI-powered threat detection and response systems: Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to continuously monitor 5G UC networks for potential security breaches. These systems can quickly identify and respond to threats, enhancing the overall security posture of the network.
- Quantum-resistant cryptography for future-proofing: Development and implementation of quantum-resistant encryption methods to protect 5G UC networks against potential threats from quantum computing. This ensures long-term security and data protection in the face of evolving technological capabilities.
- Multi-layer security architecture for critical infrastructure: Design and deployment of a comprehensive, multi-layered security framework specifically for 5G UC networks supporting critical national infrastructure. This approach combines physical, network, and application-level security measures to create a robust defense against various types of threats.
02 Network slicing for national security applications
Utilization of network slicing technology in 5G UC to create isolated, secure network segments for critical national security operations. This allows for dedicated resources and enhanced protection for sensitive communications and data transmission.Expand Specific Solutions03 AI-powered threat detection and response
Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to continuously monitor 5G UC networks for potential security threats. These systems can quickly identify anomalies, predict potential attacks, and initiate automated responses to mitigate risks.Expand Specific Solutions04 Quantum-resistant cryptography for future-proofing
Development and implementation of quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms to protect 5G UC networks against potential threats from quantum computing. This ensures long-term security and data protection in the face of evolving technological capabilities.Expand Specific Solutions05 Multi-layer security architecture for critical infrastructure
Design and deployment of a comprehensive, multi-layered security architecture for 5G UC networks supporting critical national infrastructure. This includes physical security measures, software-defined networking, and real-time monitoring to ensure robust protection against diverse threats.Expand Specific Solutions
Key 5G UC Security Players
The 5G UC (Ultra Capacity) technology for enhanced national security is in a rapidly evolving phase, with significant market growth potential. The market is characterized by intense competition among major telecom players and equipment manufacturers. Companies like Ericsson, Nokia, Samsung, and Huawei are at the forefront of developing 5G UC solutions, leveraging their extensive experience in telecommunications infrastructure. The technology's maturity is advancing quickly, with these firms investing heavily in R&D to enhance security features, network reliability, and data protection capabilities. As national security concerns drive demand, telecom operators such as T-Mobile, DISH Wireless, and China Telecom are actively implementing and testing 5G UC networks, focusing on secure communication channels for government and defense applications.
Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
Technical Solution: Ericsson's 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) technology focuses on enhancing national security through advanced network capabilities. Their solution incorporates AI-driven threat detection, real-time network slicing for prioritized emergency communications, and quantum-resistant encryption protocols[1]. Ericsson's 5G UC infrastructure supports ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) crucial for critical national security applications, enabling rapid response times in emergency situations[3]. The company has also developed specialized hardware with built-in security features to protect against physical tampering and cyber attacks, ensuring the integrity of sensitive communications[5].
Strengths: Strong focus on AI-driven security, advanced encryption, and specialized hardware. Weaknesses: Potential over-reliance on proprietary technologies, which may limit interoperability with other systems.
Nokia Technologies Oy
Technical Solution: Nokia's approach to 5G UC for national security leverages their expertise in end-to-end network solutions. They have developed a comprehensive security framework that includes advanced threat intelligence, automated security orchestration, and adaptive access control mechanisms[2]. Nokia's 5G UC technology incorporates network slicing capabilities that allow for the creation of isolated, secure virtual networks for different government agencies and critical infrastructure[4]. Additionally, Nokia has implemented machine learning algorithms for anomaly detection and predictive maintenance, enhancing the overall resilience of national security communications[6].
Strengths: Comprehensive end-to-end security solutions and advanced network slicing capabilities. Weaknesses: May require significant infrastructure upgrades for full implementation, potentially increasing costs for national security agencies.
Core 5G UC Security Innovations
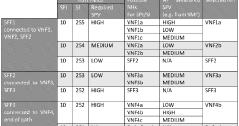
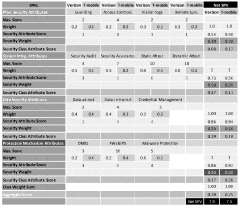
Determining and communicating security posture attributes
PatentWO2018075930A1
Innovation
- A framework is developed to derive and measure a Security Posture Value (SPV) based on a 360° security assessment, considering physical and cyber security attributes, and stakeholder policies, to ensure secure delivery of 5G services by evaluating the trustworthiness of network slices and individual network functions.
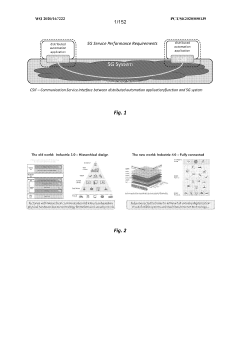
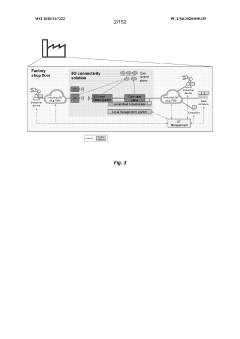
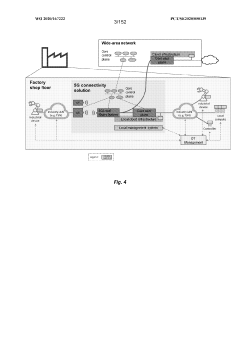
Industrial automation with 5g and beyond
PatentWO2020167222A2
Innovation
- The integration of 5G wireless networks with Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) techniques, including methods for establishing TSN data streams, configuring data packets, and managing radio resources, to provide deterministic and reliable communication services within industrial environments.
Regulatory Framework for 5G UC
The regulatory framework for 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) in the context of national security is a complex and evolving landscape. As 5G technology continues to advance, governments and regulatory bodies are working to establish comprehensive guidelines that balance innovation with security concerns.
At the core of this framework is the need to protect critical infrastructure and sensitive data from potential threats. Regulatory bodies are implementing stringent security standards for 5G networks, particularly those used in government and defense applications. These standards often include requirements for end-to-end encryption, network segmentation, and robust authentication mechanisms.
One key aspect of the regulatory framework is the vetting of equipment suppliers and service providers. Many countries have introduced measures to assess the security risks associated with different vendors, with some nations implementing restrictions or bans on certain suppliers deemed to pose potential security threats. This has led to a shift in the global 5G supply chain and increased scrutiny of network components.
Spectrum allocation and management also play a crucial role in the regulatory framework. Governments are carefully allocating 5G frequency bands, considering both technical performance and national security implications. Some countries are reserving specific frequency ranges for military and government use, ensuring secure and dedicated channels for critical communications.
Data localization and sovereignty regulations are becoming increasingly prevalent in the 5G UC landscape. Many nations are implementing rules that require sensitive data to be stored and processed within their borders, aiming to maintain control over critical information and reduce the risk of foreign interference.
Cybersecurity regulations for 5G networks are being developed and refined to address the unique challenges posed by this technology. These include measures to protect against DDoS attacks, network slicing vulnerabilities, and potential exploits in IoT devices connected to 5G networks. Regulatory bodies are also focusing on incident response and reporting mechanisms to ensure rapid detection and mitigation of security breaches.
International cooperation and standardization efforts are shaping the global regulatory framework for 5G UC. Organizations such as the ITU, 3GPP, and GSMA are working to develop common security standards and best practices. However, geopolitical tensions and differing national priorities have led to some fragmentation in the global approach to 5G security regulations.
As the technology continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are expected to adapt and expand. Future regulations may address emerging concerns such as quantum-resistant encryption, AI-powered network security, and the integration of 5G with other critical technologies like satellite communications and edge computing.
At the core of this framework is the need to protect critical infrastructure and sensitive data from potential threats. Regulatory bodies are implementing stringent security standards for 5G networks, particularly those used in government and defense applications. These standards often include requirements for end-to-end encryption, network segmentation, and robust authentication mechanisms.
One key aspect of the regulatory framework is the vetting of equipment suppliers and service providers. Many countries have introduced measures to assess the security risks associated with different vendors, with some nations implementing restrictions or bans on certain suppliers deemed to pose potential security threats. This has led to a shift in the global 5G supply chain and increased scrutiny of network components.
Spectrum allocation and management also play a crucial role in the regulatory framework. Governments are carefully allocating 5G frequency bands, considering both technical performance and national security implications. Some countries are reserving specific frequency ranges for military and government use, ensuring secure and dedicated channels for critical communications.
Data localization and sovereignty regulations are becoming increasingly prevalent in the 5G UC landscape. Many nations are implementing rules that require sensitive data to be stored and processed within their borders, aiming to maintain control over critical information and reduce the risk of foreign interference.
Cybersecurity regulations for 5G networks are being developed and refined to address the unique challenges posed by this technology. These include measures to protect against DDoS attacks, network slicing vulnerabilities, and potential exploits in IoT devices connected to 5G networks. Regulatory bodies are also focusing on incident response and reporting mechanisms to ensure rapid detection and mitigation of security breaches.
International cooperation and standardization efforts are shaping the global regulatory framework for 5G UC. Organizations such as the ITU, 3GPP, and GSMA are working to develop common security standards and best practices. However, geopolitical tensions and differing national priorities have led to some fragmentation in the global approach to 5G security regulations.
As the technology continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks are expected to adapt and expand. Future regulations may address emerging concerns such as quantum-resistant encryption, AI-powered network security, and the integration of 5G with other critical technologies like satellite communications and edge computing.
International Cooperation in 5G Security
International cooperation in 5G security is crucial for addressing the implications of 5G UC for enhanced national security. As nations worldwide deploy 5G networks, collaboration becomes essential to establish common standards, share best practices, and mitigate potential risks. This cooperation extends beyond traditional allies, encompassing a broader range of countries and international organizations.
One key aspect of international cooperation is the development of shared security protocols and standards. By working together, nations can create a unified approach to 5G security, ensuring interoperability and reducing vulnerabilities across borders. This collaboration often takes place through international bodies such as the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP).
Information sharing is another critical component of international cooperation in 5G security. Countries can benefit from exchanging threat intelligence, vulnerability assessments, and mitigation strategies. This exchange helps in identifying and addressing potential security risks more effectively, particularly those that may have cross-border implications.
Joint research and development initiatives also play a significant role in enhancing 5G security on a global scale. By pooling resources and expertise, nations can accelerate the development of advanced security technologies and solutions. These collaborative efforts often focus on areas such as quantum-resistant cryptography, AI-driven threat detection, and secure network architectures.
Capacity building and knowledge transfer are essential elements of international cooperation, particularly in supporting developing nations. Advanced countries can assist others in building robust 5G security frameworks, providing training, and sharing best practices. This approach helps in creating a more secure global 5G ecosystem by addressing potential weak links in the international network.
Diplomatic efforts and policy coordination are crucial for aligning national security interests in the context of 5G. Through bilateral and multilateral agreements, nations can establish common ground on issues such as supply chain security, data protection, and the handling of cross-border cybersecurity incidents. These agreements often involve commitments to transparency, mutual assistance, and adherence to international norms.
However, international cooperation in 5G security also faces challenges. Geopolitical tensions, competing national interests, and differing approaches to data privacy and surveillance can complicate collaborative efforts. Overcoming these obstacles requires sustained diplomatic engagement, trust-building measures, and a commitment to finding common ground on critical security issues.
One key aspect of international cooperation is the development of shared security protocols and standards. By working together, nations can create a unified approach to 5G security, ensuring interoperability and reducing vulnerabilities across borders. This collaboration often takes place through international bodies such as the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP).
Information sharing is another critical component of international cooperation in 5G security. Countries can benefit from exchanging threat intelligence, vulnerability assessments, and mitigation strategies. This exchange helps in identifying and addressing potential security risks more effectively, particularly those that may have cross-border implications.
Joint research and development initiatives also play a significant role in enhancing 5G security on a global scale. By pooling resources and expertise, nations can accelerate the development of advanced security technologies and solutions. These collaborative efforts often focus on areas such as quantum-resistant cryptography, AI-driven threat detection, and secure network architectures.
Capacity building and knowledge transfer are essential elements of international cooperation, particularly in supporting developing nations. Advanced countries can assist others in building robust 5G security frameworks, providing training, and sharing best practices. This approach helps in creating a more secure global 5G ecosystem by addressing potential weak links in the international network.
Diplomatic efforts and policy coordination are crucial for aligning national security interests in the context of 5G. Through bilateral and multilateral agreements, nations can establish common ground on issues such as supply chain security, data protection, and the handling of cross-border cybersecurity incidents. These agreements often involve commitments to transparency, mutual assistance, and adherence to international norms.
However, international cooperation in 5G security also faces challenges. Geopolitical tensions, competing national interests, and differing approaches to data privacy and surveillance can complicate collaborative efforts. Overcoming these obstacles requires sustained diplomatic engagement, trust-building measures, and a commitment to finding common ground on critical security issues.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!