The Potential of 5G UC in Transforming the Publishing Industry
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
5G UC in Publishing: Background and Objectives
The advent of 5G technology has ushered in a new era of connectivity, promising unprecedented speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity. Within this technological revolution, 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) stands out as a game-changer, offering enhanced capabilities that could significantly transform various industries, including publishing. The publishing industry, which has already undergone substantial digital transformation, now faces the potential for even more radical changes with the introduction of 5G UC.
The evolution of publishing has seen a shift from traditional print media to digital formats, with e-books, online magazines, and interactive content becoming increasingly prevalent. However, the limitations of current network technologies have constrained the full potential of digital publishing. 5G UC presents an opportunity to overcome these barriers and unlock new possibilities for content creation, distribution, and consumption.
The primary objective of exploring 5G UC in the publishing industry is to identify and leverage the technology's capabilities to enhance the entire publishing ecosystem. This includes improving the speed and efficiency of content delivery, enabling more immersive and interactive reading experiences, and facilitating new forms of content that were previously impractical or impossible due to technological constraints.
One of the key areas of focus is the potential for 5G UC to enable real-time collaboration and content creation. With ultra-low latency and high bandwidth, authors, editors, and designers could work together seamlessly across vast distances, as if they were in the same room. This could revolutionize the editorial process and significantly reduce the time-to-market for new publications.
Another critical aspect is the enhancement of content consumption. 5G UC could pave the way for more sophisticated augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) experiences integrated into books and magazines. Readers could potentially interact with 3D models, explore virtual environments, or engage with multimedia content seamlessly embedded within text, all without the need for separate devices or applications.
Furthermore, 5G UC's capacity for handling massive amounts of data could enable publishers to deliver high-quality video and audio content alongside traditional text, creating rich, multi-sensory reading experiences. This convergence of media types could blur the lines between different forms of content, leading to entirely new formats of publishing.
As we explore the potential of 5G UC in transforming the publishing industry, it is crucial to consider both the technological advancements and the evolving expectations of readers. The goal is not only to improve existing processes but also to reimagine what publishing could become in a world of ubiquitous, high-speed connectivity. This exploration will set the stage for understanding the profound impact that 5G UC could have on the future of publishing, from content creation to distribution and consumption.
The evolution of publishing has seen a shift from traditional print media to digital formats, with e-books, online magazines, and interactive content becoming increasingly prevalent. However, the limitations of current network technologies have constrained the full potential of digital publishing. 5G UC presents an opportunity to overcome these barriers and unlock new possibilities for content creation, distribution, and consumption.
The primary objective of exploring 5G UC in the publishing industry is to identify and leverage the technology's capabilities to enhance the entire publishing ecosystem. This includes improving the speed and efficiency of content delivery, enabling more immersive and interactive reading experiences, and facilitating new forms of content that were previously impractical or impossible due to technological constraints.
One of the key areas of focus is the potential for 5G UC to enable real-time collaboration and content creation. With ultra-low latency and high bandwidth, authors, editors, and designers could work together seamlessly across vast distances, as if they were in the same room. This could revolutionize the editorial process and significantly reduce the time-to-market for new publications.
Another critical aspect is the enhancement of content consumption. 5G UC could pave the way for more sophisticated augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) experiences integrated into books and magazines. Readers could potentially interact with 3D models, explore virtual environments, or engage with multimedia content seamlessly embedded within text, all without the need for separate devices or applications.
Furthermore, 5G UC's capacity for handling massive amounts of data could enable publishers to deliver high-quality video and audio content alongside traditional text, creating rich, multi-sensory reading experiences. This convergence of media types could blur the lines between different forms of content, leading to entirely new formats of publishing.
As we explore the potential of 5G UC in transforming the publishing industry, it is crucial to consider both the technological advancements and the evolving expectations of readers. The goal is not only to improve existing processes but also to reimagine what publishing could become in a world of ubiquitous, high-speed connectivity. This exploration will set the stage for understanding the profound impact that 5G UC could have on the future of publishing, from content creation to distribution and consumption.
Market Demand Analysis for 5G-Enabled Publishing
The publishing industry is experiencing a significant transformation driven by the advent of 5G technology, particularly 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity). This advanced network infrastructure is creating new opportunities and reshaping market demands within the publishing sector. The demand for 5G-enabled publishing solutions is rapidly growing as consumers and businesses seek faster, more immersive, and interactive content experiences.
One of the primary drivers of market demand is the increasing consumption of digital content across various platforms. With 5G UC's high-speed connectivity and low latency, publishers can deliver rich multimedia content, including high-definition video, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) experiences, seamlessly to mobile devices. This capability is particularly attractive to educational publishers, who can now offer interactive textbooks and immersive learning experiences that were previously limited by network constraints.
The rise of on-demand content and personalized reading experiences is another factor fueling the demand for 5G-enabled publishing. Readers now expect instant access to a vast library of books, magazines, and newspapers, with personalized recommendations and real-time updates. 5G UC's enhanced bandwidth and reduced latency enable publishers to meet these expectations by providing faster content delivery and more sophisticated recommendation algorithms that can process large amounts of data in real-time.
In the professional and academic publishing sectors, there is a growing demand for collaborative tools and real-time information sharing. 5G UC facilitates seamless remote collaboration, allowing researchers, authors, and editors to work together on complex projects with minimal lag or disruption. This capability is particularly valuable in fields such as scientific publishing, where large datasets and complex visualizations need to be shared and manipulated in real-time.
The market for interactive and gamified content in publishing is also expanding, driven by 5G UC's capabilities. Publishers are exploring new formats that blend traditional text with interactive elements, creating engaging experiences for readers. This trend is especially prominent in children's publishing and educational materials, where gamification can significantly enhance learning outcomes and reader engagement.
Furthermore, the demand for location-based and context-aware content is increasing. 5G UC's improved geolocation capabilities allow publishers to deliver hyper-localized content and advertisements, creating new revenue streams and enhancing the relevance of published materials to specific audiences.
As the publishing industry continues to evolve, the market demand for 5G-enabled solutions is expected to grow substantially. Publishers who embrace these technologies early are likely to gain a competitive advantage, meeting the evolving needs of readers and creating new value propositions in an increasingly digital and connected world.
One of the primary drivers of market demand is the increasing consumption of digital content across various platforms. With 5G UC's high-speed connectivity and low latency, publishers can deliver rich multimedia content, including high-definition video, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) experiences, seamlessly to mobile devices. This capability is particularly attractive to educational publishers, who can now offer interactive textbooks and immersive learning experiences that were previously limited by network constraints.
The rise of on-demand content and personalized reading experiences is another factor fueling the demand for 5G-enabled publishing. Readers now expect instant access to a vast library of books, magazines, and newspapers, with personalized recommendations and real-time updates. 5G UC's enhanced bandwidth and reduced latency enable publishers to meet these expectations by providing faster content delivery and more sophisticated recommendation algorithms that can process large amounts of data in real-time.
In the professional and academic publishing sectors, there is a growing demand for collaborative tools and real-time information sharing. 5G UC facilitates seamless remote collaboration, allowing researchers, authors, and editors to work together on complex projects with minimal lag or disruption. This capability is particularly valuable in fields such as scientific publishing, where large datasets and complex visualizations need to be shared and manipulated in real-time.
The market for interactive and gamified content in publishing is also expanding, driven by 5G UC's capabilities. Publishers are exploring new formats that blend traditional text with interactive elements, creating engaging experiences for readers. This trend is especially prominent in children's publishing and educational materials, where gamification can significantly enhance learning outcomes and reader engagement.
Furthermore, the demand for location-based and context-aware content is increasing. 5G UC's improved geolocation capabilities allow publishers to deliver hyper-localized content and advertisements, creating new revenue streams and enhancing the relevance of published materials to specific audiences.
As the publishing industry continues to evolve, the market demand for 5G-enabled solutions is expected to grow substantially. Publishers who embrace these technologies early are likely to gain a competitive advantage, meeting the evolving needs of readers and creating new value propositions in an increasingly digital and connected world.
Current State and Challenges of 5G UC in Publishing
The integration of 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) technology in the publishing industry is still in its early stages, with significant potential for transformation. Currently, the adoption of 5G UC in publishing is limited, primarily due to the nascent state of the technology and the traditional nature of many publishing processes. However, several pioneering companies and institutions are exploring its applications, particularly in areas such as digital content delivery, interactive e-books, and augmented reality (AR) enhanced publications.
One of the main challenges facing the implementation of 5G UC in publishing is the need for substantial infrastructure investment. Many publishing houses, especially smaller ones, may find it difficult to justify the costs associated with upgrading their systems to fully leverage 5G UC capabilities. Additionally, there is a lack of standardization across the industry, which can hinder interoperability and slow down widespread adoption.
Another significant challenge is the skills gap within the publishing workforce. The integration of 5G UC requires a blend of traditional publishing expertise with advanced technological knowledge. Many publishers are struggling to find or train employees who can effectively bridge this gap, potentially slowing the industry's digital transformation.
Data security and privacy concerns also pose challenges to the adoption of 5G UC in publishing. As more content is delivered through high-speed networks, ensuring the protection of intellectual property and user data becomes increasingly complex. Publishers must navigate stringent regulations like GDPR while implementing robust security measures to maintain consumer trust.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of 5G UC in publishing are substantial. The technology promises to enable near-instantaneous content delivery, even for large files such as high-resolution images or interactive multimedia. This could revolutionize the e-book and digital magazine markets, allowing for more immersive and dynamic reading experiences.
Furthermore, 5G UC opens up new possibilities for location-based services and personalized content delivery. Publishers could potentially offer hyper-localized content or augmented reality experiences tied to specific geographical locations, enhancing engagement and creating new revenue streams.
The current state of 5G UC in publishing also reveals a geographical disparity in adoption and development. Countries with more advanced 5G infrastructure, such as South Korea, China, and parts of the United States, are leading the way in exploring innovative applications for the publishing industry. This creates both opportunities and challenges for global publishers seeking to maintain competitiveness across different markets.
One of the main challenges facing the implementation of 5G UC in publishing is the need for substantial infrastructure investment. Many publishing houses, especially smaller ones, may find it difficult to justify the costs associated with upgrading their systems to fully leverage 5G UC capabilities. Additionally, there is a lack of standardization across the industry, which can hinder interoperability and slow down widespread adoption.
Another significant challenge is the skills gap within the publishing workforce. The integration of 5G UC requires a blend of traditional publishing expertise with advanced technological knowledge. Many publishers are struggling to find or train employees who can effectively bridge this gap, potentially slowing the industry's digital transformation.
Data security and privacy concerns also pose challenges to the adoption of 5G UC in publishing. As more content is delivered through high-speed networks, ensuring the protection of intellectual property and user data becomes increasingly complex. Publishers must navigate stringent regulations like GDPR while implementing robust security measures to maintain consumer trust.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of 5G UC in publishing are substantial. The technology promises to enable near-instantaneous content delivery, even for large files such as high-resolution images or interactive multimedia. This could revolutionize the e-book and digital magazine markets, allowing for more immersive and dynamic reading experiences.
Furthermore, 5G UC opens up new possibilities for location-based services and personalized content delivery. Publishers could potentially offer hyper-localized content or augmented reality experiences tied to specific geographical locations, enhancing engagement and creating new revenue streams.
The current state of 5G UC in publishing also reveals a geographical disparity in adoption and development. Countries with more advanced 5G infrastructure, such as South Korea, China, and parts of the United States, are leading the way in exploring innovative applications for the publishing industry. This creates both opportunities and challenges for global publishers seeking to maintain competitiveness across different markets.
Existing 5G UC Solutions for Publishing Sector
01 5G Ultra-Capacity Network Architecture
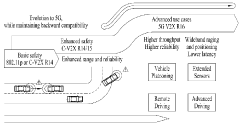
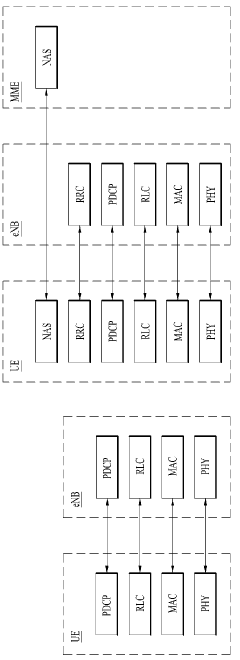
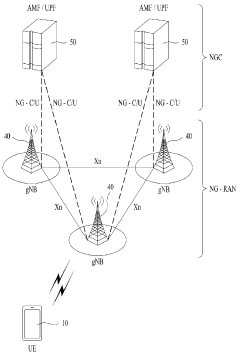
5G UC refers to an advanced network architecture that provides ultra-high capacity and low latency. It utilizes a combination of mid-band and high-band (mmWave) spectrum to deliver enhanced performance. This architecture enables faster data speeds, improved network efficiency, and support for a higher number of connected devices.- 5G Ultra-Capacity Network Architecture: 5G UC refers to an advanced network architecture that utilizes mid-band and high-band spectrum to deliver enhanced capacity and performance. This architecture enables faster data speeds, lower latency, and improved network reliability compared to standard 5G networks. It incorporates advanced technologies such as massive MIMO, beamforming, and carrier aggregation to optimize spectrum usage and network efficiency.
- Spectrum Management in 5G UC: Efficient spectrum management is crucial for 5G UC networks. This involves dynamic allocation of frequency bands, including mid-band (2.5 GHz to 6 GHz) and high-band (mmWave) spectrum. Advanced techniques are employed to maximize spectrum utilization, such as dynamic spectrum sharing, carrier aggregation, and flexible numerology, enabling the network to adapt to varying traffic demands and environmental conditions.
- 5G UC Device Capabilities: Devices supporting 5G UC require specific hardware and software capabilities to fully utilize the enhanced network features. This includes advanced antenna designs, support for higher order modulation schemes, and the ability to process multiple carrier signals simultaneously. These devices often incorporate AI-driven algorithms for optimizing network selection and performance based on real-time conditions.
- Network Slicing in 5G UC: Network slicing is a key feature of 5G UC, allowing the creation of multiple virtual networks tailored to specific use cases or applications. This technology enables efficient resource allocation and customized quality of service for different types of traffic, such as IoT, autonomous vehicles, or high-bandwidth multimedia applications, all running on the same physical infrastructure.
- Edge Computing Integration with 5G UC: 5G UC networks are designed to work seamlessly with edge computing infrastructure, bringing computational resources closer to end-users and devices. This integration reduces latency, improves data processing efficiency, and enables new applications that require real-time responsiveness. Edge computing in 5G UC supports advanced services such as augmented reality, industrial IoT, and smart city applications.
02 Spectrum Management in 5G UC
Efficient spectrum management is crucial for 5G UC networks. This involves dynamic allocation of frequency resources, carrier aggregation techniques, and advanced spectrum sharing methods. These approaches optimize the use of available spectrum to maximize capacity and coverage in ultra-capacity networks.Expand Specific Solutions03 Beamforming and MIMO Technologies in 5G UC
5G UC networks heavily rely on advanced beamforming and massive MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) technologies. These techniques enable precise directional transmission and reception of signals, improving signal quality, reducing interference, and enhancing overall network capacity and coverage.Expand Specific Solutions04 Network Slicing for 5G UC Services
Network slicing is a key feature of 5G UC networks, allowing the creation of multiple virtual networks tailored to specific service requirements. This enables efficient resource allocation and optimization for diverse use cases, such as enhanced mobile broadband, massive IoT, and ultra-reliable low-latency communications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Edge Computing Integration in 5G UC
5G UC networks incorporate edge computing capabilities to bring processing power closer to end-users. This integration reduces latency, improves application performance, and enables new use cases that require real-time data processing. Edge computing also helps offload traffic from the core network, enhancing overall network efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in 5G UC and Digital Publishing
The 5G UC technology in the publishing industry is in its early stages of development, with significant potential for growth. The market size is expanding as more publishers explore 5G UC applications. While the technology is not yet fully mature, major players like ZTE, Ericsson, Samsung, and Huawei are driving innovation. Telecom giants such as AT&T, T-Mobile, and China Telecom are also investing heavily in 5G infrastructure. Tech companies like Qualcomm, Apple, and Intel are developing compatible hardware and software solutions. This competitive landscape suggests rapid advancements and increasing adoption of 5G UC in publishing over the coming years.
Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
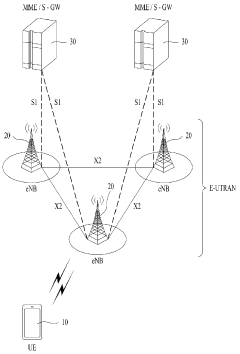
Technical Solution: Ericsson's 5G UC solution for the publishing industry focuses on creating a robust network infrastructure that can support advanced publishing applications. Their approach includes the deployment of 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) solutions that provide high-capacity, low-latency connectivity essential for real-time content delivery and interactive publishing platforms. Ericsson has developed specific use cases for the media and entertainment sector, which can be applied to publishing, such as remote production and cloud-based content creation[5]. The company's 5G Core network solutions enable network slicing, allowing publishers to have dedicated virtual networks with guaranteed quality of service for critical applications. Ericsson has also implemented AI and machine learning algorithms within their network management systems to optimize content delivery based on user behavior and network conditions[6].
Strengths: Comprehensive network infrastructure solutions, expertise in large-scale deployments, and advanced network management capabilities. Weaknesses: Less focus on end-user devices and applications specific to publishing.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung's approach to leveraging 5G UC in the publishing industry combines their expertise in mobile devices, displays, and network equipment. Their solution includes the development of 5G-enabled tablets and e-readers with high-resolution displays optimized for digital content consumption. Samsung has integrated their 5G modems into these devices, ensuring fast and reliable connectivity for downloading and streaming content. The company has also developed a cloud-based platform that utilizes 5G networks to enable seamless synchronization of content across multiple devices, allowing users to switch between reading on a smartphone, tablet, or e-reader without losing their place[7]. Samsung's technology supports advanced features such as real-time language translation for international publications and haptic feedback for enhanced interactive e-books. Additionally, their 5G network solutions, including small cells and massive MIMO antennas, contribute to creating the infrastructure necessary for high-bandwidth, low-latency publishing applications[8].
Strengths: Integrated hardware and software solutions, strong presence in consumer electronics, and comprehensive 5G network equipment. Weaknesses: Potential ecosystem lock-in, competition from specialized e-reader manufacturers.
Core Innovations in 5G UC for Publishing
Communication method and apparatus
PatentPendingEP4344303A1
Innovation
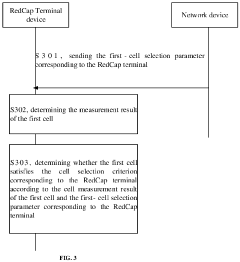
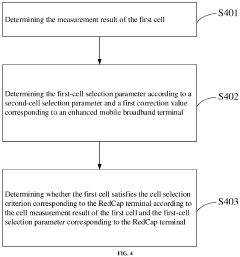
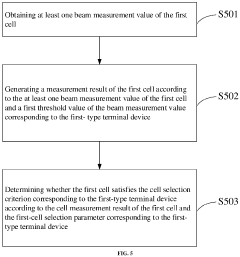
- A communication method and apparatus that determine whether a cell satisfies a cell selection criterion for RedCap terminals using a first-cell selection parameter, which is configured based on the terminal's capability and differs from that of non-RedCap terminals, to ensure successful cell camping.
Method of operating UE in relation to as configuration in wireless communication system
PatentActiveIN202014047058A
Innovation
- A method is introduced where a UE performs an AS configuration procedure with another UE and transmits a radio resource control (RRC) message to the base station (BS) upon failure, including information about the destination ID of a unicast link, allowing the BS to identify and release related resources.
Regulatory Framework for 5G UC in Publishing
The regulatory framework for 5G UC in the publishing industry is evolving rapidly to keep pace with technological advancements. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are working to establish guidelines that balance innovation with consumer protection and fair competition. These regulations aim to address key areas such as spectrum allocation, network security, data privacy, and content distribution.
Spectrum allocation is a critical aspect of 5G UC regulation in publishing. Regulatory bodies are tasked with ensuring fair and efficient distribution of radio frequencies to enable high-speed, low-latency communications essential for advanced publishing applications. This includes allocating dedicated spectrum bands for 5G UC services and implementing dynamic spectrum sharing mechanisms to maximize utilization.
Network security regulations for 5G UC in publishing focus on protecting sensitive content and user data. Regulatory frameworks mandate robust encryption standards, authentication protocols, and cybersecurity measures to safeguard against unauthorized access and data breaches. Publishers and service providers are required to implement end-to-end security solutions and regularly audit their systems to ensure compliance.
Data privacy regulations play a crucial role in shaping the 5G UC landscape for publishing. Frameworks such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States set stringent requirements for data collection, storage, and processing. Publishers leveraging 5G UC technologies must adhere to these regulations, implementing transparent data handling practices and obtaining explicit user consent for data usage.
Content distribution regulations in the 5G UC era address issues of net neutrality, content moderation, and intellectual property rights. Regulatory bodies are working to ensure fair access to 5G UC networks for all content providers, preventing discriminatory practices that could stifle competition. Additionally, regulations are being developed to address the challenges of real-time content moderation and copyright protection in high-speed, low-latency environments.
Interoperability and standardization are key focus areas for 5G UC regulations in publishing. Regulatory frameworks are promoting the adoption of open standards and interoperable technologies to prevent vendor lock-in and foster innovation. This includes mandating support for common protocols and interfaces, enabling seamless integration of diverse publishing platforms and services across the 5G UC ecosystem.
As the 5G UC landscape continues to evolve, regulatory bodies are adopting adaptive approaches to keep pace with technological advancements. This includes implementing sandbox environments for testing new publishing technologies and services, as well as establishing collaborative forums between industry stakeholders and regulators to address emerging challenges and opportunities in the 5G UC publishing ecosystem.
Spectrum allocation is a critical aspect of 5G UC regulation in publishing. Regulatory bodies are tasked with ensuring fair and efficient distribution of radio frequencies to enable high-speed, low-latency communications essential for advanced publishing applications. This includes allocating dedicated spectrum bands for 5G UC services and implementing dynamic spectrum sharing mechanisms to maximize utilization.
Network security regulations for 5G UC in publishing focus on protecting sensitive content and user data. Regulatory frameworks mandate robust encryption standards, authentication protocols, and cybersecurity measures to safeguard against unauthorized access and data breaches. Publishers and service providers are required to implement end-to-end security solutions and regularly audit their systems to ensure compliance.
Data privacy regulations play a crucial role in shaping the 5G UC landscape for publishing. Frameworks such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States set stringent requirements for data collection, storage, and processing. Publishers leveraging 5G UC technologies must adhere to these regulations, implementing transparent data handling practices and obtaining explicit user consent for data usage.
Content distribution regulations in the 5G UC era address issues of net neutrality, content moderation, and intellectual property rights. Regulatory bodies are working to ensure fair access to 5G UC networks for all content providers, preventing discriminatory practices that could stifle competition. Additionally, regulations are being developed to address the challenges of real-time content moderation and copyright protection in high-speed, low-latency environments.
Interoperability and standardization are key focus areas for 5G UC regulations in publishing. Regulatory frameworks are promoting the adoption of open standards and interoperable technologies to prevent vendor lock-in and foster innovation. This includes mandating support for common protocols and interfaces, enabling seamless integration of diverse publishing platforms and services across the 5G UC ecosystem.
As the 5G UC landscape continues to evolve, regulatory bodies are adopting adaptive approaches to keep pace with technological advancements. This includes implementing sandbox environments for testing new publishing technologies and services, as well as establishing collaborative forums between industry stakeholders and regulators to address emerging challenges and opportunities in the 5G UC publishing ecosystem.
Economic Impact of 5G UC on Publishing Industry
The economic impact of 5G UC on the publishing industry is expected to be transformative, ushering in a new era of digital content creation, distribution, and consumption. The enhanced capabilities of 5G UC, including ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and massive device connectivity, are poised to revolutionize various aspects of the publishing ecosystem.
One of the most significant economic impacts will be the acceleration of digital transformation within the industry. Publishers will be able to leverage 5G UC to create and deliver more immersive and interactive content, potentially increasing consumer engagement and willingness to pay for premium digital experiences. This shift could lead to new revenue streams and business models, such as augmented reality (AR) enhanced e-books or real-time collaborative writing platforms.
The improved connectivity and speed offered by 5G UC will also enable more efficient content distribution. Publishers can expect reduced costs associated with content delivery, as large files and high-quality multimedia can be transmitted seamlessly. This efficiency gain may result in faster time-to-market for new publications and the ability to update content in real-time, keeping information current and relevant.
Furthermore, 5G UC's capacity for edge computing and IoT integration opens up possibilities for personalized content delivery and targeted advertising. Publishers can harness real-time data analytics to tailor content recommendations and advertisements to individual readers, potentially increasing conversion rates and advertising revenues.
The technology is also likely to impact the workforce within the publishing industry. While it may lead to some job displacement in traditional roles, it is expected to create new opportunities in areas such as AR content creation, data analytics, and digital platform management. This shift may necessitate significant investment in workforce reskilling and upskilling programs.
From a market perspective, 5G UC could lower barriers to entry for smaller publishers and independent authors by providing access to advanced publishing tools and distribution channels. This democratization of publishing may lead to increased competition and innovation within the industry, potentially challenging established players to adapt and evolve their business strategies.
In conclusion, while the full economic impact of 5G UC on the publishing industry is yet to be realized, it is clear that the technology has the potential to drive significant growth, innovation, and structural changes within the sector. Publishers who successfully leverage these capabilities may find themselves at a competitive advantage in an increasingly digital-first market.
One of the most significant economic impacts will be the acceleration of digital transformation within the industry. Publishers will be able to leverage 5G UC to create and deliver more immersive and interactive content, potentially increasing consumer engagement and willingness to pay for premium digital experiences. This shift could lead to new revenue streams and business models, such as augmented reality (AR) enhanced e-books or real-time collaborative writing platforms.
The improved connectivity and speed offered by 5G UC will also enable more efficient content distribution. Publishers can expect reduced costs associated with content delivery, as large files and high-quality multimedia can be transmitted seamlessly. This efficiency gain may result in faster time-to-market for new publications and the ability to update content in real-time, keeping information current and relevant.
Furthermore, 5G UC's capacity for edge computing and IoT integration opens up possibilities for personalized content delivery and targeted advertising. Publishers can harness real-time data analytics to tailor content recommendations and advertisements to individual readers, potentially increasing conversion rates and advertising revenues.
The technology is also likely to impact the workforce within the publishing industry. While it may lead to some job displacement in traditional roles, it is expected to create new opportunities in areas such as AR content creation, data analytics, and digital platform management. This shift may necessitate significant investment in workforce reskilling and upskilling programs.
From a market perspective, 5G UC could lower barriers to entry for smaller publishers and independent authors by providing access to advanced publishing tools and distribution channels. This democratization of publishing may lead to increased competition and innovation within the industry, potentially challenging established players to adapt and evolve their business strategies.
In conclusion, while the full economic impact of 5G UC on the publishing industry is yet to be realized, it is clear that the technology has the potential to drive significant growth, innovation, and structural changes within the sector. Publishers who successfully leverage these capabilities may find themselves at a competitive advantage in an increasingly digital-first market.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!