What are the Implications of 5G UC for Enhanced Global Diplomacy?
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
5G UC Diplomacy Background and Objectives
The advent of 5G technology has ushered in a new era of connectivity, with 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) representing the pinnacle of this technological revolution. In the realm of global diplomacy, 5G UC holds immense potential to transform international relations and enhance diplomatic processes. This technological leap offers unprecedented opportunities for real-time communication, data exchange, and collaborative decision-making on a global scale.
The primary objective of leveraging 5G UC in diplomacy is to facilitate more efficient and effective international cooperation. By providing ultra-fast, low-latency connections, 5G UC can enable seamless virtual meetings, immersive telepresence experiences, and rapid information sharing among diplomatic entities worldwide. This enhanced connectivity aims to bridge geographical gaps and foster closer ties between nations, potentially leading to more productive negotiations and swifter resolution of global challenges.
Historically, diplomatic communications have evolved from traditional methods such as written correspondence and face-to-face meetings to more modern approaches involving video conferencing and digital platforms. The introduction of 5G UC represents the next significant milestone in this evolution, promising to overcome limitations of previous technologies and create new paradigms for international engagement.
One of the key goals in implementing 5G UC for diplomacy is to enhance crisis management capabilities. The technology's ability to support real-time data transmission and analysis can prove crucial during international emergencies, allowing for rapid coordination and response among global leaders and diplomatic corps. This improved responsiveness has the potential to mitigate conflicts and address humanitarian crises more effectively.
Furthermore, 5G UC aims to democratize access to diplomatic processes by enabling smaller nations and remote regions to participate more fully in global discussions. By reducing the need for extensive physical infrastructure and travel, this technology can level the playing field in international relations, potentially leading to more inclusive and diverse diplomatic engagements.
Another objective of 5G UC in diplomacy is to facilitate the secure exchange of sensitive information. The technology's advanced encryption capabilities and network slicing features offer promising solutions for maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of diplomatic communications, addressing longstanding concerns about cybersecurity in international relations.
As we explore the implications of 5G UC for enhanced global diplomacy, it is essential to consider both the opportunities and challenges that this technology presents. While the potential benefits are significant, issues such as equitable access, technological sovereignty, and the digital divide must be carefully addressed to ensure that 5G UC truly serves as a tool for global cooperation rather than a source of new geopolitical tensions.
The primary objective of leveraging 5G UC in diplomacy is to facilitate more efficient and effective international cooperation. By providing ultra-fast, low-latency connections, 5G UC can enable seamless virtual meetings, immersive telepresence experiences, and rapid information sharing among diplomatic entities worldwide. This enhanced connectivity aims to bridge geographical gaps and foster closer ties between nations, potentially leading to more productive negotiations and swifter resolution of global challenges.
Historically, diplomatic communications have evolved from traditional methods such as written correspondence and face-to-face meetings to more modern approaches involving video conferencing and digital platforms. The introduction of 5G UC represents the next significant milestone in this evolution, promising to overcome limitations of previous technologies and create new paradigms for international engagement.
One of the key goals in implementing 5G UC for diplomacy is to enhance crisis management capabilities. The technology's ability to support real-time data transmission and analysis can prove crucial during international emergencies, allowing for rapid coordination and response among global leaders and diplomatic corps. This improved responsiveness has the potential to mitigate conflicts and address humanitarian crises more effectively.
Furthermore, 5G UC aims to democratize access to diplomatic processes by enabling smaller nations and remote regions to participate more fully in global discussions. By reducing the need for extensive physical infrastructure and travel, this technology can level the playing field in international relations, potentially leading to more inclusive and diverse diplomatic engagements.
Another objective of 5G UC in diplomacy is to facilitate the secure exchange of sensitive information. The technology's advanced encryption capabilities and network slicing features offer promising solutions for maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of diplomatic communications, addressing longstanding concerns about cybersecurity in international relations.
As we explore the implications of 5G UC for enhanced global diplomacy, it is essential to consider both the opportunities and challenges that this technology presents. While the potential benefits are significant, issues such as equitable access, technological sovereignty, and the digital divide must be carefully addressed to ensure that 5G UC truly serves as a tool for global cooperation rather than a source of new geopolitical tensions.
Global Demand for 5G UC in Diplomatic Communications
The global demand for 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) in diplomatic communications is rapidly growing as nations recognize its potential to revolutionize international relations and enhance global diplomacy. This advanced technology offers unprecedented speed, reliability, and security, making it an invaluable tool for diplomatic missions worldwide.
Diplomatic communications require secure, real-time, and high-quality connections to facilitate sensitive discussions, negotiations, and information exchange between governments. 5G UC meets these demands by providing ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and enhanced security features. This enables seamless video conferencing, secure data transmission, and immersive virtual environments for diplomatic engagements.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital diplomacy, further driving the demand for 5G UC in diplomatic communications. As face-to-face meetings became challenging, diplomatic missions quickly adapted to virtual platforms, highlighting the need for robust and reliable communication infrastructure.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and the Internet of Things are increasingly being integrated into diplomatic processes. 5G UC provides the necessary foundation to support these advanced applications, enabling more sophisticated and efficient diplomatic operations.
Developing nations are particularly keen on adopting 5G UC for diplomatic communications as it allows them to leapfrog traditional infrastructure limitations and participate more effectively in global diplomacy. This technology can help bridge the digital divide and ensure more equitable representation in international affairs.
Major diplomatic hubs and international organizations are investing heavily in 5G UC infrastructure to enhance their communication capabilities. The United Nations, for instance, is exploring ways to leverage 5G UC to improve coordination among member states and streamline its peacekeeping operations.
As geopolitical tensions rise and cyber threats become more sophisticated, the demand for secure communication channels in diplomacy is at an all-time high. 5G UC's advanced encryption and network slicing capabilities offer a robust solution to these security concerns, making it an attractive option for diplomatic missions.
The integration of 5G UC in diplomatic communications also aligns with the broader trend of digital transformation in government services. Many nations are digitalizing their diplomatic processes, from visa applications to cultural exchange programs, necessitating a robust and scalable communication infrastructure.
Diplomatic communications require secure, real-time, and high-quality connections to facilitate sensitive discussions, negotiations, and information exchange between governments. 5G UC meets these demands by providing ultra-low latency, high bandwidth, and enhanced security features. This enables seamless video conferencing, secure data transmission, and immersive virtual environments for diplomatic engagements.
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of digital diplomacy, further driving the demand for 5G UC in diplomatic communications. As face-to-face meetings became challenging, diplomatic missions quickly adapted to virtual platforms, highlighting the need for robust and reliable communication infrastructure.
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and the Internet of Things are increasingly being integrated into diplomatic processes. 5G UC provides the necessary foundation to support these advanced applications, enabling more sophisticated and efficient diplomatic operations.
Developing nations are particularly keen on adopting 5G UC for diplomatic communications as it allows them to leapfrog traditional infrastructure limitations and participate more effectively in global diplomacy. This technology can help bridge the digital divide and ensure more equitable representation in international affairs.
Major diplomatic hubs and international organizations are investing heavily in 5G UC infrastructure to enhance their communication capabilities. The United Nations, for instance, is exploring ways to leverage 5G UC to improve coordination among member states and streamline its peacekeeping operations.
As geopolitical tensions rise and cyber threats become more sophisticated, the demand for secure communication channels in diplomacy is at an all-time high. 5G UC's advanced encryption and network slicing capabilities offer a robust solution to these security concerns, making it an attractive option for diplomatic missions.
The integration of 5G UC in diplomatic communications also aligns with the broader trend of digital transformation in government services. Many nations are digitalizing their diplomatic processes, from visa applications to cultural exchange programs, necessitating a robust and scalable communication infrastructure.
5G UC Technology Status and Challenges in Diplomacy
The current status of 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) technology in the realm of global diplomacy presents both significant advancements and notable challenges. As nations worldwide continue to deploy and expand their 5G networks, the implications for diplomatic relations and international cooperation are becoming increasingly apparent.
One of the primary technological achievements in this domain is the enhanced connectivity and communication capabilities offered by 5G UC. Diplomatic missions and international organizations can now leverage high-speed, low-latency connections to facilitate more efficient and secure communications. This has led to improvements in real-time translation services, virtual meetings, and the exchange of large data sets, all of which are crucial for modern diplomatic endeavors.
However, the implementation of 5G UC in diplomatic settings faces several technical hurdles. Security concerns remain at the forefront, as the increased connectivity also expands the potential attack surface for cyber threats. Ensuring end-to-end encryption and developing robust authentication protocols for sensitive diplomatic communications over 5G networks continue to be significant challenges.
Interoperability issues also pose a considerable obstacle. As different countries adopt varying 5G standards and technologies, ensuring seamless communication between diplomatic entities across borders becomes more complex. This fragmentation in 5G implementation can hinder the smooth flow of information and collaboration essential for effective diplomacy.
The geographical distribution of 5G UC technology in diplomatic contexts is uneven, reflecting broader global disparities in technological infrastructure. While some nations have rapidly integrated 5G into their diplomatic operations, others lag behind due to economic constraints or political considerations. This digital divide can potentially exacerbate existing inequalities in international relations and diplomatic influence.
Another critical challenge lies in the management of electromagnetic spectrum allocation for diplomatic use of 5G UC. As the demand for bandwidth increases, coordinating spectrum usage across borders and ensuring priority access for diplomatic communications during crises becomes increasingly complex.
Furthermore, the energy consumption of 5G infrastructure presents both technical and diplomatic challenges. As nations strive to meet climate goals, balancing the power requirements of extensive 5G networks with environmental commitments becomes a point of international negotiation and cooperation.
In conclusion, while 5G UC technology offers transformative potential for enhancing global diplomacy, its current status is characterized by a mix of promising advancements and significant technical and geopolitical challenges. Addressing these issues will require continued international collaboration, technical innovation, and diplomatic finesse to fully harness the benefits of 5G UC for global diplomatic relations.
One of the primary technological achievements in this domain is the enhanced connectivity and communication capabilities offered by 5G UC. Diplomatic missions and international organizations can now leverage high-speed, low-latency connections to facilitate more efficient and secure communications. This has led to improvements in real-time translation services, virtual meetings, and the exchange of large data sets, all of which are crucial for modern diplomatic endeavors.
However, the implementation of 5G UC in diplomatic settings faces several technical hurdles. Security concerns remain at the forefront, as the increased connectivity also expands the potential attack surface for cyber threats. Ensuring end-to-end encryption and developing robust authentication protocols for sensitive diplomatic communications over 5G networks continue to be significant challenges.
Interoperability issues also pose a considerable obstacle. As different countries adopt varying 5G standards and technologies, ensuring seamless communication between diplomatic entities across borders becomes more complex. This fragmentation in 5G implementation can hinder the smooth flow of information and collaboration essential for effective diplomacy.
The geographical distribution of 5G UC technology in diplomatic contexts is uneven, reflecting broader global disparities in technological infrastructure. While some nations have rapidly integrated 5G into their diplomatic operations, others lag behind due to economic constraints or political considerations. This digital divide can potentially exacerbate existing inequalities in international relations and diplomatic influence.
Another critical challenge lies in the management of electromagnetic spectrum allocation for diplomatic use of 5G UC. As the demand for bandwidth increases, coordinating spectrum usage across borders and ensuring priority access for diplomatic communications during crises becomes increasingly complex.
Furthermore, the energy consumption of 5G infrastructure presents both technical and diplomatic challenges. As nations strive to meet climate goals, balancing the power requirements of extensive 5G networks with environmental commitments becomes a point of international negotiation and cooperation.
In conclusion, while 5G UC technology offers transformative potential for enhancing global diplomacy, its current status is characterized by a mix of promising advancements and significant technical and geopolitical challenges. Addressing these issues will require continued international collaboration, technical innovation, and diplomatic finesse to fully harness the benefits of 5G UC for global diplomatic relations.
Current 5G UC Implementations in Global Diplomacy
01 5G Ultra-Capacity Network Architecture
5G UC refers to an advanced network architecture that provides enhanced capacity and performance in 5G networks. It utilizes a combination of mid-band and high-band spectrum to deliver faster speeds, lower latency, and increased network capacity compared to standard 5G deployments.- 5G Ultra-Capacity Network Architecture: 5G UC refers to an advanced network architecture that provides enhanced capacity and performance in 5G networks. It utilizes a combination of mid-band and high-band spectrum to deliver faster speeds, lower latency, and increased network capacity compared to standard 5G deployments.
- Spectrum Utilization in 5G UC: 5G UC leverages a wide range of spectrum bands, including mid-band (2.5 GHz to 6 GHz) and millimeter-wave frequencies (24 GHz and above). This multi-band approach allows for improved coverage, capacity, and speed in urban and high-density areas.
- Advanced Antenna Technologies for 5G UC: 5G UC implementations often incorporate advanced antenna technologies such as Massive MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) and beamforming. These technologies enable more efficient use of spectrum, improved signal quality, and increased network capacity.
- Network Slicing and Virtualization in 5G UC: 5G UC networks utilize network slicing and virtualization techniques to create multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure. This allows for optimized resource allocation and tailored services for different use cases and applications.
- Edge Computing Integration with 5G UC: 5G UC networks often integrate edge computing capabilities to reduce latency and improve overall network performance. This integration enables real-time processing and data analysis closer to the end-user, supporting applications such as augmented reality, autonomous vehicles, and industrial IoT.
02 Spectrum Utilization in 5G UC
5G UC leverages a wide range of spectrum bands, including mid-band (2.5 GHz to 6 GHz) and millimeter-wave (mmWave) frequencies. This multi-band approach allows for improved coverage, capacity, and speed in urban and high-density areas.Expand Specific Solutions03 Advanced Antenna Technologies for 5G UC
5G UC implementations often incorporate advanced antenna technologies such as Massive MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) and beamforming. These technologies enhance signal quality, increase network capacity, and improve overall performance in ultra-capacity deployments.Expand Specific Solutions04 Network Slicing and Virtualization in 5G UC
5G UC networks utilize network slicing and virtualization techniques to efficiently allocate network resources and provide customized services for different use cases. This enables operators to offer tailored experiences for various applications and industries.Expand Specific Solutions05 Edge Computing Integration with 5G UC
5G UC networks often integrate edge computing capabilities to reduce latency and improve performance for demanding applications. This integration allows for faster data processing and enables new use cases in areas such as augmented reality, autonomous vehicles, and industrial IoT.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in 5G UC Diplomatic Solutions
The 5G UC (Ultra Capacity) technology for enhanced global diplomacy is in its early development stage, with the market still emerging. The potential market size is significant, given the global nature of diplomatic communications. Technologically, it's progressing rapidly, with major players like Samsung, Ericsson, and Huawei leading the way. These companies are investing heavily in research and development to enhance 5G capabilities for secure, high-speed diplomatic communications. Other key players such as Qualcomm, Nokia, and IBM are also contributing to the advancement of this technology, focusing on areas like network infrastructure, security protocols, and AI-driven diplomatic tools. The competition is intense, with companies vying to establish themselves as leaders in this niche but potentially influential market.
Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
Technical Solution: Ericsson's 5G UC solution for global diplomacy focuses on creating a robust, secure, and flexible network infrastructure. Their approach includes the deployment of private 5G networks for diplomatic missions, ensuring confidentiality and reliability. Ericsson's technology enables seamless integration of IoT devices, AI-powered analytics, and cloud services to enhance diplomatic operations[5]. They have also developed specialized software for remote participation in international forums, featuring advanced holographic communication capabilities[6].
Strengths: Strong presence in global telecommunications infrastructure and extensive experience in network security. Weaknesses: Intense competition in the 5G market and potential geopolitical challenges in certain regions.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Huawei's 5G UC (Ultra-Connectivity) solution focuses on enhancing global diplomacy through advanced communication technologies. Their approach integrates AI-driven network optimization, edge computing, and secure communication channels to facilitate seamless international collaboration. Huawei's 5G UC platform supports real-time language translation, high-definition video conferencing, and immersive virtual reality experiences for diplomatic meetings[1]. The company has also developed a specialized diplomatic communications suite that ensures end-to-end encryption and protection against cyber threats, crucial for sensitive international negotiations[3].
Strengths: Advanced technological capabilities, global market presence, and strong R&D investments. Weaknesses: Geopolitical tensions and security concerns in some Western countries may limit adoption.
Core Innovations in 5G UC for Diplomatic Use
Base station, terminal, and communication method
PatentPendingUS20250151034A1
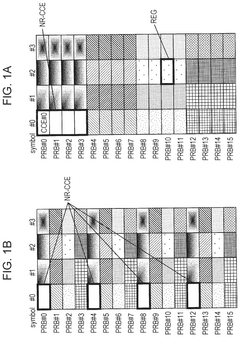
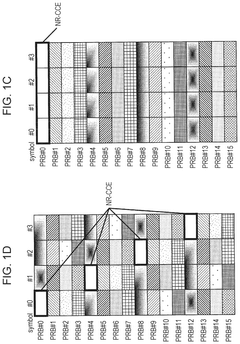
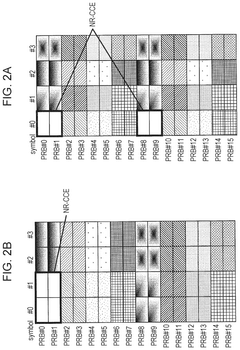
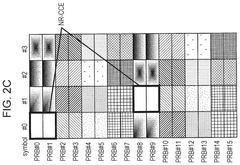
Innovation
- The solution involves allocating downlink control signals to a control channel region constituted by a plurality of CCEs, where the number of resource element groups (REGs) per CCE is a power of 2, and the bundling size indicating the number of REGs included in the REGs that constitute the CCE and arranged in adjacent resource blocks is also a power of 2.
Base station, terminal, and communication method
PatentPendingUS20250151034A1
Innovation
- The solution involves allocating downlink control signals to a control channel region constituted by a plurality of CCEs, where the number of resource element groups (REGs) per CCE is a power of 2, and the bundling size indicating the number of REGs included in the REGs that constitute the CCE and arranged in adjacent resource blocks is also a power of 2.
Cybersecurity Implications of 5G UC in Diplomacy
The integration of 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) technology in global diplomacy brings forth significant cybersecurity implications that demand careful consideration. As diplomatic communications increasingly rely on advanced telecommunications infrastructure, the enhanced capabilities of 5G UC introduce both opportunities and challenges in the realm of cybersecurity.
One of the primary concerns is the increased attack surface that 5G UC networks present. With a higher density of connected devices and more complex network architecture, potential vulnerabilities multiply, providing malicious actors with a broader range of entry points. This necessitates a comprehensive reassessment of existing security protocols and the development of more robust defense mechanisms tailored to the 5G UC environment.
The ultra-low latency and high bandwidth of 5G UC enable real-time data exchange and video conferencing at unprecedented quality levels, potentially revolutionizing diplomatic interactions. However, this also raises the stakes for data protection and encryption. Sensitive diplomatic communications transmitted over 5G UC networks require state-of-the-art encryption methods to safeguard against interception and unauthorized access.
Network slicing, a key feature of 5G UC, allows for the creation of virtual, isolated network segments. This capability can be leveraged to establish dedicated, secure channels for diplomatic communications, enhancing confidentiality and integrity. However, it also introduces new challenges in managing and securing these network slices, requiring advanced orchestration and monitoring tools.
The global nature of 5G UC deployment introduces geopolitical considerations in cybersecurity. Different countries and regions may implement varying security standards and protocols, potentially creating inconsistencies in the overall security landscape. This diversity necessitates increased international cooperation and the establishment of common cybersecurity frameworks specific to diplomatic applications of 5G UC.
Edge computing, facilitated by 5G UC, brings data processing closer to the source, potentially reducing the risk of long-distance data transmission interception. However, it also distributes sensitive information across a wider geographic area, necessitating robust security measures at edge locations. Diplomatic missions and consulates leveraging edge computing must implement stringent physical and digital security protocols to protect these distributed data processing nodes.
As artificial intelligence and machine learning become more prevalent in diplomatic analysis and decision-making processes, the high-speed, high-capacity nature of 5G UC networks amplifies both the potential and the risks. While these technologies can enhance threat detection and response, they also introduce new vectors for sophisticated cyber attacks, such as adversarial machine learning techniques aimed at manipulating diplomatic intelligence.
In conclusion, the cybersecurity implications of 5G UC in diplomacy are far-reaching and multifaceted. While the technology offers unprecedented opportunities for enhanced global communication and collaboration, it also demands a paradigm shift in cybersecurity strategies. Diplomatic entities must invest in cutting-edge security solutions, foster international cooperation on cybersecurity standards, and maintain a proactive stance in identifying and mitigating emerging threats in the 5G UC landscape.
One of the primary concerns is the increased attack surface that 5G UC networks present. With a higher density of connected devices and more complex network architecture, potential vulnerabilities multiply, providing malicious actors with a broader range of entry points. This necessitates a comprehensive reassessment of existing security protocols and the development of more robust defense mechanisms tailored to the 5G UC environment.
The ultra-low latency and high bandwidth of 5G UC enable real-time data exchange and video conferencing at unprecedented quality levels, potentially revolutionizing diplomatic interactions. However, this also raises the stakes for data protection and encryption. Sensitive diplomatic communications transmitted over 5G UC networks require state-of-the-art encryption methods to safeguard against interception and unauthorized access.
Network slicing, a key feature of 5G UC, allows for the creation of virtual, isolated network segments. This capability can be leveraged to establish dedicated, secure channels for diplomatic communications, enhancing confidentiality and integrity. However, it also introduces new challenges in managing and securing these network slices, requiring advanced orchestration and monitoring tools.
The global nature of 5G UC deployment introduces geopolitical considerations in cybersecurity. Different countries and regions may implement varying security standards and protocols, potentially creating inconsistencies in the overall security landscape. This diversity necessitates increased international cooperation and the establishment of common cybersecurity frameworks specific to diplomatic applications of 5G UC.
Edge computing, facilitated by 5G UC, brings data processing closer to the source, potentially reducing the risk of long-distance data transmission interception. However, it also distributes sensitive information across a wider geographic area, necessitating robust security measures at edge locations. Diplomatic missions and consulates leveraging edge computing must implement stringent physical and digital security protocols to protect these distributed data processing nodes.
As artificial intelligence and machine learning become more prevalent in diplomatic analysis and decision-making processes, the high-speed, high-capacity nature of 5G UC networks amplifies both the potential and the risks. While these technologies can enhance threat detection and response, they also introduce new vectors for sophisticated cyber attacks, such as adversarial machine learning techniques aimed at manipulating diplomatic intelligence.
In conclusion, the cybersecurity implications of 5G UC in diplomacy are far-reaching and multifaceted. While the technology offers unprecedented opportunities for enhanced global communication and collaboration, it also demands a paradigm shift in cybersecurity strategies. Diplomatic entities must invest in cutting-edge security solutions, foster international cooperation on cybersecurity standards, and maintain a proactive stance in identifying and mitigating emerging threats in the 5G UC landscape.
Geopolitical Impact of 5G UC Adoption
The adoption of 5G Ultra-Capacity (UC) technology is poised to have significant geopolitical implications, reshaping the landscape of global diplomacy and international relations. As nations race to implement and leverage this advanced telecommunications infrastructure, new power dynamics are emerging that could alter the balance of global influence.
One of the primary geopolitical impacts of 5G UC adoption is the potential for increased economic competitiveness. Countries that successfully deploy and integrate 5G UC networks are likely to gain a substantial advantage in the global digital economy. This technology enables faster data transmission, lower latency, and greater connectivity, which can drive innovation, enhance productivity, and foster the development of new industries. As a result, early adopters of 5G UC may experience accelerated economic growth and improved global standing.
The deployment of 5G UC also has implications for national security and cyber sovereignty. Nations that control the development and implementation of 5G UC infrastructure may gain strategic advantages in terms of data security and intelligence gathering. This has led to concerns about technological dependencies and the potential for foreign influence through critical infrastructure. Consequently, debates around 5G UC adoption have become intertwined with broader geopolitical tensions, particularly between major powers like the United States and China.
Furthermore, 5G UC technology has the potential to reshape diplomatic channels and international cooperation. Enhanced connectivity and communication capabilities could facilitate more frequent and immersive virtual diplomatic engagements, reducing the need for physical travel and potentially democratizing access to international forums. This could lead to more inclusive global governance structures and enable smaller nations to have a greater voice in international affairs.
The adoption of 5G UC may also exacerbate the digital divide between nations, creating new forms of geopolitical inequality. Countries that lack the resources or technological capacity to implement 5G UC networks may find themselves at a disadvantage in global negotiations and economic partnerships. This could lead to a new era of "digital colonialism," where technologically advanced nations exert influence over less developed countries through control of critical digital infrastructure.
Lastly, the global rollout of 5G UC is likely to intensify competition for technological leadership and standard-setting. Nations and companies that successfully establish their 5G UC standards and protocols as global norms may gain long-term strategic advantages. This has led to increased investment in research and development, as well as efforts to form international alliances and partnerships to promote specific technological approaches.
One of the primary geopolitical impacts of 5G UC adoption is the potential for increased economic competitiveness. Countries that successfully deploy and integrate 5G UC networks are likely to gain a substantial advantage in the global digital economy. This technology enables faster data transmission, lower latency, and greater connectivity, which can drive innovation, enhance productivity, and foster the development of new industries. As a result, early adopters of 5G UC may experience accelerated economic growth and improved global standing.
The deployment of 5G UC also has implications for national security and cyber sovereignty. Nations that control the development and implementation of 5G UC infrastructure may gain strategic advantages in terms of data security and intelligence gathering. This has led to concerns about technological dependencies and the potential for foreign influence through critical infrastructure. Consequently, debates around 5G UC adoption have become intertwined with broader geopolitical tensions, particularly between major powers like the United States and China.
Furthermore, 5G UC technology has the potential to reshape diplomatic channels and international cooperation. Enhanced connectivity and communication capabilities could facilitate more frequent and immersive virtual diplomatic engagements, reducing the need for physical travel and potentially democratizing access to international forums. This could lead to more inclusive global governance structures and enable smaller nations to have a greater voice in international affairs.
The adoption of 5G UC may also exacerbate the digital divide between nations, creating new forms of geopolitical inequality. Countries that lack the resources or technological capacity to implement 5G UC networks may find themselves at a disadvantage in global negotiations and economic partnerships. This could lead to a new era of "digital colonialism," where technologically advanced nations exert influence over less developed countries through control of critical digital infrastructure.
Lastly, the global rollout of 5G UC is likely to intensify competition for technological leadership and standard-setting. Nations and companies that successfully establish their 5G UC standards and protocols as global norms may gain long-term strategic advantages. This has led to increased investment in research and development, as well as efforts to form international alliances and partnerships to promote specific technological approaches.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!