Exploring the Role of 5G UC in Advancing Teletherapy Solutions
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
5G UC Teletherapy Background and Objectives
The convergence of 5G Ultra-Capacity (UC) technology and teletherapy represents a significant leap forward in healthcare delivery. As the world increasingly embraces digital solutions, the integration of advanced telecommunications with remote therapy services has become a focal point for innovation. 5G UC, with its enhanced capabilities, promises to revolutionize the landscape of teletherapy by addressing longstanding challenges and opening new avenues for patient care.
The evolution of teletherapy can be traced back to the early days of telemedicine, which began with simple telephone consultations. As technology progressed, video conferencing became the standard, allowing for more personal interactions between therapists and patients. However, these solutions were often hampered by connectivity issues, poor video quality, and limited interactivity. The advent of 5G UC technology marks a pivotal moment in this progression, offering the potential to overcome these limitations and usher in a new era of high-quality, immersive teletherapy experiences.
The primary objective of integrating 5G UC into teletherapy is to enhance the quality and accessibility of remote mental health services. This technology aims to provide near-real-time, high-definition video communications that closely mimic in-person interactions. By reducing latency and increasing bandwidth, 5G UC can support more sophisticated therapeutic tools, including virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) applications, which have shown promise in treating various mental health conditions.
Furthermore, the implementation of 5G UC in teletherapy seeks to bridge the gap in mental health care access, particularly in underserved and rural areas. By enabling reliable, high-quality remote sessions, this technology can help address the shortage of mental health professionals in certain regions and make specialized care more widely available. The goal is to create a more equitable healthcare system where geographical location does not determine the quality of mental health support one can receive.
Another critical objective is to improve the overall efficacy of teletherapy. With 5G UC's capabilities, therapists can employ more advanced diagnostic tools and monitoring systems, leading to more accurate assessments and personalized treatment plans. The technology also aims to facilitate seamless integration of wearable devices and IoT sensors, allowing for continuous monitoring of patients' vital signs and behavioral patterns, which can provide valuable insights for therapy sessions.
As we explore the role of 5G UC in advancing teletherapy solutions, it is essential to consider the broader implications for the healthcare industry. This technological integration has the potential to reshape therapeutic practices, patient engagement, and the very nature of the therapist-patient relationship. The journey towards fully realizing these objectives will require collaborative efforts from technology providers, healthcare professionals, and policymakers to ensure that the benefits of 5G UC-enabled teletherapy are maximized while addressing concerns around privacy, security, and equitable access.
The evolution of teletherapy can be traced back to the early days of telemedicine, which began with simple telephone consultations. As technology progressed, video conferencing became the standard, allowing for more personal interactions between therapists and patients. However, these solutions were often hampered by connectivity issues, poor video quality, and limited interactivity. The advent of 5G UC technology marks a pivotal moment in this progression, offering the potential to overcome these limitations and usher in a new era of high-quality, immersive teletherapy experiences.
The primary objective of integrating 5G UC into teletherapy is to enhance the quality and accessibility of remote mental health services. This technology aims to provide near-real-time, high-definition video communications that closely mimic in-person interactions. By reducing latency and increasing bandwidth, 5G UC can support more sophisticated therapeutic tools, including virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) applications, which have shown promise in treating various mental health conditions.
Furthermore, the implementation of 5G UC in teletherapy seeks to bridge the gap in mental health care access, particularly in underserved and rural areas. By enabling reliable, high-quality remote sessions, this technology can help address the shortage of mental health professionals in certain regions and make specialized care more widely available. The goal is to create a more equitable healthcare system where geographical location does not determine the quality of mental health support one can receive.
Another critical objective is to improve the overall efficacy of teletherapy. With 5G UC's capabilities, therapists can employ more advanced diagnostic tools and monitoring systems, leading to more accurate assessments and personalized treatment plans. The technology also aims to facilitate seamless integration of wearable devices and IoT sensors, allowing for continuous monitoring of patients' vital signs and behavioral patterns, which can provide valuable insights for therapy sessions.
As we explore the role of 5G UC in advancing teletherapy solutions, it is essential to consider the broader implications for the healthcare industry. This technological integration has the potential to reshape therapeutic practices, patient engagement, and the very nature of the therapist-patient relationship. The journey towards fully realizing these objectives will require collaborative efforts from technology providers, healthcare professionals, and policymakers to ensure that the benefits of 5G UC-enabled teletherapy are maximized while addressing concerns around privacy, security, and equitable access.
Teletherapy Market Demand Analysis
The teletherapy market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for remote healthcare services and advancements in telecommunications technology. The global teletherapy market size was valued at $6.5 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $22.4 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of 17.2% during the forecast period.
Several factors contribute to the rising demand for teletherapy solutions. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote healthcare services, with many patients and healthcare providers turning to virtual consultations to maintain continuity of care while minimizing the risk of virus transmission. This shift in healthcare delivery has created a lasting impact on patient preferences and provider practices.
Mental health services have emerged as a key driver of teletherapy market growth. The prevalence of mental health disorders, coupled with the shortage of mental health professionals in many regions, has led to increased demand for accessible and convenient therapy options. Teletherapy platforms offer a solution by connecting patients with therapists remotely, reducing barriers to care such as geographic limitations and stigma associated with in-person visits.
The aging population and the growing burden of chronic diseases have also contributed to the expanding teletherapy market. Elderly patients and those with mobility issues benefit from the convenience of receiving care at home, while teletherapy enables more frequent check-ins and monitoring for patients with chronic conditions.
Corporate wellness programs have increasingly incorporated teletherapy services, recognizing the importance of mental health support for employee well-being and productivity. This trend has further boosted market demand, particularly in developed economies.
Technological advancements, including the rollout of 5G networks, have enhanced the capabilities of teletherapy platforms. Improved connectivity and lower latency enable higher-quality video consultations, real-time data transmission, and the integration of advanced features such as virtual reality therapy and remote monitoring devices.
Despite the growing demand, challenges remain in the teletherapy market. Concerns about data privacy and security, regulatory hurdles, and the need for standardization in teletherapy practices are factors that need to be addressed to ensure sustainable market growth.
In conclusion, the teletherapy market is poised for continued expansion, driven by changing healthcare delivery models, increasing awareness of mental health issues, and technological advancements. The integration of 5G UC technology has the potential to further enhance teletherapy solutions, offering improved quality of care and expanding the range of services that can be delivered remotely.
Several factors contribute to the rising demand for teletherapy solutions. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the adoption of remote healthcare services, with many patients and healthcare providers turning to virtual consultations to maintain continuity of care while minimizing the risk of virus transmission. This shift in healthcare delivery has created a lasting impact on patient preferences and provider practices.
Mental health services have emerged as a key driver of teletherapy market growth. The prevalence of mental health disorders, coupled with the shortage of mental health professionals in many regions, has led to increased demand for accessible and convenient therapy options. Teletherapy platforms offer a solution by connecting patients with therapists remotely, reducing barriers to care such as geographic limitations and stigma associated with in-person visits.
The aging population and the growing burden of chronic diseases have also contributed to the expanding teletherapy market. Elderly patients and those with mobility issues benefit from the convenience of receiving care at home, while teletherapy enables more frequent check-ins and monitoring for patients with chronic conditions.
Corporate wellness programs have increasingly incorporated teletherapy services, recognizing the importance of mental health support for employee well-being and productivity. This trend has further boosted market demand, particularly in developed economies.
Technological advancements, including the rollout of 5G networks, have enhanced the capabilities of teletherapy platforms. Improved connectivity and lower latency enable higher-quality video consultations, real-time data transmission, and the integration of advanced features such as virtual reality therapy and remote monitoring devices.
Despite the growing demand, challenges remain in the teletherapy market. Concerns about data privacy and security, regulatory hurdles, and the need for standardization in teletherapy practices are factors that need to be addressed to ensure sustainable market growth.
In conclusion, the teletherapy market is poised for continued expansion, driven by changing healthcare delivery models, increasing awareness of mental health issues, and technological advancements. The integration of 5G UC technology has the potential to further enhance teletherapy solutions, offering improved quality of care and expanding the range of services that can be delivered remotely.
5G UC Technology Status and Challenges
The current state of 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) technology in the context of teletherapy solutions is rapidly evolving, with significant advancements and challenges. 5G UC, characterized by its high-band spectrum utilization, offers unprecedented speeds and low latency, making it particularly suitable for demanding applications like teletherapy.
In terms of technological progress, 5G UC networks have been successfully deployed in several major urban areas globally. These networks demonstrate peak speeds of up to 3 Gbps and average speeds of 300-400 Mbps, significantly outperforming previous generations of cellular technology. This high-speed connectivity is crucial for real-time, high-quality video consultations and data transmission in teletherapy applications.
However, the widespread implementation of 5G UC for teletherapy faces several challenges. One primary obstacle is the limited coverage area of 5G UC networks. Due to the high-frequency spectrum used, 5G UC signals have shorter range and are more susceptible to interference from physical obstacles, potentially limiting access in rural or less developed areas where teletherapy could be most beneficial.
Another significant challenge is the need for substantial infrastructure investment. The deployment of 5G UC requires a dense network of small cells and advanced antenna systems, which can be costly and time-consuming to install, especially in areas with complex urban landscapes or sparse populations.
Interoperability and standardization present additional hurdles. As teletherapy solutions evolve to leverage 5G UC capabilities, ensuring compatibility across different platforms, devices, and network providers becomes crucial. The development of universal standards for 5G UC-enabled teletherapy applications is still in progress, which can lead to fragmentation in the market and potential compatibility issues.
Data security and privacy concerns also pose significant challenges. The increased bandwidth and connectivity of 5G UC networks, while beneficial for teletherapy, also expand the potential attack surface for cybersecurity threats. Ensuring robust encryption and secure data transmission protocols is paramount, especially given the sensitive nature of medical information exchanged during teletherapy sessions.
From a geographical perspective, the development and implementation of 5G UC technology for teletherapy solutions vary significantly. Countries like South Korea, China, and the United States are at the forefront, with extensive 5G UC network coverage in major cities. However, many developing nations lag behind, creating a potential digital divide in access to advanced teletherapy services.
In conclusion, while 5G UC technology holds immense promise for revolutionizing teletherapy solutions, its current status is characterized by rapid advancements coupled with significant implementation challenges. Overcoming these obstacles will be crucial for realizing the full potential of 5G UC in enhancing teletherapy accessibility and effectiveness on a global scale.
In terms of technological progress, 5G UC networks have been successfully deployed in several major urban areas globally. These networks demonstrate peak speeds of up to 3 Gbps and average speeds of 300-400 Mbps, significantly outperforming previous generations of cellular technology. This high-speed connectivity is crucial for real-time, high-quality video consultations and data transmission in teletherapy applications.
However, the widespread implementation of 5G UC for teletherapy faces several challenges. One primary obstacle is the limited coverage area of 5G UC networks. Due to the high-frequency spectrum used, 5G UC signals have shorter range and are more susceptible to interference from physical obstacles, potentially limiting access in rural or less developed areas where teletherapy could be most beneficial.
Another significant challenge is the need for substantial infrastructure investment. The deployment of 5G UC requires a dense network of small cells and advanced antenna systems, which can be costly and time-consuming to install, especially in areas with complex urban landscapes or sparse populations.
Interoperability and standardization present additional hurdles. As teletherapy solutions evolve to leverage 5G UC capabilities, ensuring compatibility across different platforms, devices, and network providers becomes crucial. The development of universal standards for 5G UC-enabled teletherapy applications is still in progress, which can lead to fragmentation in the market and potential compatibility issues.
Data security and privacy concerns also pose significant challenges. The increased bandwidth and connectivity of 5G UC networks, while beneficial for teletherapy, also expand the potential attack surface for cybersecurity threats. Ensuring robust encryption and secure data transmission protocols is paramount, especially given the sensitive nature of medical information exchanged during teletherapy sessions.
From a geographical perspective, the development and implementation of 5G UC technology for teletherapy solutions vary significantly. Countries like South Korea, China, and the United States are at the forefront, with extensive 5G UC network coverage in major cities. However, many developing nations lag behind, creating a potential digital divide in access to advanced teletherapy services.
In conclusion, while 5G UC technology holds immense promise for revolutionizing teletherapy solutions, its current status is characterized by rapid advancements coupled with significant implementation challenges. Overcoming these obstacles will be crucial for realizing the full potential of 5G UC in enhancing teletherapy accessibility and effectiveness on a global scale.
Current 5G UC Teletherapy Solutions
01 5G Ultra Capacity Network Architecture
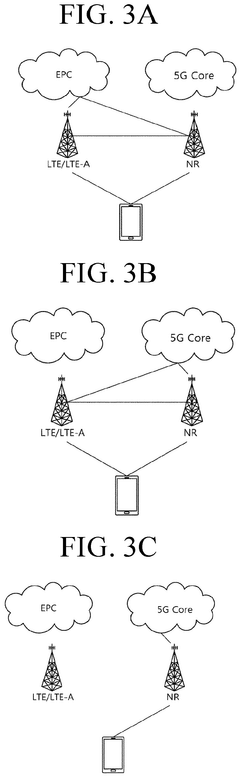
5G Ultra Capacity (UC) refers to an advanced network architecture that utilizes mid-band and high-band spectrum to deliver enhanced capacity and performance. This architecture enables faster data speeds, lower latency, and improved network efficiency compared to standard 5G networks. It incorporates advanced technologies such as massive MIMO, beamforming, and carrier aggregation to maximize spectrum utilization and network capacity.- 5G Ultra Capacity network architecture: 5G Ultra Capacity (UC) refers to an advanced network architecture that utilizes mid-band and high-band spectrum to deliver enhanced capacity, speed, and coverage. This technology combines multiple frequency bands and advanced antenna systems to provide significantly faster data rates and lower latency compared to standard 5G networks.
- Spectrum aggregation and carrier integration: 5G UC employs spectrum aggregation techniques to combine multiple frequency bands, including mid-band and mmWave spectrum. This approach allows for increased bandwidth and improved network performance. Carrier integration is used to seamlessly combine different spectrum resources, enabling higher data throughput and more efficient use of available frequencies.
- Advanced antenna technologies for 5G UC: 5G Ultra Capacity networks utilize advanced antenna technologies such as Massive MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) and beamforming. These techniques enable more focused and efficient signal transmission, improving coverage, capacity, and overall network performance in dense urban areas and challenging environments.
- Network slicing and virtualization for 5G UC: Network slicing and virtualization technologies are employed in 5G UC networks to create multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure. This allows for optimized resource allocation and customized network configurations for different use cases and applications, enhancing overall network efficiency and flexibility.
- Edge computing integration with 5G UC: 5G Ultra Capacity networks incorporate edge computing capabilities to bring processing power closer to end-users and devices. This integration reduces latency, improves response times, and enables new applications such as augmented reality, autonomous vehicles, and industrial IoT. Edge computing also helps offload traffic from the core network, further enhancing overall network performance.
02 Resource Allocation and Management in 5G UC
Efficient resource allocation and management are crucial for 5G UC networks to optimize performance. This includes dynamic spectrum allocation, intelligent scheduling algorithms, and adaptive power control mechanisms. These techniques ensure that network resources are utilized effectively to meet varying user demands and traffic patterns, ultimately improving the overall quality of service and user experience in high-capacity scenarios.Expand Specific Solutions03 5G UC Device and Infrastructure Integration
The integration of 5G UC-capable devices and network infrastructure is essential for leveraging the full potential of Ultra Capacity networks. This involves the development of advanced chipsets, antennas, and radio frequency components that can support higher frequency bands and complex signal processing. Additionally, it requires the deployment of dense small cell networks and the upgrade of existing macro cell sites to support 5G UC capabilities.Expand Specific Solutions04 5G UC Security and Privacy Enhancements
As 5G UC networks handle increased data traffic and support more critical applications, robust security and privacy measures are paramount. This includes advanced encryption techniques, secure authentication protocols, and network slicing for isolated and protected communication channels. These enhancements aim to safeguard user data, prevent unauthorized access, and ensure the integrity of network operations in high-capacity environments.Expand Specific Solutions05 5G UC Performance Optimization and Quality of Service
Continuous optimization of 5G UC networks is necessary to maintain high performance and quality of service. This involves real-time network monitoring, predictive analytics, and AI-driven optimization algorithms. These techniques help identify and resolve network issues proactively, balance load across the network, and ensure consistent high-speed connectivity even in densely populated areas or during peak usage times.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in 5G UC Teletherapy
The 5G UC (Ultra Capacity) technology in teletherapy solutions is in an early growth stage, with the market poised for significant expansion. The global teletherapy market size is projected to reach billions of dollars in the coming years, driven by increasing demand for remote healthcare services. While the technology is still evolving, major players like Samsung Electronics, Ericsson, and Qualcomm are making substantial investments in 5G UC development. These companies, along with telecom operators like DISH Wireless and NTT Docomo, are working to enhance network capabilities and device compatibility. The involvement of healthcare institutions like West China Hospital of Sichuan University indicates growing interest in practical applications, though widespread adoption is still in progress.
Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
Technical Solution: Ericsson has developed a comprehensive 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) solution for teletherapy applications. Their approach integrates high-bandwidth, low-latency 5G networks with edge computing capabilities to enable real-time, high-quality video consultations and remote patient monitoring. Ericsson's 5G UC technology supports multi-access edge computing (MEC) to process data closer to the source, reducing latency to less than 10 milliseconds[1]. This allows for seamless transmission of high-resolution medical imaging and real-time biosensor data. The company has also implemented advanced network slicing techniques, allocating dedicated virtual network resources for critical teletherapy services, ensuring consistent performance and security[3].
Strengths: Extensive 5G infrastructure expertise, strong partnerships with healthcare providers, and advanced network slicing capabilities. Weaknesses: Reliance on healthcare partners for domain-specific knowledge and potential regulatory challenges in different markets.
NTT Docomo, Inc.
Technical Solution: NTT Docomo has pioneered 5G UC solutions for teletherapy, focusing on ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) for remote medical procedures. Their system utilizes millimeter-wave (mmWave) frequencies to achieve data rates up to 20 Gbps, enabling high-fidelity transmission of 3D medical imaging and haptic feedback for telesurgery applications[2]. NTT Docomo has also developed a unique network architecture that combines 5G with AI-driven predictive quality of service (QoS) management, ensuring stable connections even in challenging network conditions. The company's teletherapy platform incorporates advanced security measures, including quantum key distribution for encryption, to protect sensitive patient data[4].
Strengths: Cutting-edge URLLC technology, strong focus on telesurgery applications, and advanced security features. Weaknesses: Limited global presence compared to some competitors and potential high implementation costs for healthcare providers.
Core 5G UC Teletherapy Innovations
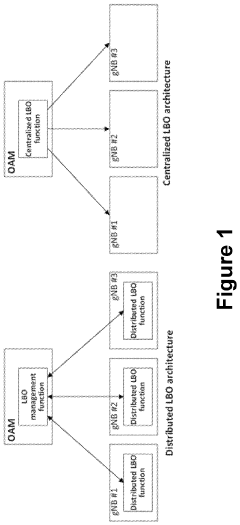
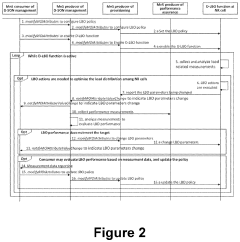
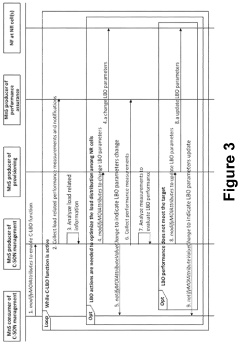
Load balancing optimization for 5G self-organizing networks
PatentActiveUS11963041B2
Innovation
- The implementation of distributed and centralized Load Balancing Optimization (LBO) functions within the SON framework, which allows for policy management, performance measurement, and parameter adjustment to optimize traffic distribution and handover processes automatically, enabling efficient resource utilization and quality maintenance.
Method and apparatus for uplink transmission in wireless communication system
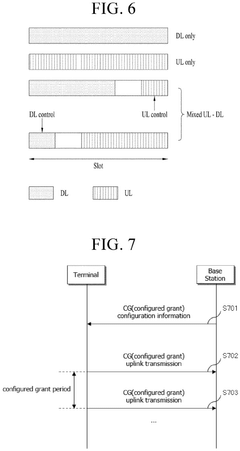
PatentPendingEP4459914A1
Innovation
- The method involves configuring unused transmission occasion (UTO)-uplink control information (UCI) to indicate unused PUSCH transmission occasions, allowing terminals to dynamically indicate unused areas for repurposing, and optimizing resource allocation within CG periods to enhance transmission efficiency.
Regulatory Framework for 5G UC in Healthcare
The regulatory framework for 5G UC in healthcare is a complex and evolving landscape that requires careful consideration of various factors. As 5G Ultra-Capacity (UC) technology continues to advance and integrate into teletherapy solutions, it is crucial to establish a comprehensive regulatory structure that ensures patient safety, data privacy, and quality of care.
One of the primary regulatory challenges is the need to balance innovation with patient protection. Regulatory bodies must create guidelines that allow for the rapid development and deployment of 5G UC-enabled teletherapy solutions while maintaining stringent safety standards. This includes establishing protocols for remote patient monitoring, real-time data transmission, and virtual consultations.
Data privacy and security regulations play a critical role in the 5G UC healthcare ecosystem. With the increased bandwidth and low latency of 5G UC, vast amounts of sensitive patient data can be transmitted in real-time. Regulatory frameworks must address issues such as data encryption, secure storage, and authorized access to ensure compliance with existing healthcare privacy laws, such as HIPAA in the United States.
Interoperability standards are another key aspect of the regulatory framework. As 5G UC enables seamless communication between various medical devices and systems, regulators must establish guidelines for interoperability to ensure that different teletherapy solutions can work together effectively and securely.
The regulatory framework should also address the issue of liability in 5G UC-enabled teletherapy. Clear guidelines must be established to determine responsibility in cases of system failures, data breaches, or misdiagnosis resulting from technical issues. This includes defining the roles and responsibilities of healthcare providers, technology vendors, and network operators.
Regulatory bodies must also consider the global nature of 5G UC technology and its potential for cross-border healthcare services. International cooperation and harmonization of regulations will be essential to ensure consistent standards and facilitate the growth of global teletherapy solutions.
As 5G UC technology continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks must remain flexible and adaptable. Regular reviews and updates to regulations will be necessary to keep pace with technological advancements and emerging challenges in the field of teletherapy.
One of the primary regulatory challenges is the need to balance innovation with patient protection. Regulatory bodies must create guidelines that allow for the rapid development and deployment of 5G UC-enabled teletherapy solutions while maintaining stringent safety standards. This includes establishing protocols for remote patient monitoring, real-time data transmission, and virtual consultations.
Data privacy and security regulations play a critical role in the 5G UC healthcare ecosystem. With the increased bandwidth and low latency of 5G UC, vast amounts of sensitive patient data can be transmitted in real-time. Regulatory frameworks must address issues such as data encryption, secure storage, and authorized access to ensure compliance with existing healthcare privacy laws, such as HIPAA in the United States.
Interoperability standards are another key aspect of the regulatory framework. As 5G UC enables seamless communication between various medical devices and systems, regulators must establish guidelines for interoperability to ensure that different teletherapy solutions can work together effectively and securely.
The regulatory framework should also address the issue of liability in 5G UC-enabled teletherapy. Clear guidelines must be established to determine responsibility in cases of system failures, data breaches, or misdiagnosis resulting from technical issues. This includes defining the roles and responsibilities of healthcare providers, technology vendors, and network operators.
Regulatory bodies must also consider the global nature of 5G UC technology and its potential for cross-border healthcare services. International cooperation and harmonization of regulations will be essential to ensure consistent standards and facilitate the growth of global teletherapy solutions.
As 5G UC technology continues to evolve, regulatory frameworks must remain flexible and adaptable. Regular reviews and updates to regulations will be necessary to keep pace with technological advancements and emerging challenges in the field of teletherapy.
5G UC Teletherapy Security and Privacy Considerations
The integration of 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) technology in teletherapy solutions brings significant advancements in connectivity and performance, but it also introduces new security and privacy considerations that must be carefully addressed. As teletherapy sessions involve the transmission of sensitive patient information, ensuring robust security measures is paramount.
One of the primary security concerns in 5G UC teletherapy is data encryption. The high-speed, low-latency nature of 5G networks necessitates advanced encryption protocols to protect patient data during transmission. Implementing end-to-end encryption and secure communication channels is essential to prevent unauthorized access and maintain patient confidentiality.
Authentication and access control mechanisms also play a crucial role in securing 5G UC teletherapy systems. Multi-factor authentication, biometric verification, and secure token-based access can help ensure that only authorized healthcare providers and patients can access the teletherapy platform and sensitive medical information.
Network segmentation and isolation are important strategies to enhance security in 5G UC teletherapy environments. By creating separate virtual networks for different types of traffic, healthcare organizations can isolate sensitive patient data from other network traffic, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Privacy considerations in 5G UC teletherapy extend beyond data protection to include patient consent and data ownership. Clear policies and procedures must be established to obtain informed consent from patients regarding the collection, use, and storage of their personal health information. Additionally, patients should have control over their data and the ability to access, modify, or delete their information as needed.
The increased bandwidth and lower latency of 5G UC networks enable more sophisticated teletherapy applications, such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) therapy sessions. While these technologies offer enhanced treatment options, they also introduce new privacy risks, such as the potential for capturing and storing detailed patient movements and behaviors. Implementing strict data minimization practices and anonymization techniques is crucial to protect patient privacy in these advanced teletherapy scenarios.
Compliance with healthcare regulations and data protection laws, such as HIPAA in the United States or GDPR in Europe, is a critical aspect of 5G UC teletherapy security and privacy. Healthcare providers must ensure that their teletherapy platforms and practices adhere to these regulations, including proper data handling, storage, and breach notification procedures.
As 5G UC networks rely on a more distributed architecture, including edge computing, security measures must extend to these distributed components. Implementing robust security protocols at network edges and ensuring secure communication between edge devices and central servers is essential to maintain the overall security of the teletherapy ecosystem.
One of the primary security concerns in 5G UC teletherapy is data encryption. The high-speed, low-latency nature of 5G networks necessitates advanced encryption protocols to protect patient data during transmission. Implementing end-to-end encryption and secure communication channels is essential to prevent unauthorized access and maintain patient confidentiality.
Authentication and access control mechanisms also play a crucial role in securing 5G UC teletherapy systems. Multi-factor authentication, biometric verification, and secure token-based access can help ensure that only authorized healthcare providers and patients can access the teletherapy platform and sensitive medical information.
Network segmentation and isolation are important strategies to enhance security in 5G UC teletherapy environments. By creating separate virtual networks for different types of traffic, healthcare organizations can isolate sensitive patient data from other network traffic, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Privacy considerations in 5G UC teletherapy extend beyond data protection to include patient consent and data ownership. Clear policies and procedures must be established to obtain informed consent from patients regarding the collection, use, and storage of their personal health information. Additionally, patients should have control over their data and the ability to access, modify, or delete their information as needed.
The increased bandwidth and lower latency of 5G UC networks enable more sophisticated teletherapy applications, such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) therapy sessions. While these technologies offer enhanced treatment options, they also introduce new privacy risks, such as the potential for capturing and storing detailed patient movements and behaviors. Implementing strict data minimization practices and anonymization techniques is crucial to protect patient privacy in these advanced teletherapy scenarios.
Compliance with healthcare regulations and data protection laws, such as HIPAA in the United States or GDPR in Europe, is a critical aspect of 5G UC teletherapy security and privacy. Healthcare providers must ensure that their teletherapy platforms and practices adhere to these regulations, including proper data handling, storage, and breach notification procedures.
As 5G UC networks rely on a more distributed architecture, including edge computing, security measures must extend to these distributed components. Implementing robust security protocols at network edges and ensuring secure communication between edge devices and central servers is essential to maintain the overall security of the teletherapy ecosystem.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!