Emerging Trends in Transparent Cellophane Applications
JUL 9, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Cellophane Evolution
Cellophane, a transparent film made from regenerated cellulose, has undergone significant evolution since its accidental discovery in 1908 by Swiss chemist Jacques Brandenberger. Initially developed as a protective coating for tablecloths, cellophane's potential as a versatile packaging material was quickly recognized, leading to its widespread adoption in various industries.
The early stages of cellophane development focused on improving its moisture resistance and heat-sealing properties. In the 1920s, DuPont acquired the rights to produce cellophane in the United States, marking a pivotal moment in its commercialization. The company invested heavily in research and development, leading to breakthroughs such as moisture-proof cellophane in 1927, which dramatically expanded its applications in food packaging.
Throughout the mid-20th century, cellophane continued to evolve with advancements in production techniques and the introduction of new additives. The 1950s and 1960s saw the development of heat-shrinkable cellophane, further enhancing its utility in packaging applications. During this period, cellophane dominated the flexible packaging market, particularly in the food industry.
However, the 1970s and 1980s brought challenges to cellophane's market dominance with the rise of petroleum-based plastics like polyethylene and polypropylene. These materials offered improved barrier properties and lower production costs, leading to a decline in cellophane usage. Despite this setback, cellophane maintained a niche in certain applications due to its unique properties, such as high clarity and natural biodegradability.
The late 20th and early 21st centuries have seen a resurgence of interest in cellophane, driven by growing environmental concerns and the push for sustainable packaging solutions. Recent developments have focused on enhancing cellophane's barrier properties and improving its production efficiency to compete with synthetic plastics. Innovations in nanotechnology and bio-based additives have led to new formulations of cellophane with enhanced functionality.
Today, cellophane is experiencing a renaissance as consumers and businesses seek eco-friendly alternatives to traditional plastics. Research is ongoing to develop cellophane variants with improved mechanical properties, better moisture resistance, and enhanced biodegradability. The integration of smart packaging technologies, such as indicators and sensors, into cellophane films represents an exciting frontier in its evolution.
As we look to the future, the evolution of cellophane is likely to continue along the path of sustainability and advanced functionality. Emerging trends include the development of fully compostable cellophane variants, the incorporation of antimicrobial properties for extended food preservation, and the exploration of cellophane's potential in high-tech applications beyond traditional packaging.
The early stages of cellophane development focused on improving its moisture resistance and heat-sealing properties. In the 1920s, DuPont acquired the rights to produce cellophane in the United States, marking a pivotal moment in its commercialization. The company invested heavily in research and development, leading to breakthroughs such as moisture-proof cellophane in 1927, which dramatically expanded its applications in food packaging.
Throughout the mid-20th century, cellophane continued to evolve with advancements in production techniques and the introduction of new additives. The 1950s and 1960s saw the development of heat-shrinkable cellophane, further enhancing its utility in packaging applications. During this period, cellophane dominated the flexible packaging market, particularly in the food industry.
However, the 1970s and 1980s brought challenges to cellophane's market dominance with the rise of petroleum-based plastics like polyethylene and polypropylene. These materials offered improved barrier properties and lower production costs, leading to a decline in cellophane usage. Despite this setback, cellophane maintained a niche in certain applications due to its unique properties, such as high clarity and natural biodegradability.
The late 20th and early 21st centuries have seen a resurgence of interest in cellophane, driven by growing environmental concerns and the push for sustainable packaging solutions. Recent developments have focused on enhancing cellophane's barrier properties and improving its production efficiency to compete with synthetic plastics. Innovations in nanotechnology and bio-based additives have led to new formulations of cellophane with enhanced functionality.
Today, cellophane is experiencing a renaissance as consumers and businesses seek eco-friendly alternatives to traditional plastics. Research is ongoing to develop cellophane variants with improved mechanical properties, better moisture resistance, and enhanced biodegradability. The integration of smart packaging technologies, such as indicators and sensors, into cellophane films represents an exciting frontier in its evolution.
As we look to the future, the evolution of cellophane is likely to continue along the path of sustainability and advanced functionality. Emerging trends include the development of fully compostable cellophane variants, the incorporation of antimicrobial properties for extended food preservation, and the exploration of cellophane's potential in high-tech applications beyond traditional packaging.
Market Demand Analysis
The market demand for transparent cellophane applications has been experiencing significant growth in recent years, driven by various factors across multiple industries. The packaging sector, in particular, has shown a strong appetite for innovative cellophane solutions due to their versatility, sustainability, and consumer appeal.
In the food and beverage industry, there is a growing trend towards eco-friendly packaging materials. Transparent cellophane, being biodegradable and compostable, aligns well with this shift in consumer preferences. The ability to showcase products while maintaining freshness has made cellophane an attractive option for food manufacturers and retailers. This has led to increased adoption in areas such as confectionery, baked goods, and fresh produce packaging.
The cosmetics and personal care industry has also embraced transparent cellophane for its aesthetic appeal and functional properties. The material's clarity allows brands to display their products effectively, while its barrier properties help protect sensitive formulations. This has resulted in a surge of cellophane usage in packaging for items like face masks, bath products, and gift sets.
In the pharmaceutical sector, there is a growing demand for cellophane in blister packaging and sachets. The material's excellent moisture barrier properties and compatibility with various sterilization methods make it suitable for protecting sensitive medications and medical devices. As the healthcare industry continues to expand, the demand for cellophane in this sector is expected to rise.
The e-commerce boom has further fueled the demand for transparent cellophane applications. With more consumers shopping online, there is an increased need for protective packaging that allows for visual inspection of products upon delivery. Cellophane's transparency and durability make it an ideal choice for e-commerce packaging, particularly for fashion and electronics items.
Emerging trends in smart packaging have also opened up new avenues for cellophane applications. The material's compatibility with various printing technologies has made it possible to incorporate QR codes, NFC tags, and other interactive elements directly onto the packaging. This has created opportunities for brands to enhance customer engagement and provide additional product information.
The global push towards circular economy models has positively impacted the demand for cellophane. As a renewable and biodegradable material, cellophane fits well into sustainability initiatives. Many companies are exploring ways to incorporate cellophane into their packaging strategies as part of their commitment to reducing plastic waste and improving their environmental footprint.
While the market demand for transparent cellophane applications is robust, it is important to note that challenges such as cost considerations and competition from alternative materials exist. However, ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving cellophane's properties and production efficiency are likely to address these challenges and further drive market growth in the coming years.
In the food and beverage industry, there is a growing trend towards eco-friendly packaging materials. Transparent cellophane, being biodegradable and compostable, aligns well with this shift in consumer preferences. The ability to showcase products while maintaining freshness has made cellophane an attractive option for food manufacturers and retailers. This has led to increased adoption in areas such as confectionery, baked goods, and fresh produce packaging.
The cosmetics and personal care industry has also embraced transparent cellophane for its aesthetic appeal and functional properties. The material's clarity allows brands to display their products effectively, while its barrier properties help protect sensitive formulations. This has resulted in a surge of cellophane usage in packaging for items like face masks, bath products, and gift sets.
In the pharmaceutical sector, there is a growing demand for cellophane in blister packaging and sachets. The material's excellent moisture barrier properties and compatibility with various sterilization methods make it suitable for protecting sensitive medications and medical devices. As the healthcare industry continues to expand, the demand for cellophane in this sector is expected to rise.
The e-commerce boom has further fueled the demand for transparent cellophane applications. With more consumers shopping online, there is an increased need for protective packaging that allows for visual inspection of products upon delivery. Cellophane's transparency and durability make it an ideal choice for e-commerce packaging, particularly for fashion and electronics items.
Emerging trends in smart packaging have also opened up new avenues for cellophane applications. The material's compatibility with various printing technologies has made it possible to incorporate QR codes, NFC tags, and other interactive elements directly onto the packaging. This has created opportunities for brands to enhance customer engagement and provide additional product information.
The global push towards circular economy models has positively impacted the demand for cellophane. As a renewable and biodegradable material, cellophane fits well into sustainability initiatives. Many companies are exploring ways to incorporate cellophane into their packaging strategies as part of their commitment to reducing plastic waste and improving their environmental footprint.
While the market demand for transparent cellophane applications is robust, it is important to note that challenges such as cost considerations and competition from alternative materials exist. However, ongoing research and development efforts aimed at improving cellophane's properties and production efficiency are likely to address these challenges and further drive market growth in the coming years.
Technical Challenges
The transparent cellophane industry is currently facing several significant technical challenges that are shaping its development trajectory. One of the primary obstacles is achieving enhanced barrier properties while maintaining transparency. As consumer demand for sustainable packaging grows, there is increasing pressure to improve the moisture and oxygen barrier characteristics of cellophane without compromising its clarity or recyclability.
Another major challenge lies in the production process, particularly in terms of energy efficiency and environmental impact. Traditional cellophane manufacturing methods are energy-intensive and often involve the use of harmful chemicals. Developing cleaner, more sustainable production techniques that reduce carbon footprint and minimize waste is a critical area of focus for industry players.
The pursuit of improved mechanical properties presents another technical hurdle. While cellophane offers good tensile strength, there is a need to enhance its tear resistance and flexibility without sacrificing its biodegradability. This is particularly important as cellophane finds new applications in areas such as flexible electronics and advanced packaging solutions.
Compatibility with printing and coating technologies is an ongoing challenge for transparent cellophane. As packaging designs become more complex and customized, there is a growing need for cellophane that can readily accept high-quality printing inks and functional coatings without compromising its transparency or other physical properties.
The development of smart and active packaging features in cellophane is another area presenting technical difficulties. Incorporating sensors, indicators, or active components that can monitor product freshness or provide tamper evidence, while maintaining the film's transparency and eco-friendly nature, requires significant innovation in material science and manufacturing processes.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness remain persistent challenges in the adoption of new cellophane technologies. Many promising innovations struggle to transition from laboratory scale to industrial production due to economic constraints or technical limitations in large-scale manufacturing processes.
Lastly, the industry faces the challenge of standardization and regulatory compliance. As new cellophane formulations and applications emerge, there is a need for updated standards and testing methods to ensure product safety, quality, and environmental compliance across different markets and applications.
Another major challenge lies in the production process, particularly in terms of energy efficiency and environmental impact. Traditional cellophane manufacturing methods are energy-intensive and often involve the use of harmful chemicals. Developing cleaner, more sustainable production techniques that reduce carbon footprint and minimize waste is a critical area of focus for industry players.
The pursuit of improved mechanical properties presents another technical hurdle. While cellophane offers good tensile strength, there is a need to enhance its tear resistance and flexibility without sacrificing its biodegradability. This is particularly important as cellophane finds new applications in areas such as flexible electronics and advanced packaging solutions.
Compatibility with printing and coating technologies is an ongoing challenge for transparent cellophane. As packaging designs become more complex and customized, there is a growing need for cellophane that can readily accept high-quality printing inks and functional coatings without compromising its transparency or other physical properties.
The development of smart and active packaging features in cellophane is another area presenting technical difficulties. Incorporating sensors, indicators, or active components that can monitor product freshness or provide tamper evidence, while maintaining the film's transparency and eco-friendly nature, requires significant innovation in material science and manufacturing processes.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness remain persistent challenges in the adoption of new cellophane technologies. Many promising innovations struggle to transition from laboratory scale to industrial production due to economic constraints or technical limitations in large-scale manufacturing processes.
Lastly, the industry faces the challenge of standardization and regulatory compliance. As new cellophane formulations and applications emerge, there is a need for updated standards and testing methods to ensure product safety, quality, and environmental compliance across different markets and applications.
Current Applications
01 Transparent cellophane manufacturing process
The manufacturing process of transparent cellophane involves specific techniques to achieve transparency. This may include methods for refining cellulose, chemical treatments, and extrusion processes to produce thin, clear films. The process often involves dissolving cellulose in an alkaline solution, followed by regeneration in an acid bath to create a transparent film.- Transparent cellophane production methods: Various methods for producing transparent cellophane are described, including chemical treatments and manufacturing processes to achieve transparency. These methods may involve specific additives or processing techniques to enhance the clarity of the cellophane film.
- Applications of transparent cellophane: Transparent cellophane finds applications in diverse fields such as packaging, wrapping, and protective coverings. Its transparency allows for clear visibility of the contents while providing a barrier against moisture and contaminants.
- Modifications to improve cellophane properties: Various modifications to cellophane are explored to enhance its properties, such as increased strength, improved barrier characteristics, or better adhesion. These modifications may involve chemical treatments, coatings, or the incorporation of additional materials.
- Biodegradable transparent cellophane: Development of biodegradable transparent cellophane alternatives to address environmental concerns. These materials aim to maintain the desirable properties of traditional cellophane while offering improved eco-friendliness and compostability.
- Transparent cellophane in packaging systems: Integration of transparent cellophane into various packaging systems and designs. This includes the use of cellophane in combination with other materials or in specialized packaging structures to enhance product presentation and protection.
02 Applications of transparent cellophane
Transparent cellophane finds various applications across different industries. It is commonly used in packaging for food products, consumer goods, and gifts due to its clarity and protective properties. Other applications include use in arts and crafts, as a protective layer for documents, and in certain industrial processes where a clear, thin film is required.Expand Specific Solutions03 Modifications to improve cellophane properties
Various modifications can be made to transparent cellophane to enhance its properties. These may include adding plasticizers to improve flexibility, incorporating UV inhibitors for better light resistance, or applying coatings to enhance moisture barrier properties. Some modifications aim to improve heat-sealability or printability of the cellophane film.Expand Specific Solutions04 Biodegradable and eco-friendly cellophane
Development of biodegradable and eco-friendly versions of transparent cellophane is an area of focus. This involves using sustainable raw materials, modifying the production process to reduce environmental impact, and ensuring the end product is compostable or biodegradable. These eco-friendly alternatives aim to maintain the transparency and functional properties of traditional cellophane.Expand Specific Solutions05 Composite materials incorporating transparent cellophane
Transparent cellophane is used in the creation of composite materials for various applications. This may involve laminating cellophane with other materials to create multi-layer films with enhanced properties, or incorporating cellophane into more complex structures. These composites can offer improved barrier properties, strength, or specific functionalities while maintaining transparency.Expand Specific Solutions
Industry Leaders
The transparent cellophane applications market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand in packaging and electronics industries. The market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Ubiquitous Energy and Samsung Electronics leading innovation in transparent photovoltaics and display technologies. Established players such as Corning and LG Display are also making strides in developing advanced transparent materials. The competition is intensifying as both traditional chemical companies and tech giants invest in R&D to capture market share in this emerging sector.
Sekisui Chemical Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sekisui Chemical has developed advanced transparent cellophane films with enhanced barrier properties and biodegradability. Their S-LEC™ film technology incorporates nano-scale cellulose fibers to create a highly transparent and flexible material with improved oxygen and moisture barrier characteristics[1]. The company has also introduced bio-based additives to enhance the film's compostability while maintaining its optical clarity and mechanical strength[3]. Sekisui's latest innovation involves a multi-layer cellophane structure that combines different functional layers to achieve tailored properties for specific packaging applications[5].
Strengths: Superior barrier properties, biodegradability, and versatility for various packaging needs. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and limited high-temperature applications.
Sumitomo Bakelite Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Sumitomo Bakelite has pioneered a novel approach to transparent cellophane production using their proprietary "SUMILITE™" technology. This process involves the controlled orientation of cellulose molecules during film formation, resulting in exceptional optical transparency and improved mechanical properties[2]. The company has also developed a unique surface treatment method that enhances the cellophane's printability and adhesion characteristics without compromising its clarity[4]. Additionally, Sumitomo Bakelite has introduced antimicrobial additives into their cellophane formulations, creating films with inherent bacteria-resistant properties for use in medical and food packaging applications[6].
Strengths: Enhanced optical and mechanical properties, improved printability, and antimicrobial functionality. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and limited compatibility with certain packaging processes.
Key Patents Review
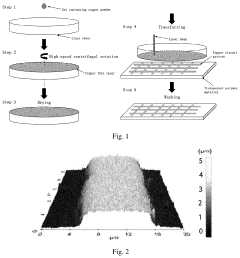
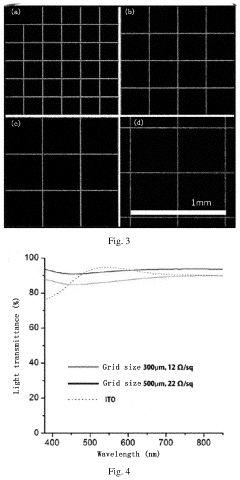
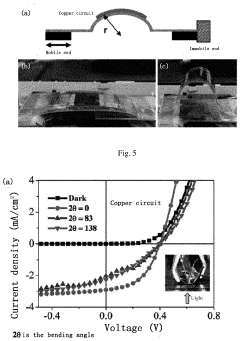
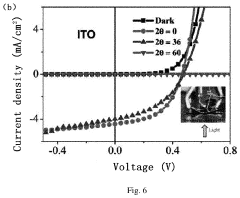
Flexible transparent copper circuit, preparation method therefor, and application thereof
PatentInactiveUS20220272830A1
Innovation
- A flexible transparent copper circuit is prepared by coating a copper powder gel on a glass sheet, drying it, and then transferring the copper film to a polymer substrate using a laser beam, allowing for a sub-micron thickness and chemical bond-free copper film that maintains conductivity and flexibility.
Compound charge transport layer for organic photovoltaic devices
PatentWO2021158624A1
Innovation
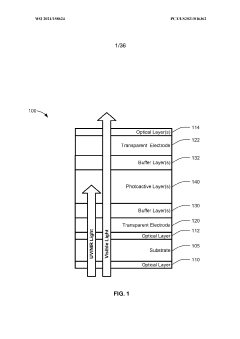
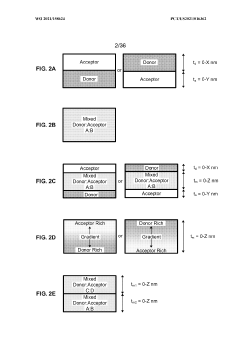
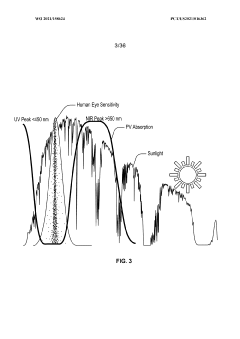
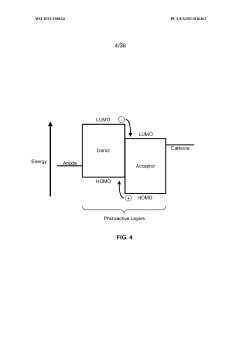
- The development of organic photovoltaic devices with a compound charge transport layer and metal-oxide interlayers that decouple energy levels from the photovoltaic cell's built-in potential, allowing for barrier-free charge transport and selective contact to photoactive layers, enabling the use of dissimilar organic materials and improving transparency and efficiency.
Sustainability Aspects
The sustainability aspects of transparent cellophane applications have gained significant attention in recent years, driven by increasing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures. As a biodegradable and compostable material derived from renewable resources, cellophane offers several advantages in terms of sustainability compared to traditional petroleum-based plastics.
One of the key sustainability benefits of cellophane is its biodegradability. Under proper conditions, cellophane can decompose naturally within a few months, significantly reducing its environmental impact compared to conventional plastics that may persist in the environment for hundreds of years. This characteristic makes cellophane an attractive option for single-use packaging applications, where rapid decomposition is desirable.
The renewable nature of cellophane's raw materials also contributes to its sustainability profile. Typically derived from wood pulp or cotton linters, cellophane production relies on regenerative resources rather than finite fossil fuels. This aspect aligns well with circular economy principles and helps reduce the carbon footprint associated with packaging materials.
Recent advancements in cellophane production techniques have further enhanced its sustainability credentials. Improved manufacturing processes have reduced water and energy consumption, minimizing the overall environmental impact of cellophane production. Additionally, innovations in coating technologies have led to the development of cellophane variants with enhanced barrier properties, expanding its potential applications while maintaining its biodegradability.
The recyclability of cellophane is another important sustainability consideration. While not widely recycled in conventional plastic recycling streams, cellophane can be composted in industrial facilities, providing an end-of-life solution that returns nutrients to the soil. Some emerging technologies are also exploring the potential for chemical recycling of cellophane, which could further improve its circularity.
However, challenges remain in fully realizing the sustainability potential of cellophane. The energy-intensive nature of its production process and the use of chemicals in manufacturing are areas that require ongoing improvement. Additionally, the proper disposal and composting infrastructure needed to handle cellophane at scale is not yet widely available in many regions.
As the demand for sustainable packaging solutions continues to grow, transparent cellophane is likely to play an increasingly important role. Future research and development efforts are expected to focus on further improving the material's environmental performance, enhancing its functional properties, and developing more efficient production and recycling methods. These advancements will be crucial in positioning cellophane as a leading sustainable alternative in various applications, from food packaging to consumer goods.
One of the key sustainability benefits of cellophane is its biodegradability. Under proper conditions, cellophane can decompose naturally within a few months, significantly reducing its environmental impact compared to conventional plastics that may persist in the environment for hundreds of years. This characteristic makes cellophane an attractive option for single-use packaging applications, where rapid decomposition is desirable.
The renewable nature of cellophane's raw materials also contributes to its sustainability profile. Typically derived from wood pulp or cotton linters, cellophane production relies on regenerative resources rather than finite fossil fuels. This aspect aligns well with circular economy principles and helps reduce the carbon footprint associated with packaging materials.
Recent advancements in cellophane production techniques have further enhanced its sustainability credentials. Improved manufacturing processes have reduced water and energy consumption, minimizing the overall environmental impact of cellophane production. Additionally, innovations in coating technologies have led to the development of cellophane variants with enhanced barrier properties, expanding its potential applications while maintaining its biodegradability.
The recyclability of cellophane is another important sustainability consideration. While not widely recycled in conventional plastic recycling streams, cellophane can be composted in industrial facilities, providing an end-of-life solution that returns nutrients to the soil. Some emerging technologies are also exploring the potential for chemical recycling of cellophane, which could further improve its circularity.
However, challenges remain in fully realizing the sustainability potential of cellophane. The energy-intensive nature of its production process and the use of chemicals in manufacturing are areas that require ongoing improvement. Additionally, the proper disposal and composting infrastructure needed to handle cellophane at scale is not yet widely available in many regions.
As the demand for sustainable packaging solutions continues to grow, transparent cellophane is likely to play an increasingly important role. Future research and development efforts are expected to focus on further improving the material's environmental performance, enhancing its functional properties, and developing more efficient production and recycling methods. These advancements will be crucial in positioning cellophane as a leading sustainable alternative in various applications, from food packaging to consumer goods.
Regulatory Landscape
The regulatory landscape for transparent cellophane applications is evolving rapidly, reflecting the growing importance of this versatile material in various industries. As environmental concerns take center stage, regulatory bodies worldwide are implementing stricter guidelines for the production, use, and disposal of cellophane products.
In the food packaging sector, which remains a primary application for transparent cellophane, regulations are becoming increasingly stringent. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recently updated its guidelines for food contact substances, including cellophane. These new regulations focus on ensuring the safety of cellophane when in direct contact with food, particularly regarding potential chemical migration.
The European Union has also tightened its regulations through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EFSA has introduced more comprehensive testing requirements for cellophane materials used in food packaging, with a particular emphasis on assessing the potential risks of nanoparticles and other additives commonly used in cellophane production.
Environmental regulations are playing a significant role in shaping the future of cellophane applications. Many countries are implementing extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, which require manufacturers to take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their cellophane products, including disposal and recycling. This has led to increased investment in biodegradable and compostable cellophane alternatives.
In response to growing concerns about plastic pollution, several jurisdictions have introduced bans or restrictions on single-use plastics, which may impact certain cellophane applications. However, cellophane's biodegradability has positioned it as a potential alternative to traditional plastics in some cases, subject to meeting specific environmental standards.
The medical and pharmaceutical industries are also experiencing regulatory changes affecting cellophane applications. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) are implementing more rigorous standards for cellophane used in medical device packaging and drug delivery systems. These regulations focus on ensuring sterility, barrier properties, and compatibility with various sterilization methods.
As the use of cellophane expands into new areas, such as electronic components and smart packaging, regulators are working to develop appropriate frameworks. For instance, the integration of conductive materials into cellophane for smart packaging applications has prompted discussions about potential electromagnetic interference and safety standards.
In conclusion, the regulatory landscape for transparent cellophane applications is characterized by increasing complexity and a focus on safety, environmental sustainability, and adaptability to emerging technologies. Manufacturers and users of cellophane products must stay informed about these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and capitalize on new opportunities in this dynamic field.
In the food packaging sector, which remains a primary application for transparent cellophane, regulations are becoming increasingly stringent. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has recently updated its guidelines for food contact substances, including cellophane. These new regulations focus on ensuring the safety of cellophane when in direct contact with food, particularly regarding potential chemical migration.
The European Union has also tightened its regulations through the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). The EFSA has introduced more comprehensive testing requirements for cellophane materials used in food packaging, with a particular emphasis on assessing the potential risks of nanoparticles and other additives commonly used in cellophane production.
Environmental regulations are playing a significant role in shaping the future of cellophane applications. Many countries are implementing extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs, which require manufacturers to take responsibility for the entire lifecycle of their cellophane products, including disposal and recycling. This has led to increased investment in biodegradable and compostable cellophane alternatives.
In response to growing concerns about plastic pollution, several jurisdictions have introduced bans or restrictions on single-use plastics, which may impact certain cellophane applications. However, cellophane's biodegradability has positioned it as a potential alternative to traditional plastics in some cases, subject to meeting specific environmental standards.
The medical and pharmaceutical industries are also experiencing regulatory changes affecting cellophane applications. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) are implementing more rigorous standards for cellophane used in medical device packaging and drug delivery systems. These regulations focus on ensuring sterility, barrier properties, and compatibility with various sterilization methods.
As the use of cellophane expands into new areas, such as electronic components and smart packaging, regulators are working to develop appropriate frameworks. For instance, the integration of conductive materials into cellophane for smart packaging applications has prompted discussions about potential electromagnetic interference and safety standards.
In conclusion, the regulatory landscape for transparent cellophane applications is characterized by increasing complexity and a focus on safety, environmental sustainability, and adaptability to emerging technologies. Manufacturers and users of cellophane products must stay informed about these evolving regulations to ensure compliance and capitalize on new opportunities in this dynamic field.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!