Residue monitoring and residue-based control
a technology of residue monitoring and control, applied in soil-working methods, adjusting devices, agriculture tools and machines, etc., can solve the problems of various sizes of residue covering tilled ground and a portion of the area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018]The following describes one or more example implementations of the disclosed system and method, as shown in the accompanying figures of the drawings described briefly above.
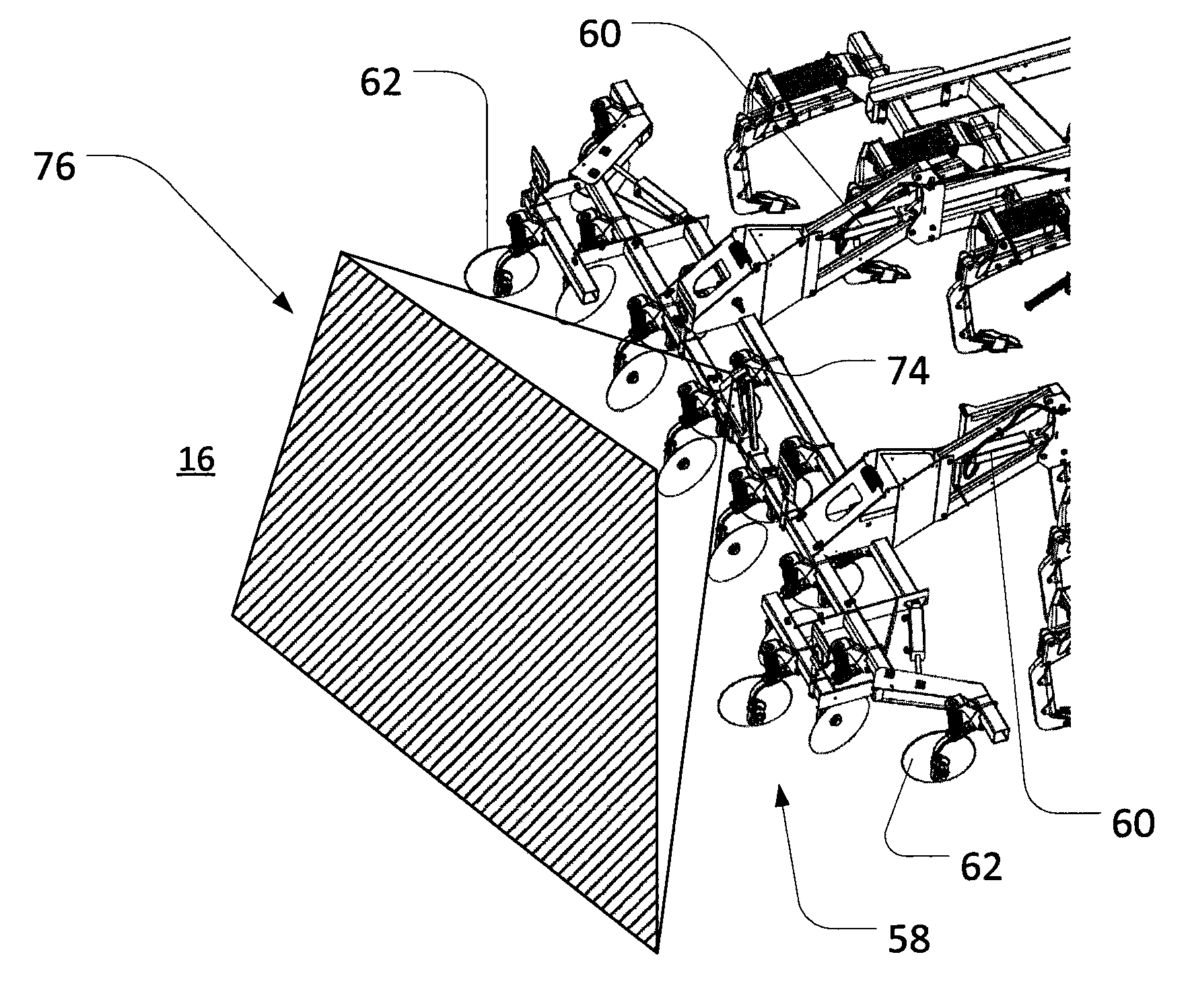
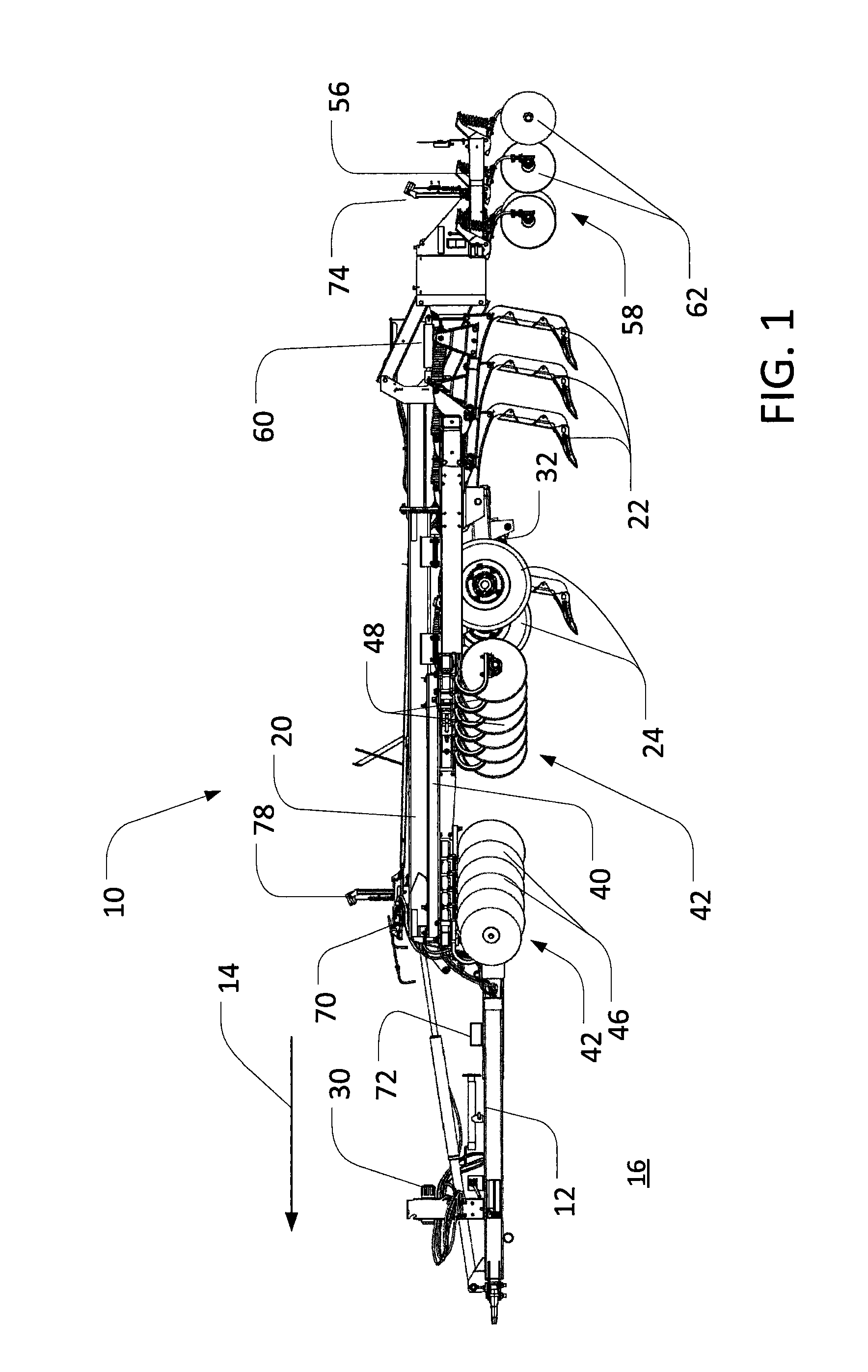
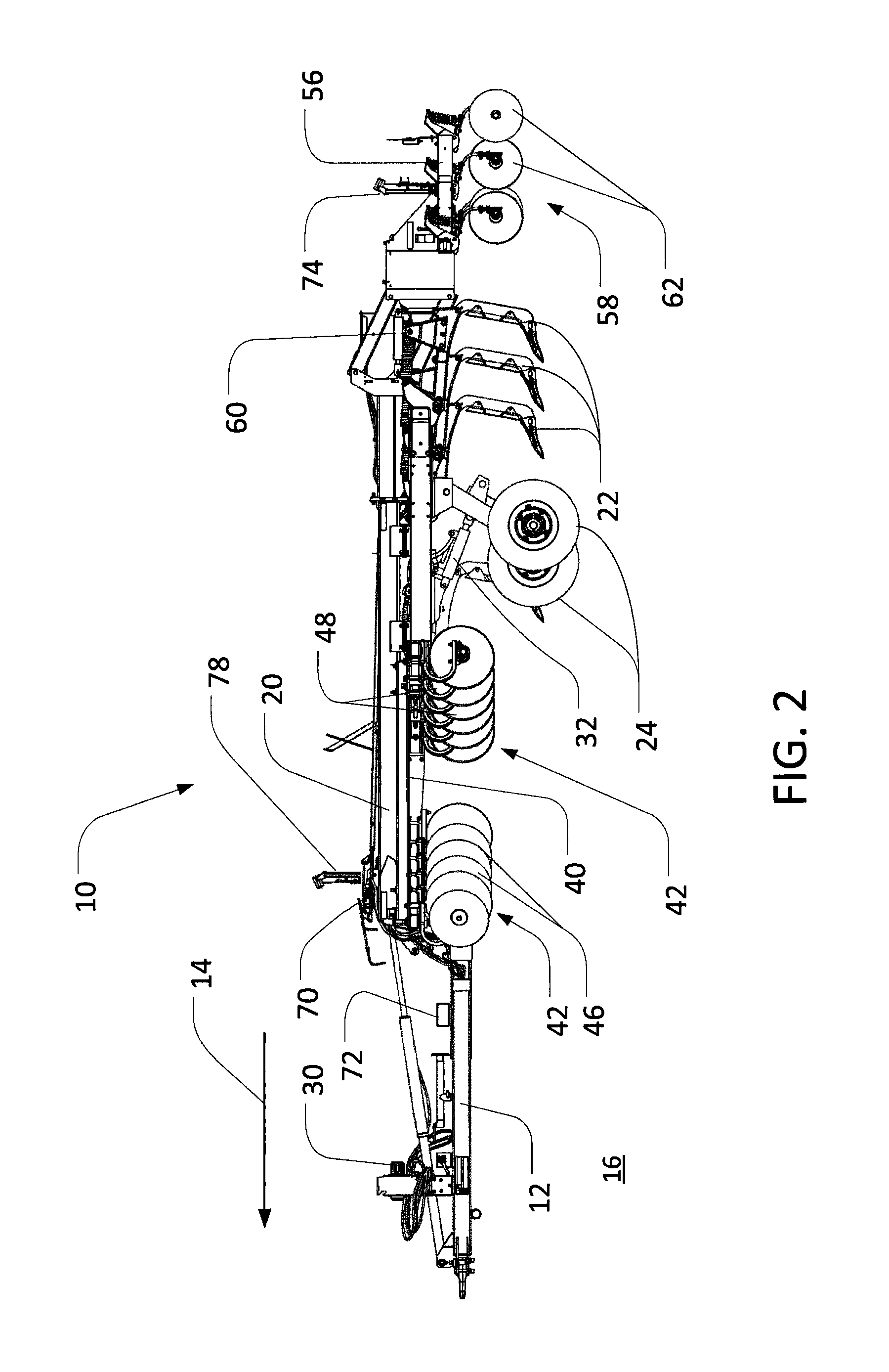
[0019]As noted above, various operations may result in residue on a field. For example, a primary tillage operation utilizing various rippers, cutting disks, and other tools may both cut and bury plant material along a field to varying degrees. Generally, after such an operation (and others), some amount of residue (i.e., cut and un-cut plant material) may be left on the field surface. Such residue may generally be characterized at least by a percent coverage (i.e., a percentage of a given area of ground that is covered by residue) and a characteristic residue size (i.e., an average, nominal, or other measurement of the length, width or area of particular pieces of residue).
[0020]In certain applications, it may be useful to understand the characteristics of residue coverage with relative accuracy. For examp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com