Implantable devices and methods for treating fecal incontinence
a technology of fecal incontinence and implantable devices, which is applied in the field of implantable devices and methods for treating fecal incontinence, can solve the problems of inconvenient patient treatment, invasive surgery that may be required, and the effect of reducing the risk of infection, less time, and less surgery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
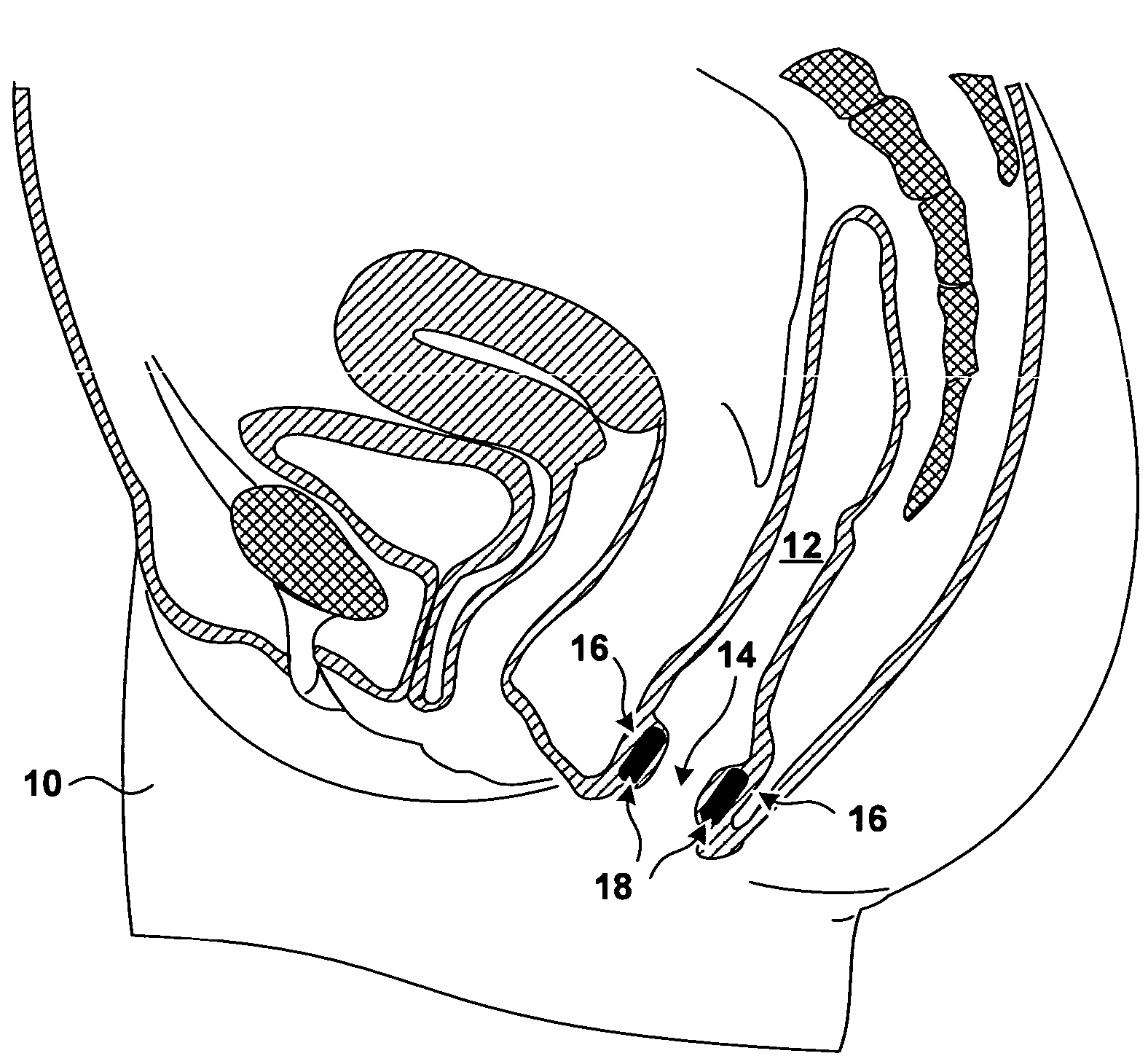
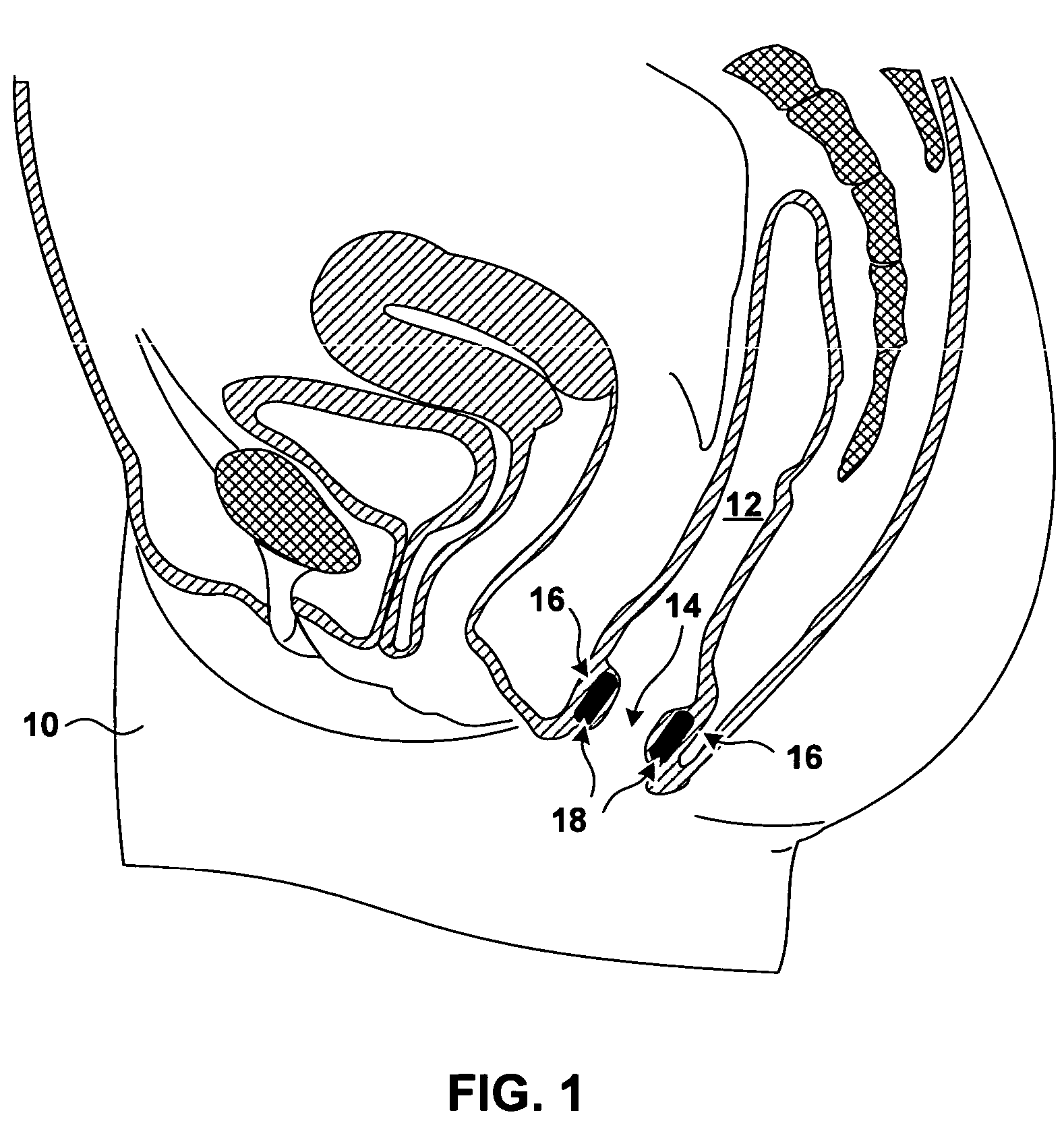
[0027]FIG. 1 is a sagittal cross section of a pelvic region of a female patient 10. In FIG. 1, the rectum 12 of patient 10 extends inferiorly and terminates with the anal opening or anal canal 14. The anal walls 16 proximate to anal opening 14 include a mucosa (not shown in FIG. 1) proximate to anal opening 14, a submuscosa (not shown in FIG. 1) beneath the mucosa, and a musculature underlying the submucosa. The underlying musculature includes an internal anal sphincter (not shown in FIG. 1) and external anal sphincter (not shown in FIG. 1). The external anal sphincter, which is under the voluntary control of patient 10, is located more distally from anal opening 14 than is the internal anal sphincter.
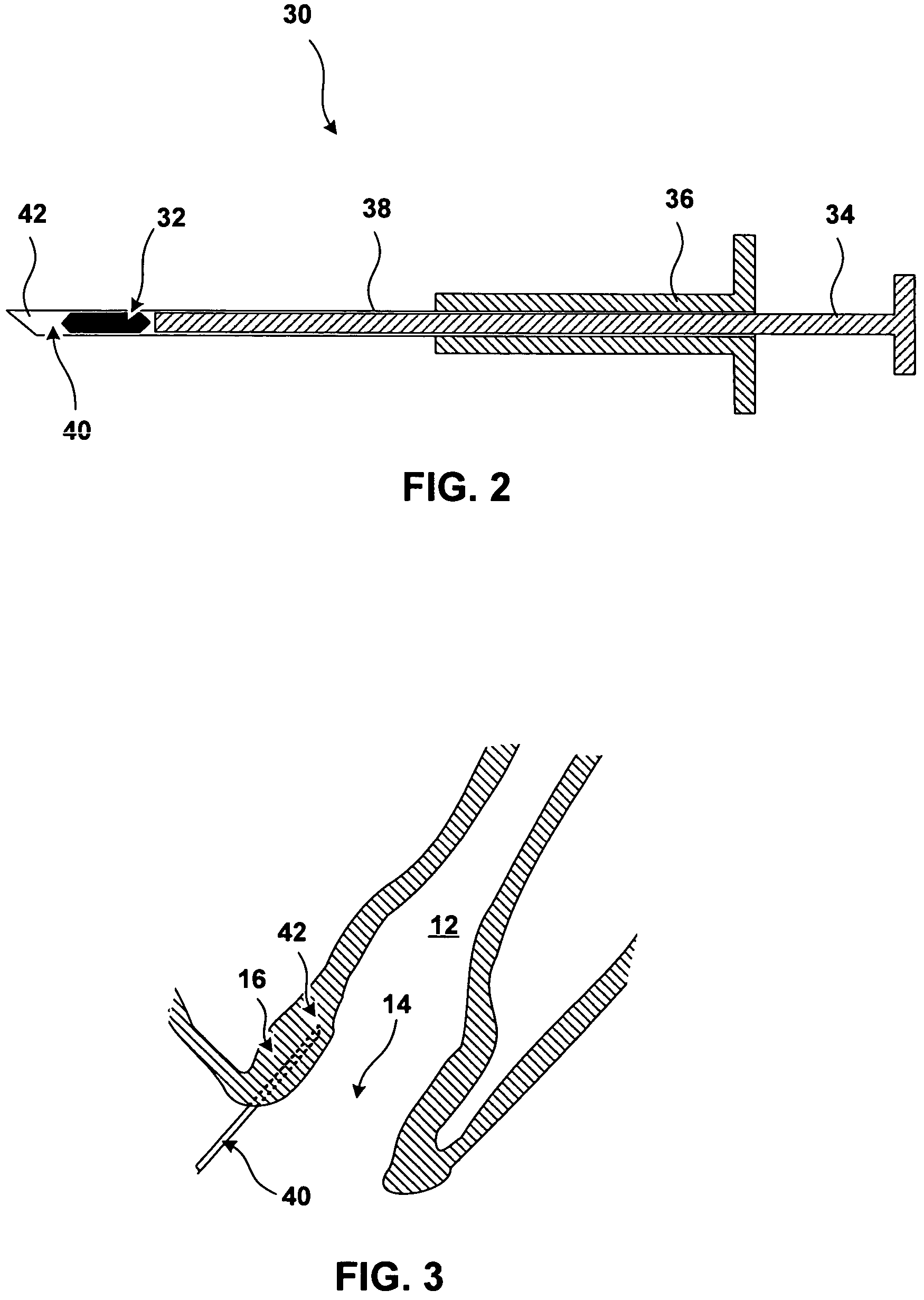
[0028]FIG. 1 further shows bulking prostheses 18 implanted in the tissue of anal walls 16. Bulking prostheses 18 have been inserted in the tissue proximate to an anal sphincter. In the specific implantation shown in FIG. 1, bulking prostheses 18 have been implanted in the submucosa bet...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com