Multimode optical fiber and optical backplane using multimode optical fiber
a multi-mode optical fiber and optical backplane technology, applied in the field of fiber optic communication, can solve problems such as the large overall diameter of fibers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
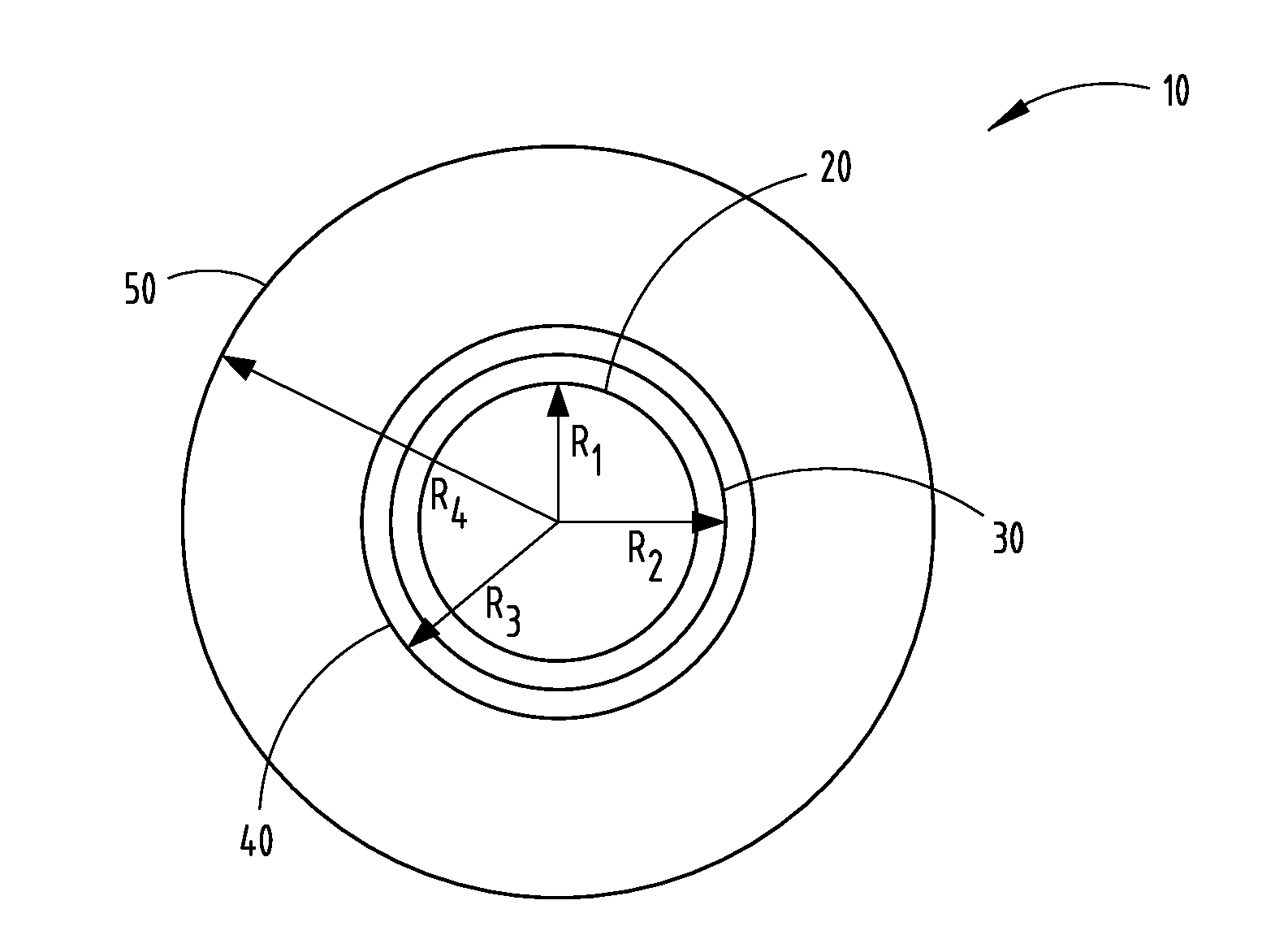
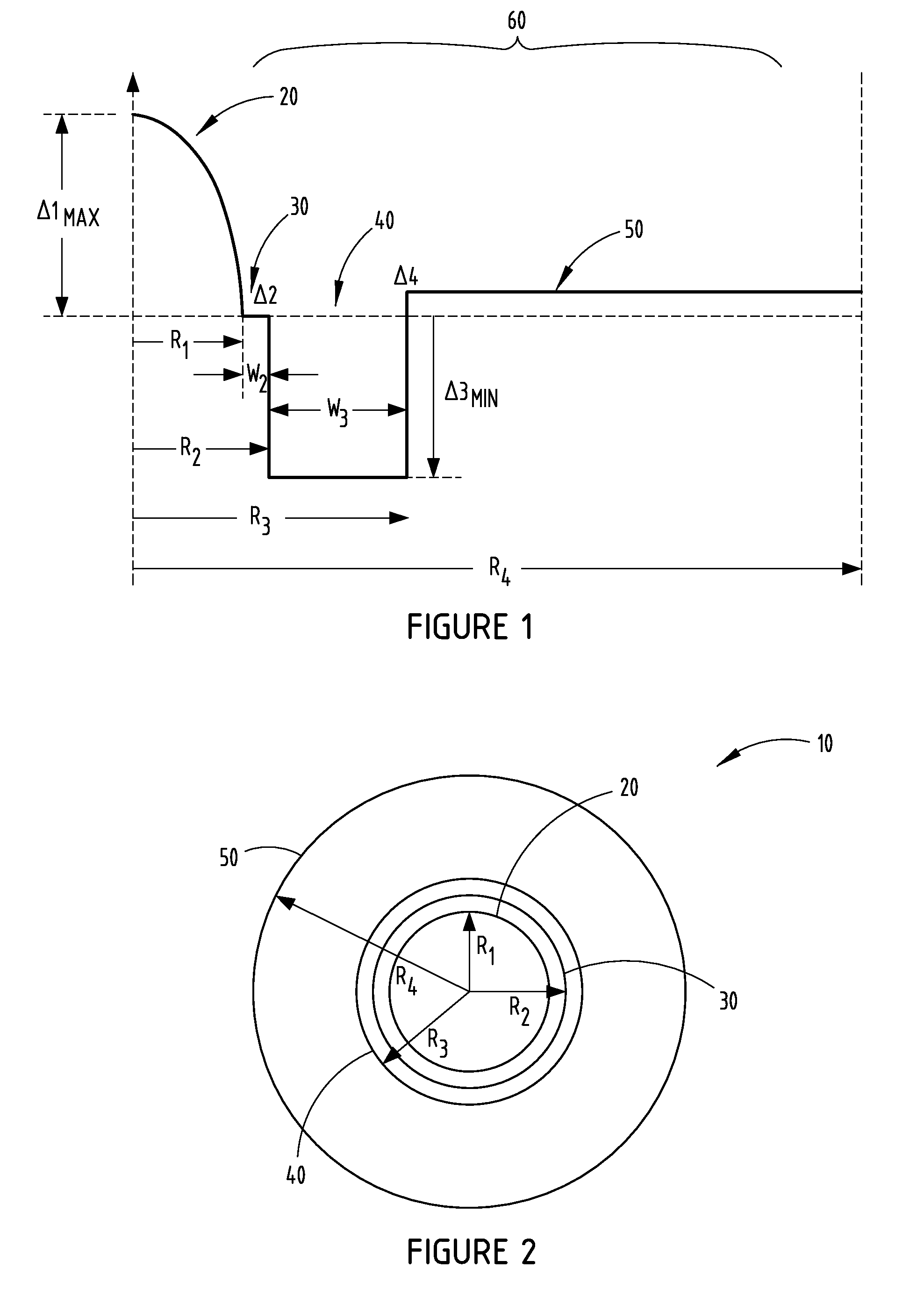
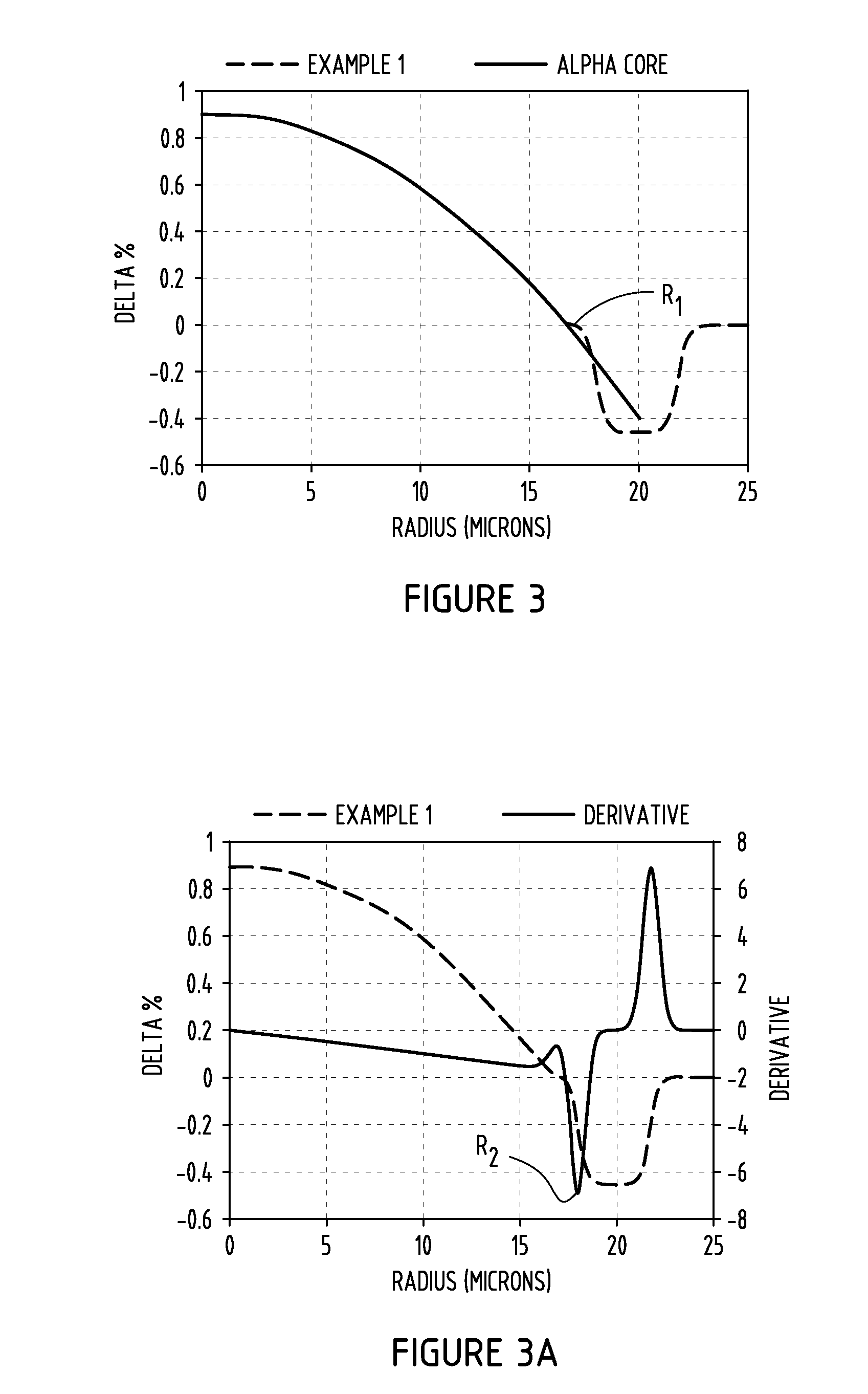
[0033]The tables 1-5 presented below summarize various examples generally arranged in five sets of embodiments of multimode fibers that were modeled having various characteristics in accordance with the embodiments disclosed herein and compared to a comparative fiber shown in FIG. 1. Various calculations of the parameters of the multi-mode fibers were calculated. These parameters include the relative refractive index of the core relative refractive index ΔiMAX of the core, outer core radius R1, and the graded index alpha (α) parameter. Additionally, the parameters include the inner cladding relative refractive index Δ2, the inner cladding maximum relative refractive index Δ2MAX, the outer radius of the inner annular portion of the cladding R2, and the width W2 of the inner annular portion 40. Further, the parameters include the minimum relative refractive index Δ3MIN of the depressed-index annular portion 50, and the outer radius R3 of the depressed-index annular portion 50. Further...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com