System and method for regulating cardiac triggered therapy to the brain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
second embodiment
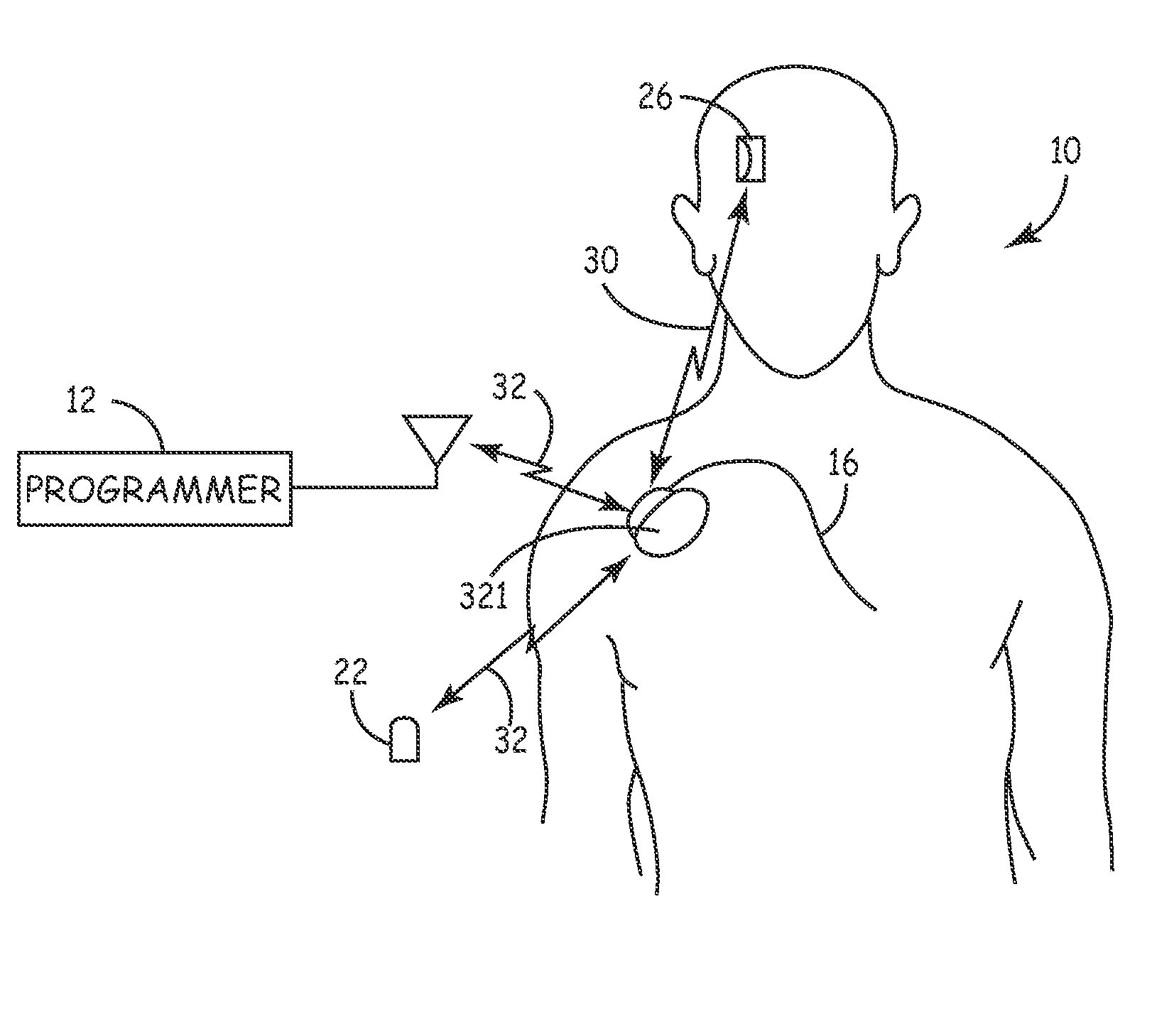
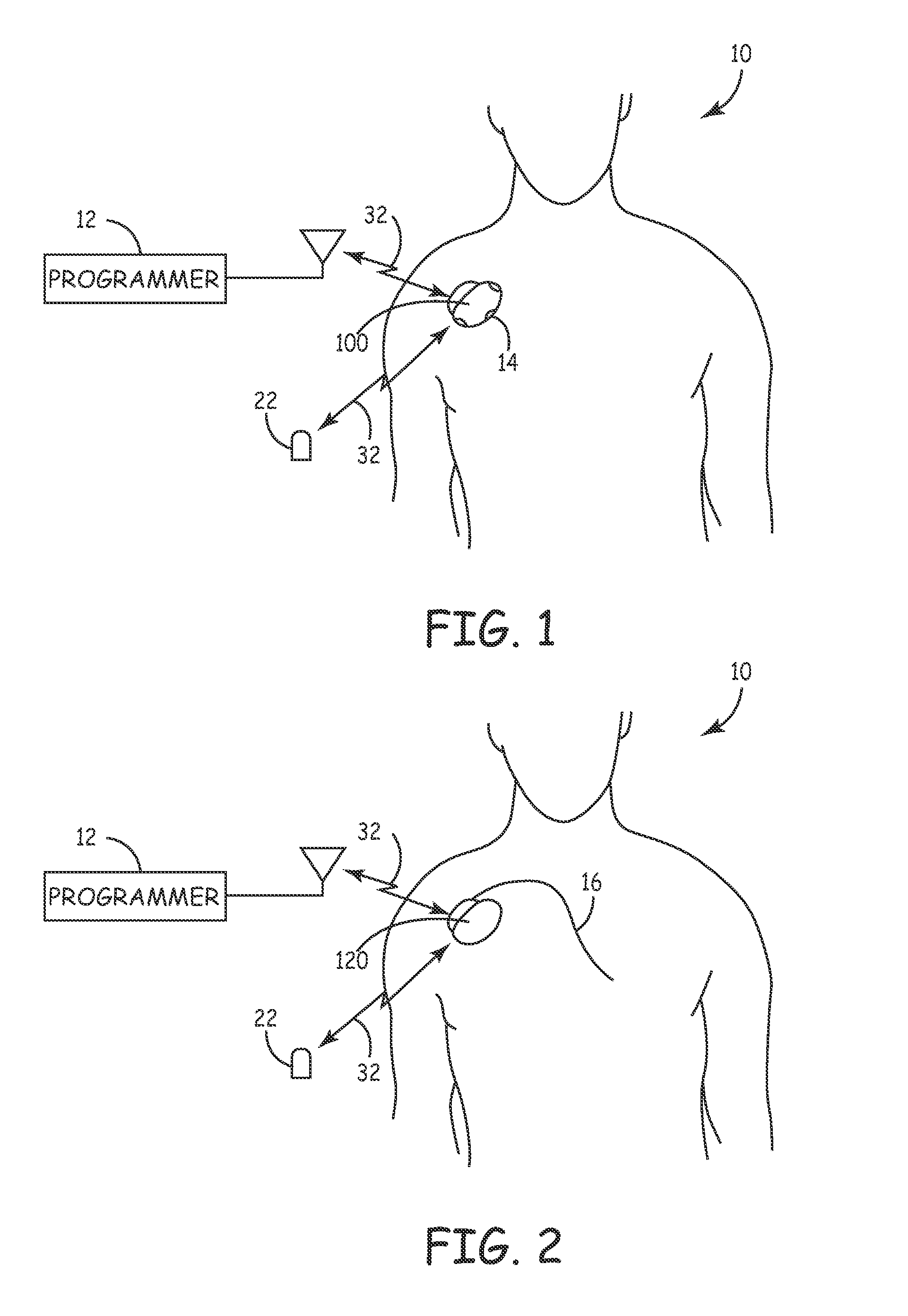
[0099]FIG. 2 is a simplified schematic view of a second embodiment core Monitor 120 implanted in a patient 10. Monitor 120 continuously senses and monitors cardiac and respiration function of patient 10 via cardiac lead(s) 16 to allow detection of neurological events and the recording of data and signals pre and post event. Stored diagnostic data is uplinked and evaluated by the patient's physician utilizing programmer 12 via a 2-way telemetry link 32. An external patient activator 22 may optionally allow the patient 10, or other care provider (not shown), to manually activate the recording of diagnostic data. Monitor 120 senses both cardiac signals and respiration parameters via standard cardiac leads implanted in the heart. Monitor 120 measures intra-cardiac impedance, varying both with the intrathoracic pressure fluctuations during respiration and with cardiac contraction is representative of the pulmonary activity and of the cardiac activity as substantially described in U.S. Pa...
third embodiment
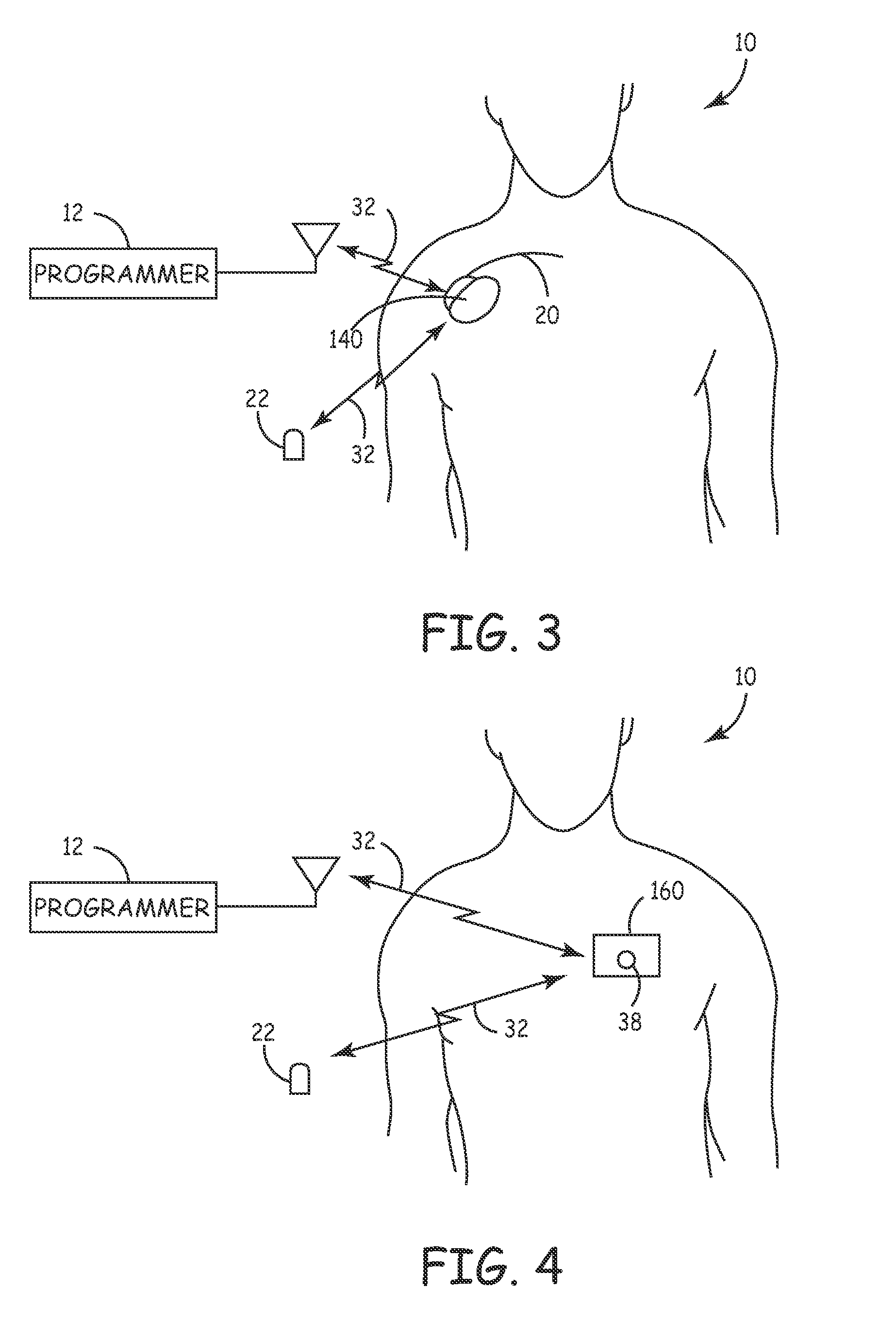
[0100]FIG. 3 is a simplified schematic view of a third embodiment core Monitor 140 implanted in a patient 10. Monitor 140 continuously senses and monitors cardiac and respiration function of patient 10 via an electrode (not shown) located distally on sensor stub 20 which is inserted subcutaneously in the thoracic area of the patient to allow detection of neurological events and the recording of data and signals pre and post event. Stored diagnostic data is uplinked and evaluated by the patient's physician utilizing programmer 12 via a 2-way telemetry link 32. An external patient activator 22 may optionally allow the patient 10, or other care provider (not shown), to manually activate the recording of diagnostic data. Monitor 140 senses cardiac signals between an electrode on the distal end of the sensor stub and the monitor case as described in conjunction with the embodiment shown in FIG. 5 in U.S. Pat. No. 5,987,352 “Minimally Invasive Implantable Device for Monitoring Physiologic...
fourth embodiment
[0101]FIG. 4 is a simplified schematic view of a fourth embodiment core Monitor 160 attached to a patient 10. External patch Monitor 160 continuously senses and monitors cardiac and respiration function of patient 10 to allow detection of neurological events and the recording of data and signals pre and post event. Stored diagnostic data is uplinked and evaluated by the patient's physician utilizing programmer 12 via a 2-way telemetry link 32. An external patient activator 22 may optionally allow the patient 10, or other care provider (not shown), to manually activate the recording of diagnostic data. Also optionally, a button 38 on the external patch monitor 160 may be activated by the patient 10 to manually activate diagnostic data recording.
[0102] External patch Monitor 160 consists of a resilient substrate affixed to the patient's skin with the use of an adhesive which provides support for an amplifier, memory, microprocessor, receiver, transmitter and other electronic component...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com