Methods for interfering with fibrosis
A technology of fibrosis and fibrosis, applied in the field of diagnosis and treatment of fibrotic diseases, which can solve problems such as uncertain results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1: animal experiments
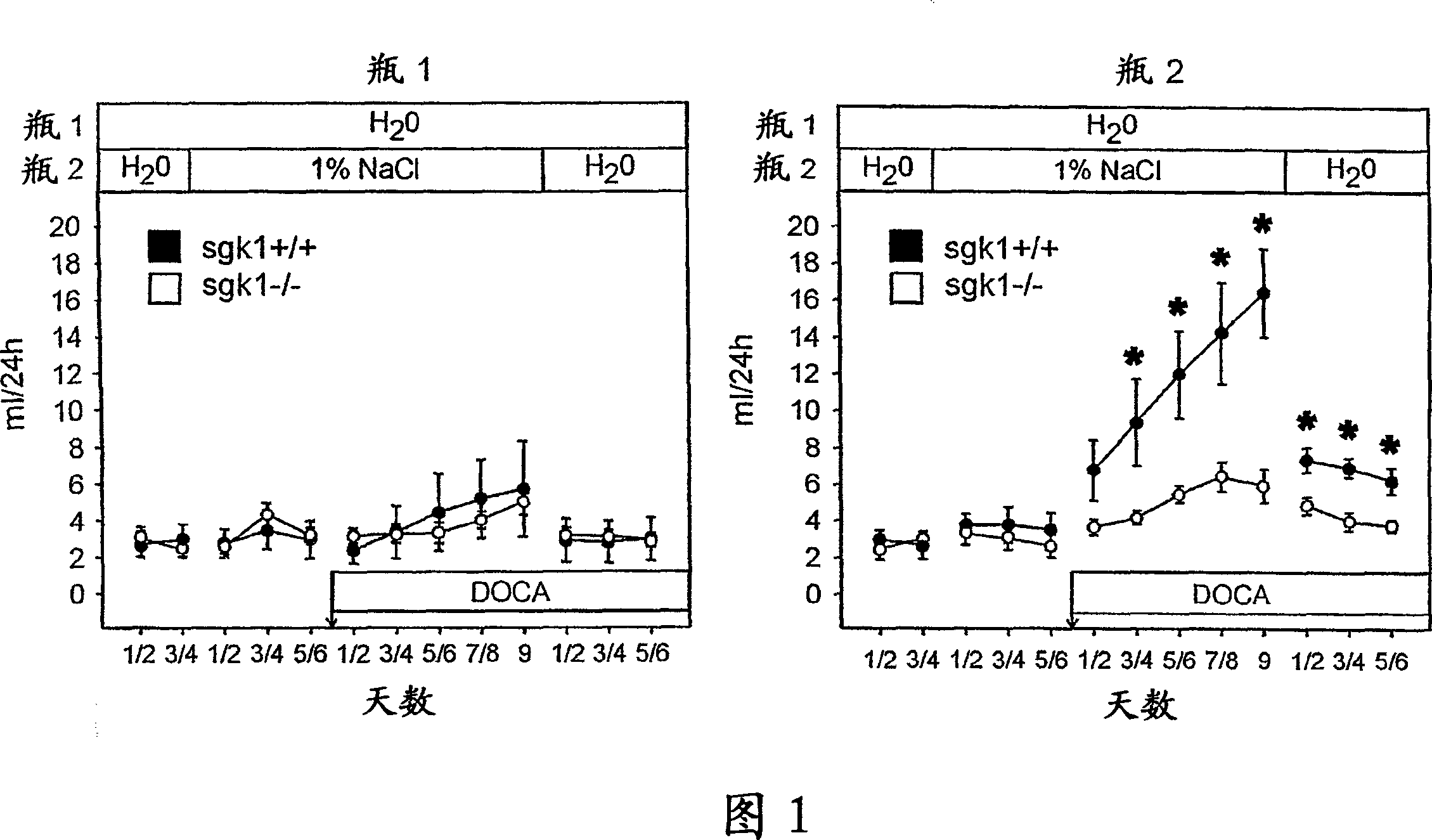
[0038]SGK1-deficient mice were generated as previously described (9). After anesthesia (peritoneal injection of medetomidine 0.5mg / kg + midazolam 5mg / kg + fentanyl 0.05mg / kg, subcutaneous injection of atipamezole 2.5 mg / kg + flumazenil 0.5mg / kg + nalox Ketone 1.2mg / kg recovery) state, respectively, to the neck region of wild-type (sgk1+ / +) and SGK1 knockout (sgk1- / -) mice were implanted with pellets releasing 50mg DOCA for 21 days (Innovative Research of America ( Innovative Research of America), Sarasota, FL). One day before DOCA pellet implantation, sgk1- / - and sgk1+ / + mice were weighed and placed individually in metabolic cages (Tecniplast Hohenpeissenberg, Germany) for 24 hours of basal urine collection. Mice had free access to standard mouse chow (Altromin, Heidenau, Germany) and tap water and / or 1% or 2% NaCl. The inner walls of the metabolic cage are siliceous, and urine is collected under water-saturated oil. Systolic arter...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: Microscopy
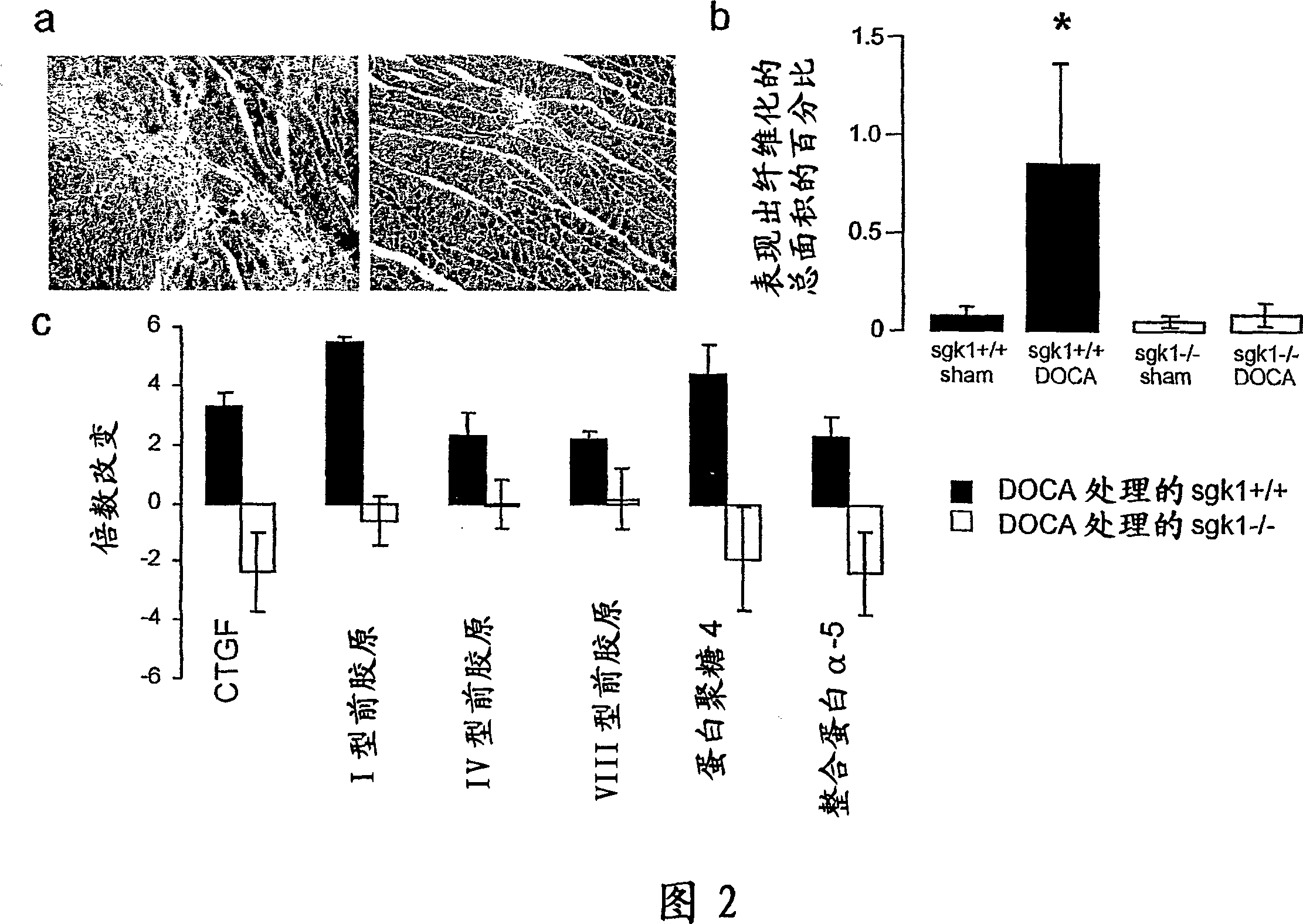
[0040] After untreated or DOCA / high salt treatment (18 days) sgk1+ / + and sgk1- / - mice were anesthetized, the hearts were quickly removed, weighed, and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde / 0.1M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.2) overnight and embedded in paraffin. 5 μm thick sections of dewaxed heart muscle were stained with H&E and Masson's trichrome (30). Stained paraffin sections were analyzed under a Zeiss Axioplan microscope (Zeiss, Jena, Germany). Areas were measured in the digitized images with an Axiocam camera and by the manufacturer's software. Total tissue area was measured with a 4× objective; fibrotic areas were identified and quantified with a 20× objective. The degree of fibrosis was then calculated as a percentage of the total tissue area.
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3: Microarray Analysis
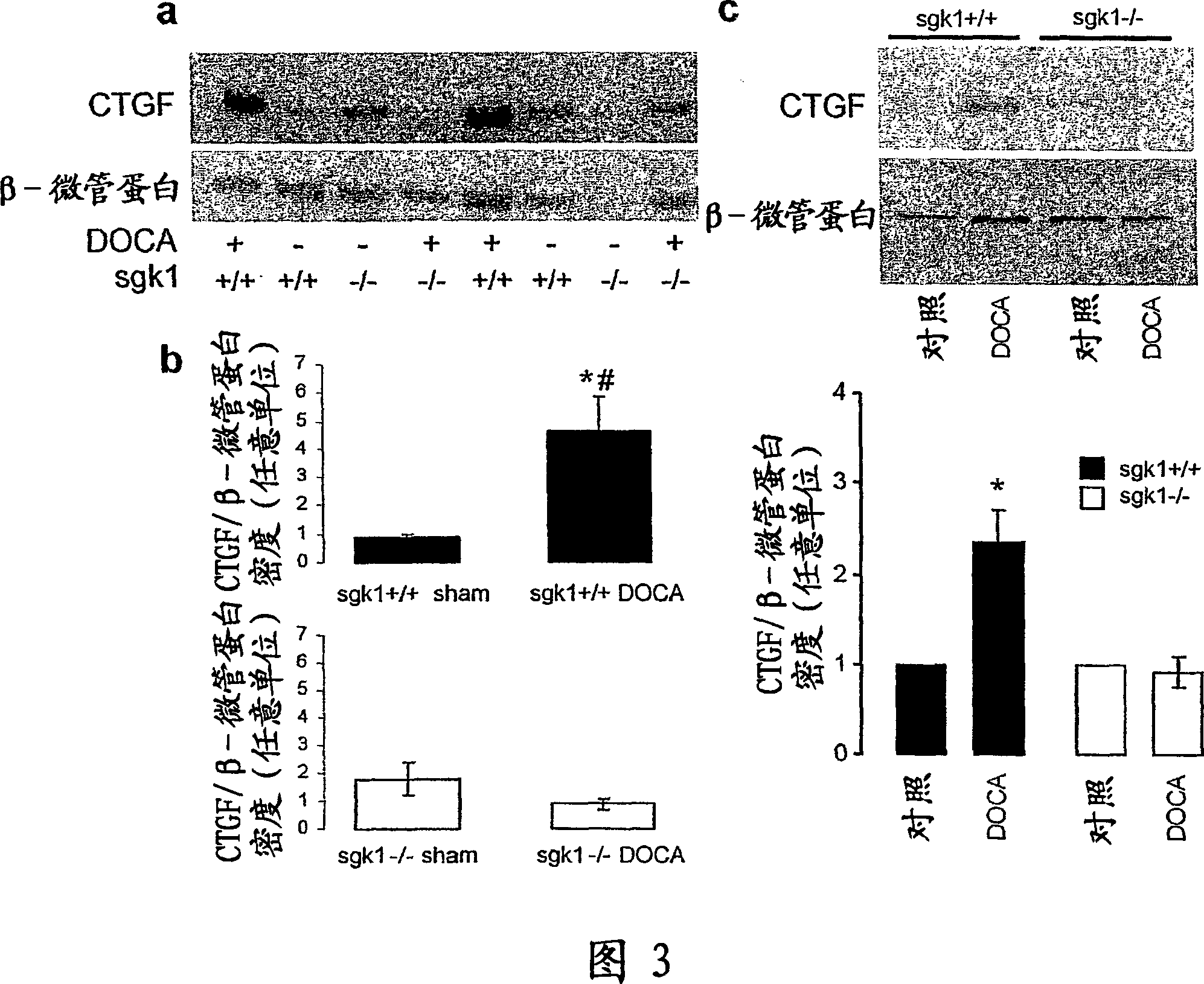
[0042] According to the manufacturer's instructions, the Qiagen RNeasy fibrous tissue medium kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) was used to extract the heart tissue of sgk1+ / + and sgk1- / - mice that were not treated or treated with DOCA / high salt (48h). total RNA. Hearts of sgk1- / - and sgk1+ / + mice treated with DOCA / high salt or sham using a commercially available kit (Invitrogen Life Technologies, Rockville, MD) and oligo-deoxythymidine (dT)24 T7 primer Total RNA undergoes second-strand synthesis. Biotin-labeled CTP and UTP were used to generate cRNA by in vitro transcription using T7 promoter-coupled double-stranded cDNA as a template and the T7 RNA Transcription Labeling Kit (ENZO Diagnostics, Farmingdale, NY). cRNA was fragmented and hybridized to a mouse genome MOE430A oligonucleotide array chip (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA). Array chips were stained with phycoerythrin-conjugated streptavidin (Molecular Probes, Invitrogen Life Technolo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com