Unified binary phase modulating and demodulating method
A modulation and demodulation, binary phase technology, applied in the field of digital information transmission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
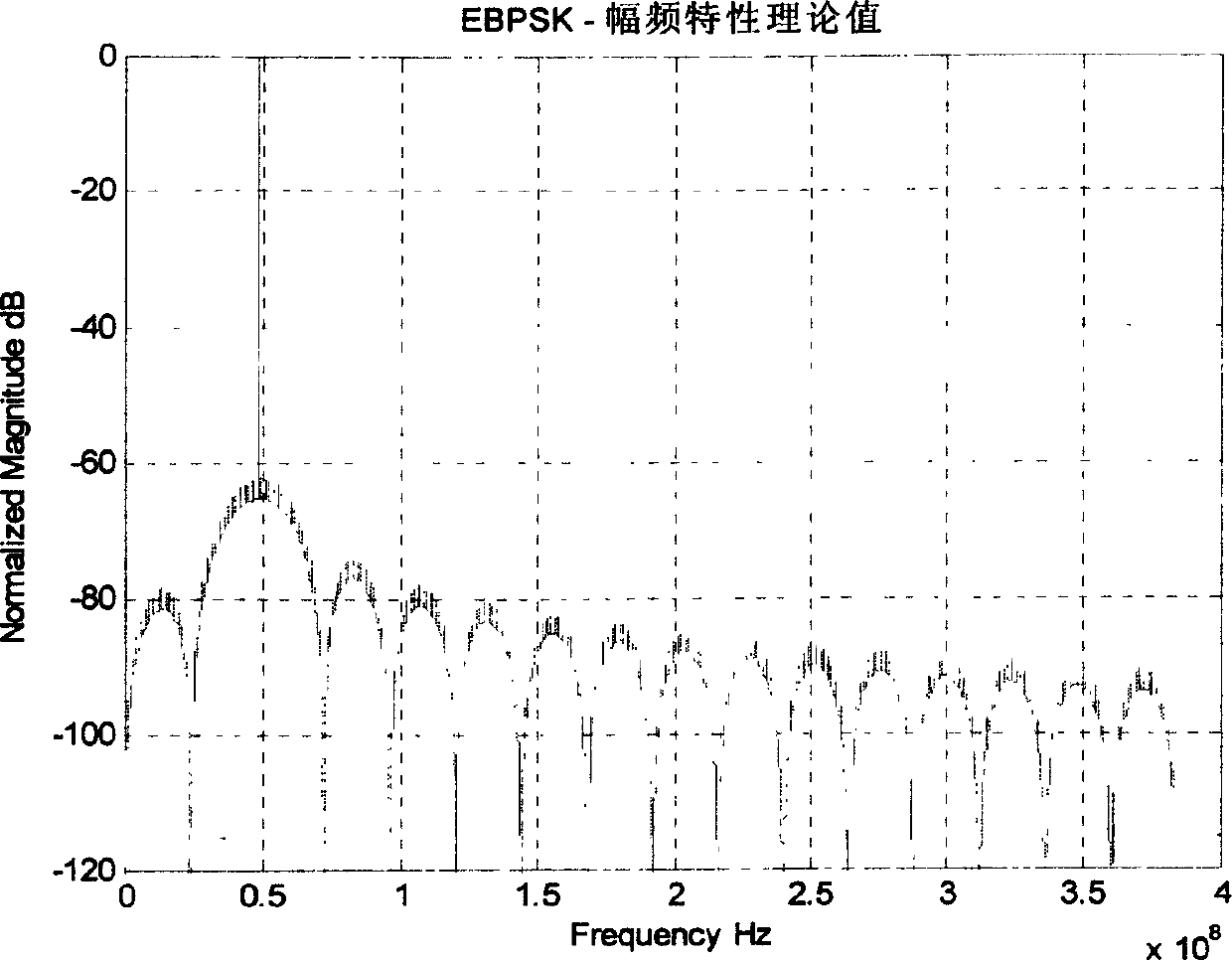
[0041] Take θ=π / 4, f c =48MHz, get the power spectrum of the EBPSK modulation signal as figure 1 Shown, where the ordinate is the power spectrum amplitude at the carrier frequency as 0dB. It can be seen from the figure that the energy of the EBPSK modulation signal is highly concentrated, and the carrier frequency amplitude is at least 60dB (1 million times) higher than other sidebands. The time domain waveform of the EBPSK modulation signal is indeed very similar to a sine wave.
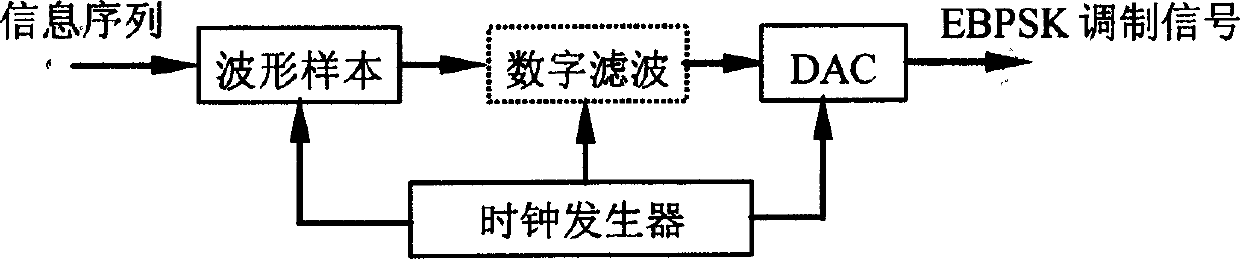
[0042] This method uses binary information symbols to directly change the sudden phase of the sinusoidal carrier to realize modulation, and uses a phase-locked loop to realize demodulation, so that the modulated signal corresponding to the digital "0" g 0 (t) is a sine wave of N carrier periods, and g corresponding to the number "1" 1 (t) is at frequency f c In the sine wave of N carrier periods of , the phase jump of the first K periods has an angle of θ; that is
[0043] f 0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com