Method for antibody purification including step where activated carbon material is used
A technology of activated carbon and antibodies, which is applied in the field of high-purity purified antibodies to achieve high virus clearance performance, reduce purification steps and production costs, and reduce the burden of impurities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0186] Embodiment 1: common method
[0187] In this example, methods commonly used in Example 2 and subsequent examples will be described.
[0188] 1) Determination of antibody concentration
[0189] Antibody concentration was determined by HPLC using a PA ID Sensor Cartridge (2.1 mm x 3 mm, Applied Biosystems) column.
[0190] 2) HCP determination
[0191] HCP was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using the third generation CHO host cell protein kit from Cygnus Technologies or the CHO|360 HCP ELISA kit from BioGENES GmbH. The HCP concentration obtained was converted to a value of ng HCP / mg antibody by dividing by the antibody concentration.
[0192] In Examples 2 to 5 the third generation CHO host cell protein kit from Cygnus Technologies was used, while in Examples 6 to 8 the CHO|360 HCP ELISA kit from BioGENES GmbH was used.
[0193] 3) PLBL2 assay
[0194] PLBL2 was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using the Hamster Phospho...
Embodiment 2
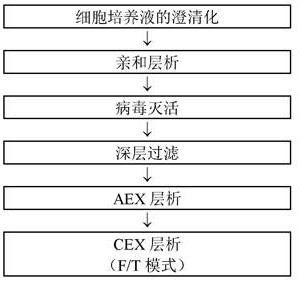
[0207] Example 2: Reference example: Purification by CEX chromatography in F / T mode (Mab A)
[0208] In this example, the removal of impurities in the purification procedure of the monoclonal antibody called Mab A will be explained according to the flowchart shown in Table 1 below.
[0209] [Table 1]
[0210]
[0211] 1) Materials and methods
[0212] The cell culture broth containing Mab A produced by CHO cells was filtered through a depth filter to remove cells, and clarified to obtain a cell culture supernatant. Cell culture supernatants were purified by protein A chromatography using KanCapA resin. After equilibrating the column with phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) containing 20 mM NaCl, load the cell culture supernatant. Then, the column was washed with phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) containing 1 M sodium chloride, and then washed with phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) containing 20 mM sodium chloride. Mab A was eluted from the column with acetate buffer (pH 3.6). Absorbance at 280 ...
Embodiment 3
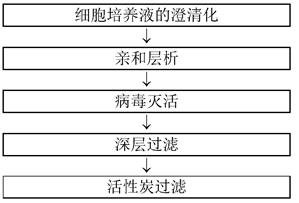
[0217] Example 3: Impurity removal using activated carbon materials (Mab A, Mab B, Mab C, Mab D)
[0218] In this example, the removal of impurities in the purification schemes of various antibodies referred to as Mab A, Mab B, Mab C, and Mab D will be explained according to the purification scheme shown in Table 3 below. It should be noted that the amino acid sequences of Mab A, Mab B, Mab C and MabD and the antigens to be bound are different from each other.
[0219] [table 3]
[0220]
[0221] 1) Impurity removal using activated carbon material (except viruses)
[0222] Millistak+(R) Pod CR40 was used as the activated carbon material. For Mab B and Mab A, antibody recovery and impurity clearance were evaluated. The depth-filtered pools of Mab B and Mab A obtained as described in Example 2 were used as loading solutions for activated carbon filters (activated carbon material loading), respectively. It should be noted that in the case of Mab B, in order to facilitate t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com