Forest three-layer scattering model determination and analysis method suitable for PolInSAR inversion
A technology of scattering model and analysis method, applied in the field of remote sensing image processing, can solve the problems such as errors and affect the inversion accuracy, and achieve the effect of high-precision vegetation parameter inversion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0026] Specific implementation mode 1: This implementation mode discloses a determination and analysis method for a forest three-layer scattering model suitable for PolInSAR inversion, including the following steps:
[0027] Step 1: Analyze the scattering characteristics of the surface layer and determine its vertical structure function form;
[0028] Step 2: Analyze the scattering characteristics of the trunk layer and determine its vertical structure function form;
[0029] Step 3: Analyze the scattering characteristics of the vegetation canopy and determine its vertical structure function form;
[0030] Step 4: Combining the vertical structure functions of the surface layer, trunk layer and vegetation canopy on the vertical structure of vegetation, derive the general three-layer scattering model of vegetation, determine the expression of interference coherence coefficient, and analyze the influence of height parameters on coherence.
specific Embodiment approach 2
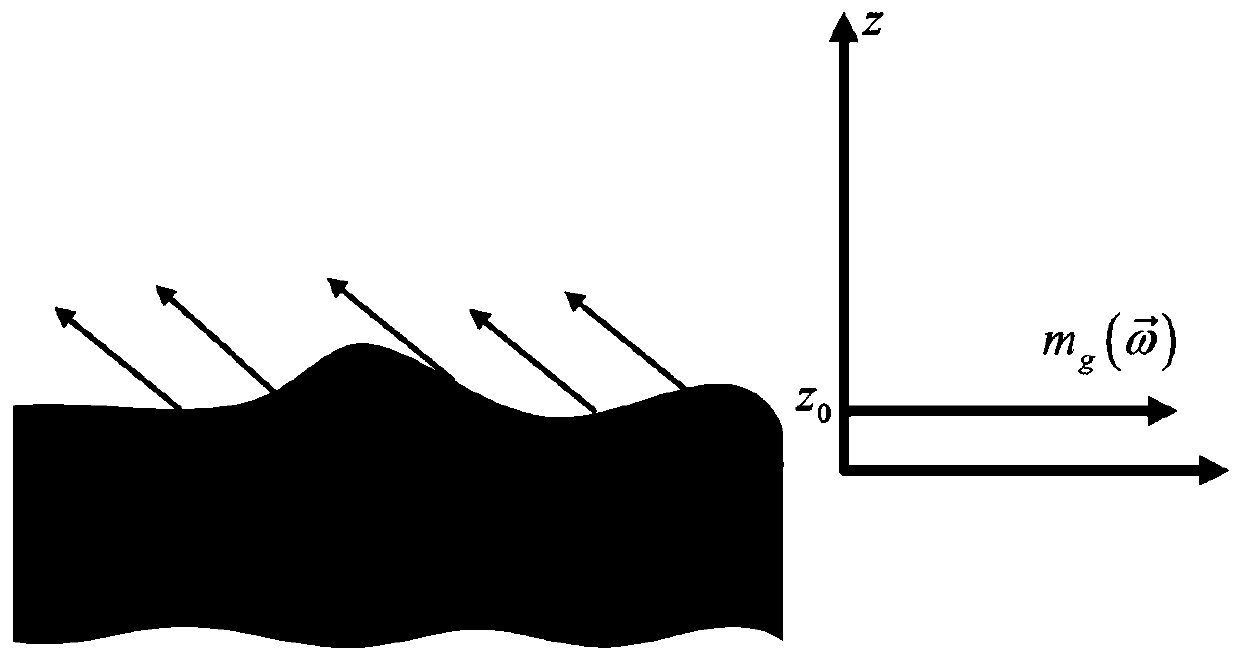
[0031] Specific implementation mode two: this implementation mode is a further description of specific implementation mode one, and the step one is specifically (see figure 1 ):
[0032] Surface scattering usually occurs in a discontinuous medium. In the L-band, electromagnetic waves can often penetrate the vegetation canopy to reach the surface, so surface scattering occurs on the surface. For surface scattering, the scattering center is at a constant height, and the vertical structure The function is reflected in the horizontal direction, so its vertical structure function is modeled as an impulse response, the expression is as follows:
[0033]
[0034] Among them, z 0 Indicates the terrain height, f g (z) represents the distribution function of the electromagnetic scattering amplitude of surface scattering in the vertical direction, Indicates the electromagnetic scattering amplitude of the surface layer, δ indicates the impulse response function, and z indicates the...
specific Embodiment approach 3
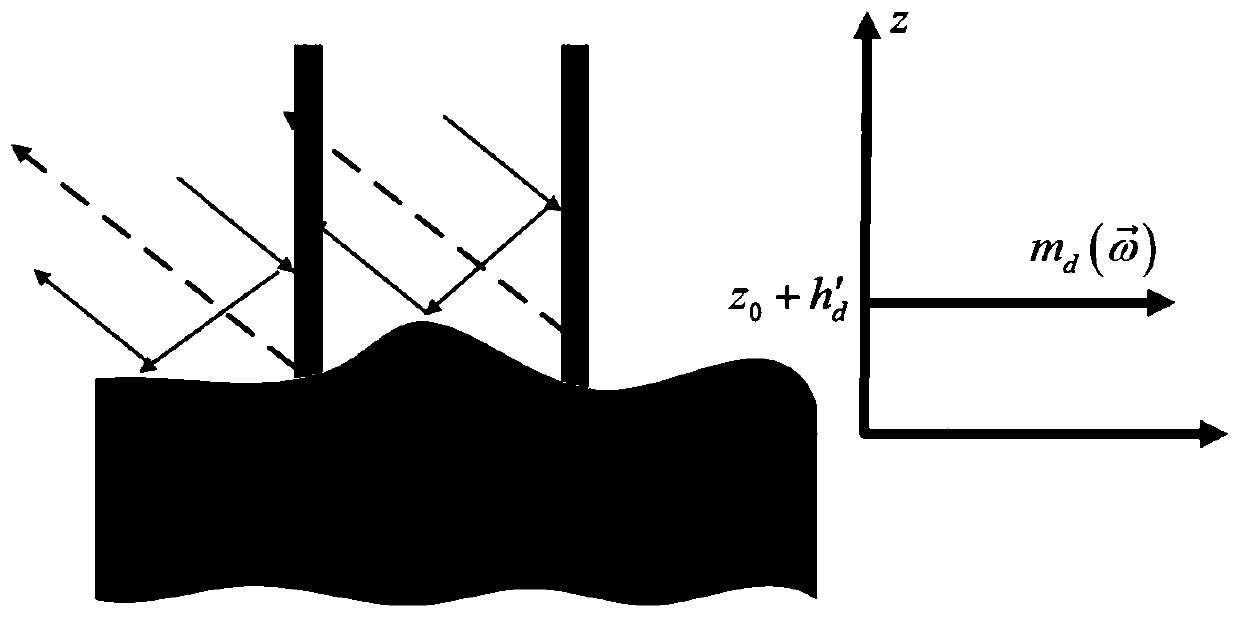
[0035] Specific implementation mode three: this implementation mode is a further description of specific implementation mode one, and the step two is specifically (see figure 2 ):
[0036] Let the height of the trunk layer be h d (Note that the height of the trunk layer here is not equal to the height of the bottom of the canopy). Even scattering is caused by the interaction of electromagnetic waves between the trunk, branches and the ground. Under the L-band, because electromagnetic waves can penetrate The canopy, so the even-order scattering exists, and the even-order scattering between the trunk, branches and the ground is equivalent to the surface scattering at a certain height from the ground surface to the bottom of the canopy, and its equivalent scattering center h d 'defined as
[0037]
[0038] Among them, h′ d Indicates the height of the equivalent scattering center of the trunk layer, θ indicates the radar incidence angle;
[0039] The corresponding vertical...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Extinction coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com