Method for repairing defects in synthetic fiber microstructure and high-strength synthetic fiber rope
A synthetic fiber, defect repair technology, applied in the direction of carbon fiber, fiber treatment, fiber type, etc., to reduce clogging, save installation costs, and improve tensile strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
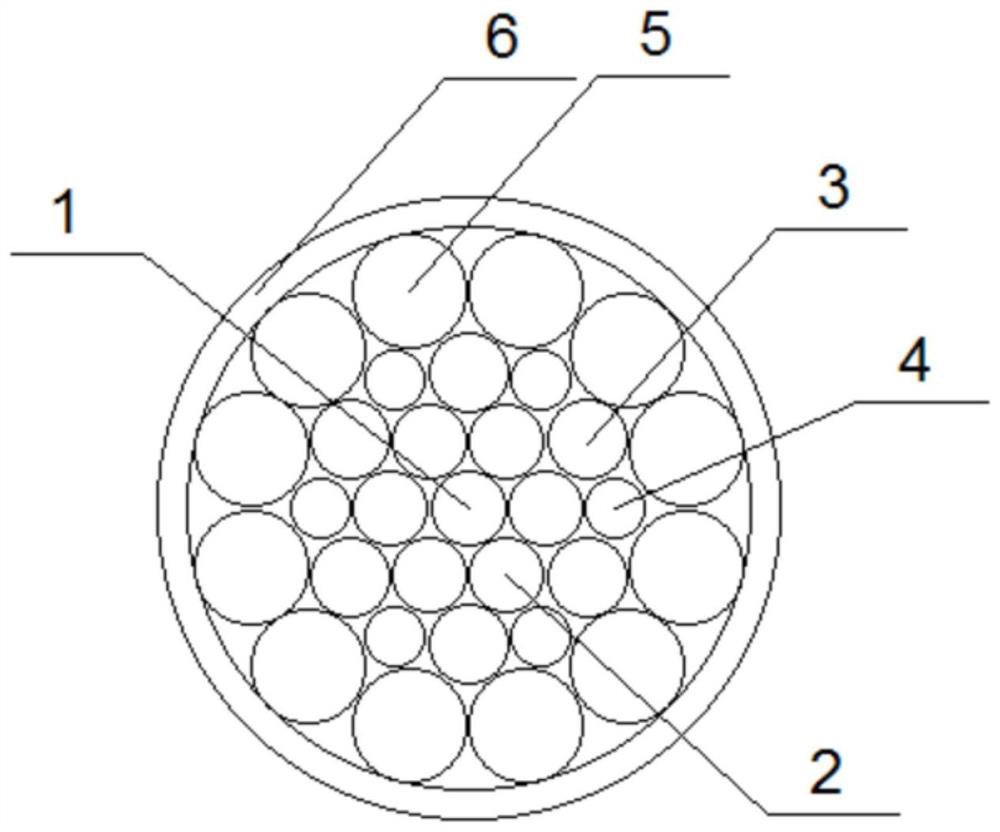
[0032] A new type of high-strength synthetic fiber rope, including strands and a covering body 6 wrapped around the strands. The strands include a central strand 1, and the periphery of the central strand is provided with a first strand layer composed of six first strands 2. The first strands 2 are all tangent to the central strand 1 and adjacent to the second strand. One strand 2 is in tangential contact, and the periphery of the first strand layer is provided with a second strand layer consisting of six second strands 3 and six third strands 4, and the second strand 3 is connected to the third strand. The strands 4 are arranged in a staggered manner, and the adjacent second strands 3 and the third strands 4 are in tangential contact, the second strands 3 and the third strands 4 are both tangent to the first strands 2, and the second strands 3. Different from the diameter of the third strand 4, the outer periphery of the second strand layer is provided with an outer strand la...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The difference from Example 1 is that the material used for the strands is a mixture of carbon fiber, aramid fiber and PBO fiber. The fibers of the strands are treated with a repairing agent, the microscopic defects of the fibers are repaired, dried and solidified, and then shaped and twisted to form strands.
[0039] The repairing method is as follows: the repairing agent is driven by pressurized nitrogen to form an aerosol, and is sprayed into the pulled synthetic fiber rope in the form of aerosol at a temperature of 60°C to 80°C, and the pulling speed of the synthetic fiber is 10 meters / second, and then continue to pull and cure through multi-stage heating. The multi-stage heating curing is specifically: the temperature of the first stage is 80°C-100°C, the temperature of the second stage is 100°C-120°C, and the temperature of the third stage is 120°C-160°C.
[0040] The restoration agent is carborane polyester and CeO 2A mixture of which CeO 2 The weight ratio ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] The difference from Example 1 is that the materials used for the strands are carbon fiber and aramid fiber. The fiber strands of the strands are treated with a repairing agent to repair the microscopic defects of the strands, then dry and solidify, and then are reshaped and twisted to form strands.
[0044] The repairing method is as follows: the repairing agent is driven by pressurized nitrogen to form an aerosol, and is sprayed into the pulled synthetic fiber rope in the form of aerosol at a temperature of 60°C to 80°C, and the pulling speed of the synthetic fiber is 5 meters / second, and then continue to pull and cure through multi-stage temperature rise. The multi-stage heating curing is specifically: the temperature of the first stage is 80°C-100°C, the temperature of the second stage is 100°C-120°C, and the temperature of the third stage is 120°C-160°C.
[0045] The restoration agent is carborane polyester and CeO 2 A mixture of which CeO 2 The weight ratio is...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com