Dandruff-removing itching-relieving scalp conditioning liquid and preparation method and applications thereof
An anti-dandruff, antipruritic, and conditioning liquid technology, applied in hair care, skin diseases, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve problems such as poor moisturizing ability, complex plant components, and unknown conditioning effects, and achieves promotion of absorption, soothing skin, and improving Effects of the sebum microenvironment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
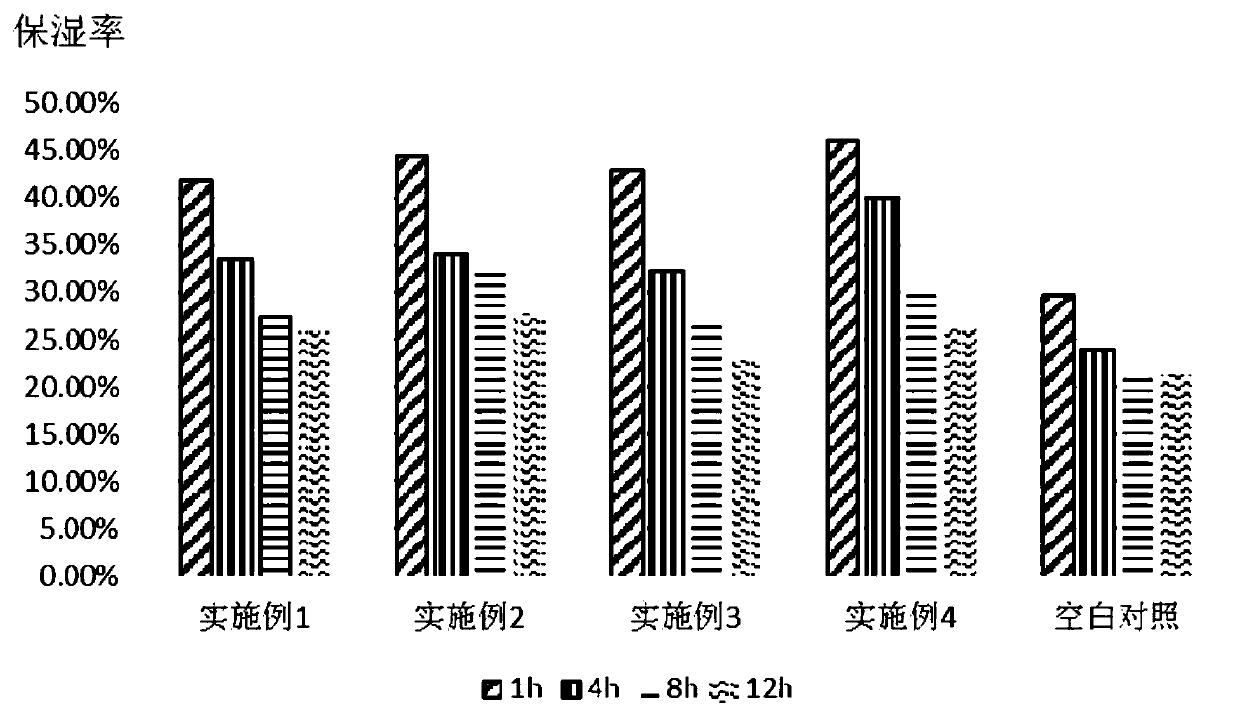
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-4
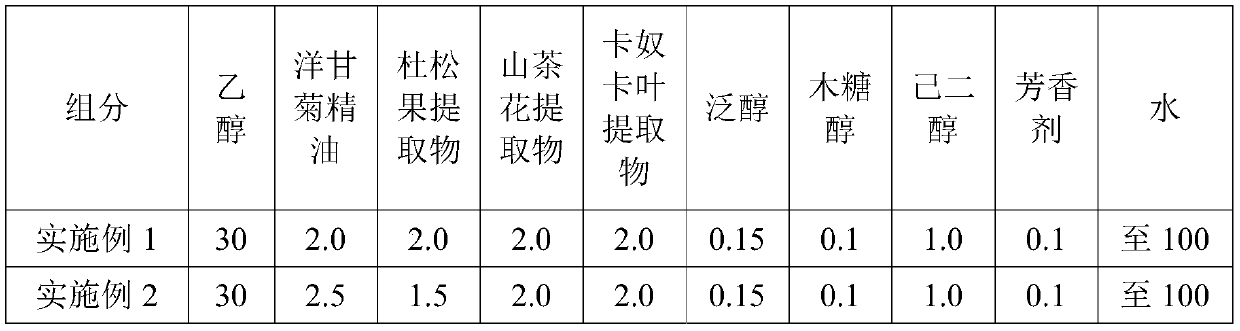
[0052] The anti-dandruff and antipruritic scalp conditioning liquids of Examples 1-4 are made of the weight percentages shown in Table 1 (that is, the numbers in the table represent weight percentages, for example, 30 represents 30%).
[0053] Table 1
[0054]
[0055]
[0056] The preparation method of the anti-dandruff and antipruritic scalp conditioning liquid described in any one of the above embodiments 1-4 is: mixing ethanol, chamomile essential oil, juniper berry extract, camellia flower extract, and Kanuka leaf extract according to the formula amount Stir, then add panthenol, xylitol, hexylene glycol and fragrance, make up the water and stir evenly.
Embodiment 5
[0062] In this example, the Malassezia antibacterial test was performed on the scalp conditioning liquids of Examples 1-5 and Comparative Examples 1-6
[0063] This example refers to the Oxford Cup Inhibition Zone indicator experiment recommended by the National Committee for Clinical Standards (NCCLS): Under aseptic conditions, draw 200 μL of indicator bacteria suspension and evenly spread it on the plate medium; add 0.1 mL of bacteriostasis to the Oxford cup respectively The sample solutions of Examples 1-4 and Comparative Examples 1-6, in which the indicator bacterium is Malassezia culture medium at 37°C for 48 hours; the Oxford cup is removed, and the diameter of each inhibition zone is accurately measured with a vernier caliper, and compared Antibacterial effect.
[0064] Among them, the experimental strain and the concentration of the bacterial solution obtained from the configuration of the strain are shown in Table 1. The Malassezia bacteriostatic test was performed on Exa...
Embodiment 6
[0069] In this example, the scalp conditioning liquids of Examples 1-4 and Comparative Examples 1-6 were subjected to a DPPH free radical scavenging test
[0070] The test principle is: DPPH is a kind of stable organic free radical, and its strongest absorption peak is at 519nm. This kind of free radical will show dark purple when added to ethanol solution. When a certain amount of antioxidant is added, the resistance can be measured at 519nm. The absorbance value after the oxidant removes DPPH and the color becomes lighter. Quantitative analysis is performed by spectrophotometry to detect the scavenging of free radicals, thereby evaluating the ability of the active ingredients with antioxidant effects in the product to scavenge free radicals. The greater the scavenging rate, the stronger the ability to scavenge free radicals. The DPPH clearance rate of the blank sample is zero. Finally, the test results of the scavenging ability of scalp conditioning liquid on DPPH free radical...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com