Dimming cylinder for debugging galvanometer coaxial core and debugging method
A coaxial, dimming technology, applied in optics, optical components, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of height deviation, large distance of the galvanometer, and inability to determine the installation position, and achieve the effect of simple and reasonable structure and good practical effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
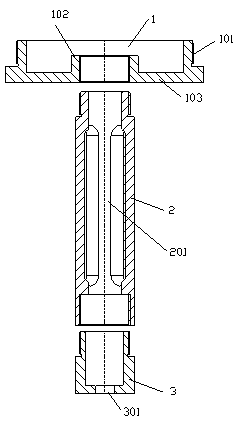
[0030] Such as figure 1 , 2 , As shown in 3 and 4, a dimmer tube for debugging the galvanometer coaxial center, including a dimmer connection cover 1, a dimmer adapter tube 2, and a dimmer joint 3, and a dimmer connection cover 1 is provided with a field lens to cooperate with The connected external thread structure 101 has a central boss 102 in the center, and is connected as a whole through a flange cover 103; The dimming joint 3 is provided with a dimming hole 301, and is connected to the lower end of the dimming socket 2; the outer thread structure 101 and the center of the dimming hole 301 are coaxially set.
[0031] Optimally, the interior of the central boss 102 is provided with an internal thread coaxial with the external thread structure 101. Correspondingly, the upper end of the dimming socket 2 is provided with an external thread, and is connected to the dimming connection cover 1 through a thread pair. Together; similarly, the lower end of the dimming adapter 2 i...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Such as Figure 5 As shown: a dimmer tube for adjusting the galvanometer coaxial center, the difference from the first embodiment is: optimized, the dimmer receiver 2 and the dimmer connection cover 1 are fixedly connected to form an integrated structure; The lower end of 2 is provided with a coaxial internal thread, and correspondingly, the upper end of the dimming joint 3 is provided with an external thread, and is connected with the dimming socket 2 through a pair of threads.
[0035] With such an arrangement, the internal thread at the lower end of the dimming connector 2 can be processed on the same positioning basis as the external thread structure 101 on the dimming connection cover 1 to ensure a high-precision coaxial center, thereby further improving the brightness of the dimming connector 3. The concentricity between the small dimming hole 301 and the external thread structure 101 is determined.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Such as Figure 6 As shown, a dimmer tube for debugging the concentric center of the vibrating mirror is different from Embodiment 1 in that: optimized, the dimmer connector 3 and the dimmer receiver 2 are fixedly connected to form an integrated structure; the dimmer receiver 2 Correspondingly, the center boss 102 is provided with an internal thread coaxial with the external thread structure 101, and is connected with the dimming socket 2 through a thread pair.
[0038] With such a setting, the dimming small hole 301 on the dimming joint 3 is coaxially processed with the external thread on the upper end of the dimming receiver 2 to ensure high-precision coaxiality, thereby further ensuring that the dimming small hole 301 and the external thread The concentricity of the structure 101.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com