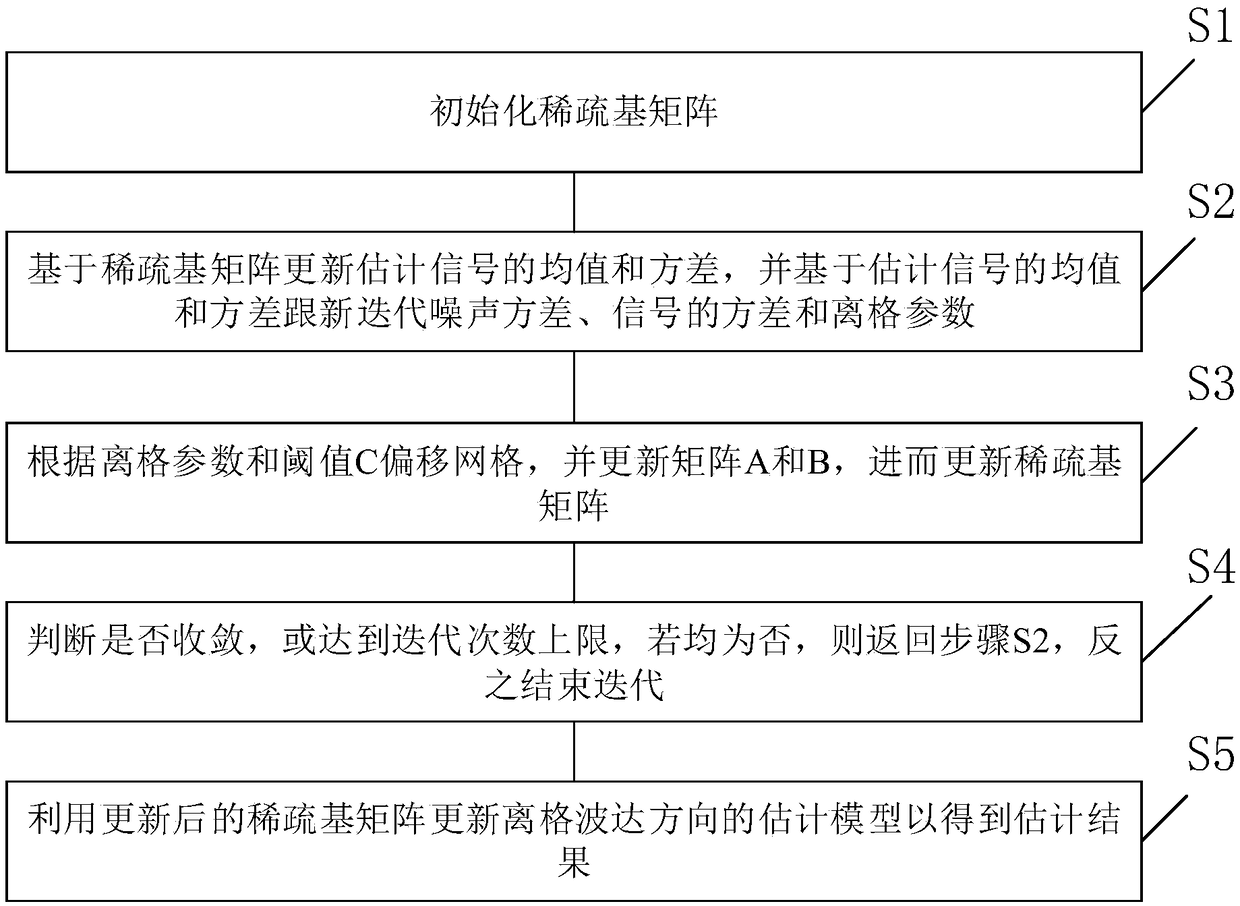
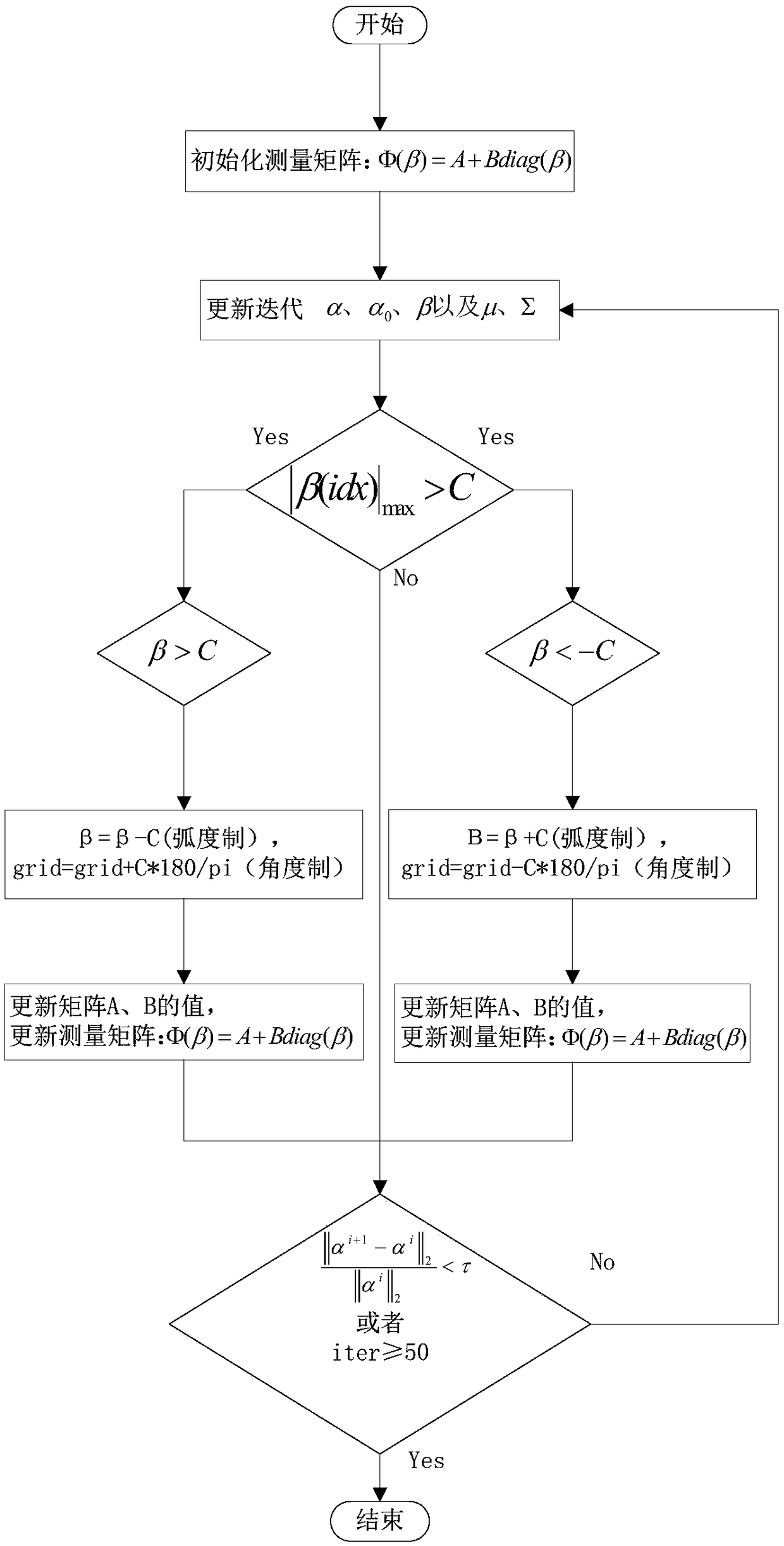
Direction-of-arrival estimation method based on off-grid sparse Bayesian
A direction-of-arrival estimation and sparse Bayesian technology, applied in the field of estimation, to achieve the effect of reducing the amount of calculation, reducing the calculation time, and improving the accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
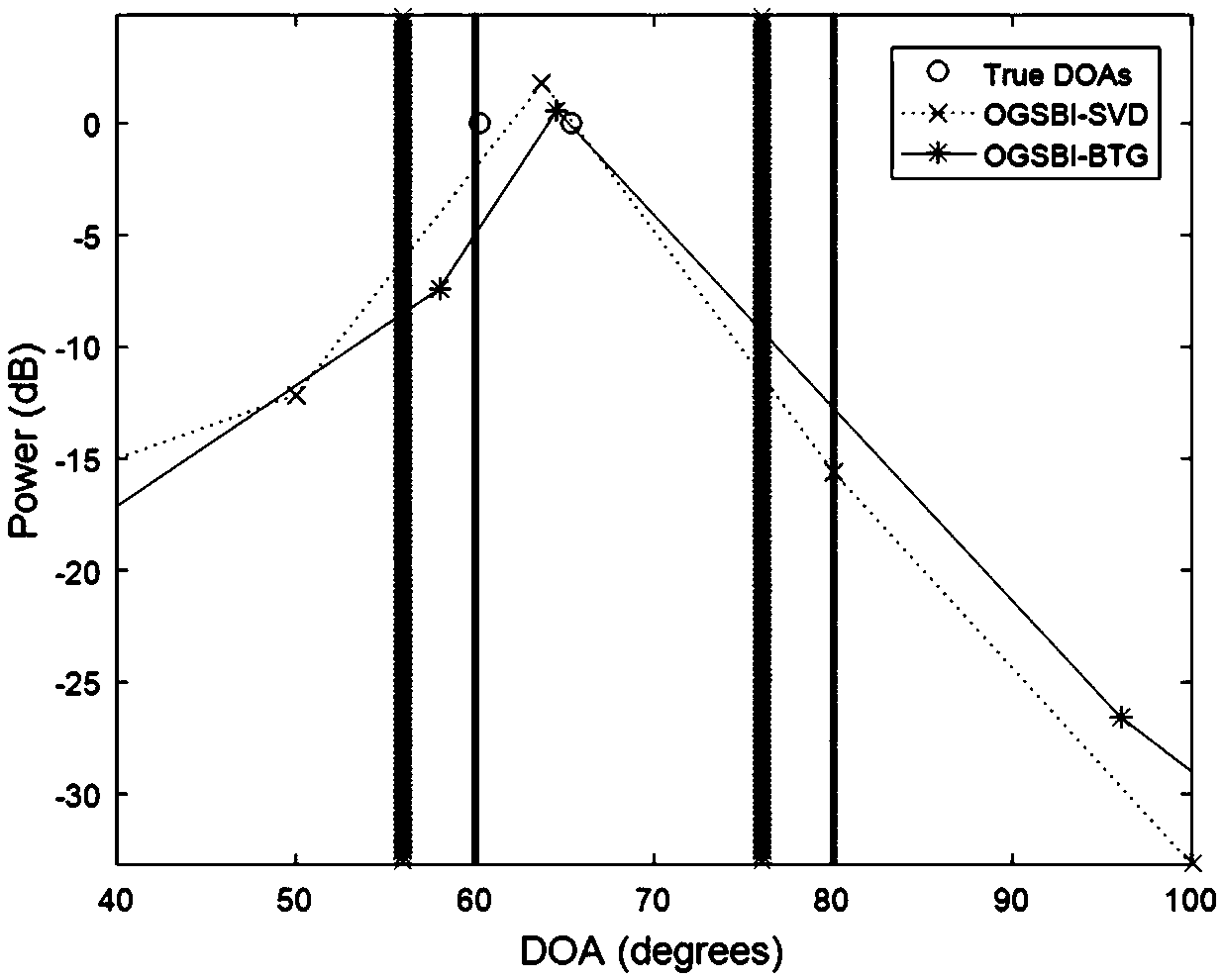
[0128] Embodiment 1: From the perspective of DOA estimation, compare the OGSBI-BTG algorithm of the present invention with the existing OGSBI-SVD algorithm (the thin vertical line is the original grid, and the thick vertical line is the offset grid). The resolution (grid spacing r) is 20, the signal-to-noise ratio SNR is 20, K=2, C=8*pi / 180, and the true DOA of the two signals are 60.2 and 65.4, respectively. available from image 3 It can be seen from the figure that the real DOA of these two signals is between the grid {60~80}, and between the grid {56~76} after migration. In the existing OGSBI-SVD algorithm, one of the DOA values It can basically be estimated that another DOA value cannot be estimated and is outside the grid; in the OGSBI-BTG algorithm of the present invention, one of the DOA estimated values is more accurate than the value estimated by the existing OGSBI-SVD algorithm, And another DOA value can be estimated basically, and these two DOA values are all ...
Embodiment 2
[0129] Embodiment 2: Using the OGSBI-BTG algorithm of the present invention to compare the existing OGSBI-SVD algorithm from the perspective of RMSE. The resolution (grid spacing r) is 20, the signal-to-noise ratio SNR is 0:3:30, K=2, C=8*pi / 180, and the two signal sources are 60.2 and 65.4 respectively. From Figure 4 It can be seen that the RMSE of the OGSBI-BTG algorithm proposed by the present invention is much smaller than that of the existing OGSBI-SVD algorithm when estimating dense DOA in the case of large grid division.
Embodiment 3
[0130]Embodiment 3: From the perspectives of estimated value, β value, and grid division, compare the OGSBI-BTG algorithm of the present invention with the existing OGSBI-SVD algorithm. The resolution (grid spacing r) is 20, the signal-to-noise ratio SNR is 20, K=2, C=8*pi / 180, and the two signal sources are 60.2 and 65.4 respectively.
[0131] Table 1 Comparison table of estimated value, value and grid division between OGSBI-BTG algorithm and existing OGSBI-SVD algorithm
[0132]
[0133]
[0134] It can be seen intuitively from Table 1 that the value of β has been adjusted. Combined with the offset of the overall grid, first set β new The value of is converted into an angle system and the grid value of the corresponding position is the estimated value. The OGSBI-BTG algorithm of the present invention is closer to the real value in estimated value than the existing OGSBI-SVD algorithm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com