An experimental device for real-time monitoring of the radial support force of vascular stents in a simulated environment
A technology of radial support and vascular stent, applied in the field of mechanical performance testing of medical devices, can solve the problems of many uncertain factors and low precision, and achieve the effect of controllable flow and temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
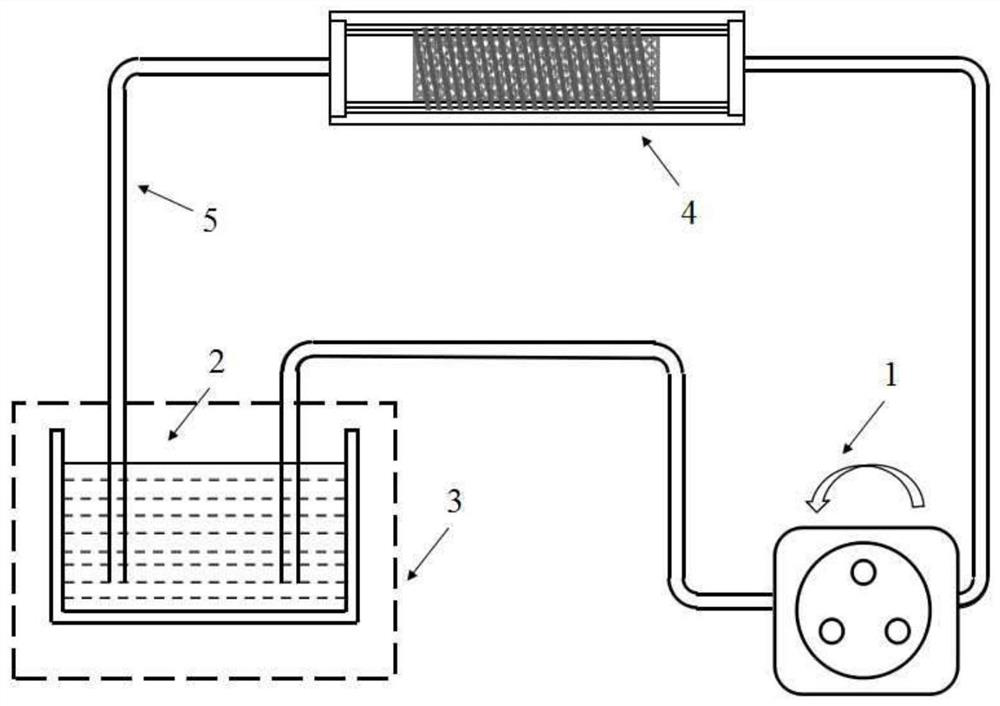
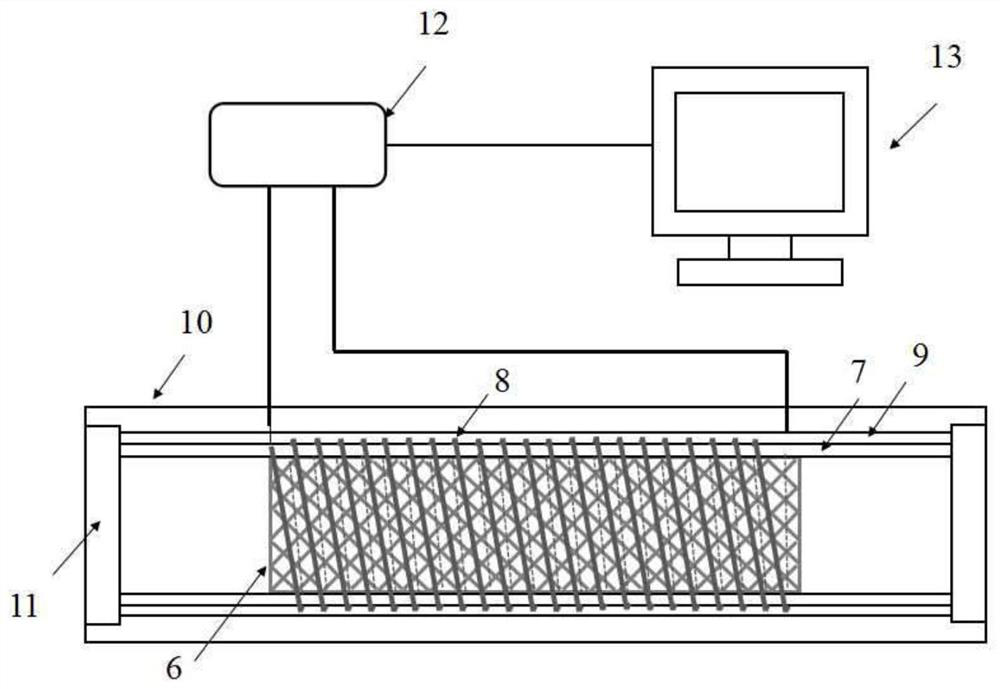
[0041] Such as figure 2 In the device shown, the vascular stent 6 selected for testing is a braided and formed WE43 magnesium alloy balloon-expandable degradable vascular stent, and the tightly gripped stent is preloaded on the balloon catheter and delivered to the inner PU transparent elastic tube 7 In the process, the balloon is inflated to the nominal pressure with the filling pressure pump, and the stent squeezes the inner PU transparent elastic tube 7, the nickel-chromium alloy resistance strain wire coil 8, and the outer PU transparent elastic tube 9, and at the same time the stent expands, and the catheter The balloon at the distal end was withdrawn after decompression and contraction. The corrosive medium used was a simulated plasma solution at a temperature of 37°C. The speed of the flow field was controlled by an adjustable-speed peristaltic pump 1. In the corrosive medium fluid, the diameter of the magnesium alloy stent The radial support force decreases with its o...
Embodiment 2
[0043] The device used is the same as that in Example 1, and the vascular stent 6 selected for testing is a self-expanding vascular stent of nickel-titanium shape memory alloy formed by laser engraving. The stent is preloaded on the delivery catheter and placed in the PU transparent elastic tube 7 , connected to the simulated blood circulation device through a silicone hose 5, the corrosive medium used is simulated plasma, the flow field velocity is controlled by an adjustable-speed peristaltic pump 1, and the temperature is adjusted to 37°C to reach the transformation temperature of the alloy, and the stent gradually deforms and expands And to generate support force for the elastic tube, choose constantan wire as the metal resistance strain wire, record the change of the average radial support force during the expansion and retraction process of the stent in real time, and study the influence of blood flow on the radial support force of the vascular stent.
[0044] In order to...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com