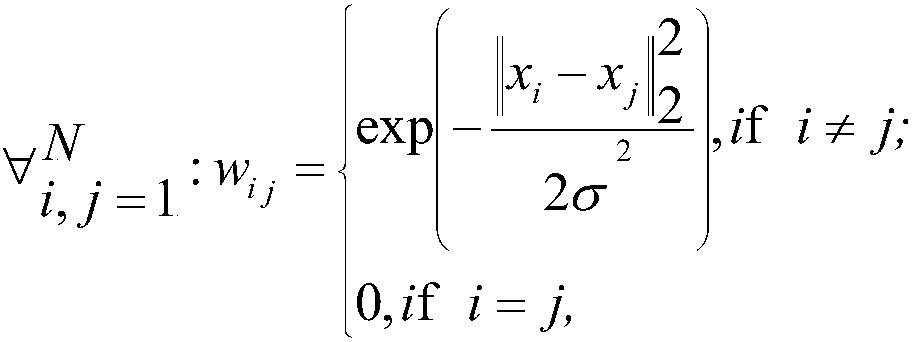Image labeling method based on multi-label learning, terminal device and storage medium
An image tagging and multi-labeling technology, which is applied in the direction of instruments, character and pattern recognition, computer parts, etc., can solve the problem that the uniqueness of tags cannot meet the needs of image tags
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
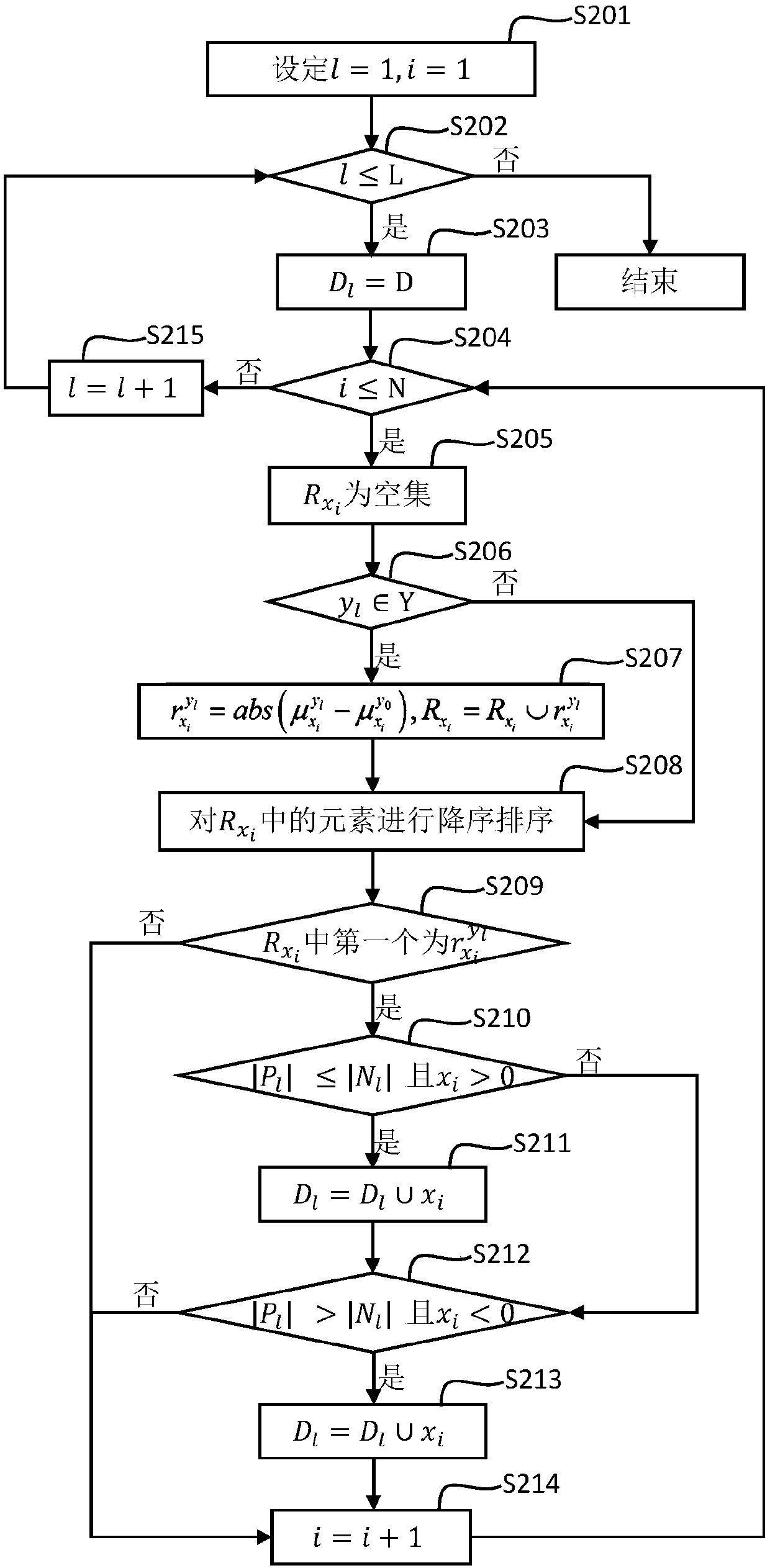
[0068] Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides an image labeling method based on multi-label learning. The purpose of multi-label learning is to define a classification model f l :x→R(l=1,2,...,L). f l A larger value means that the instance is more likely to have y l Label. The ranking function rank(·,·) can be transformed from the function f(·): For any y k ∈Y,y j ∈Y(k≠j), if f k (x i ) > f j (x i ), then rank(x i ,y k )i ,y j ). Given a threshold σ, we can define a classifier h:x→2 based on f( ) y , for an instance x i ∈ x, if f k (x i )>σ, then y j ∈h(x i ),otherwise
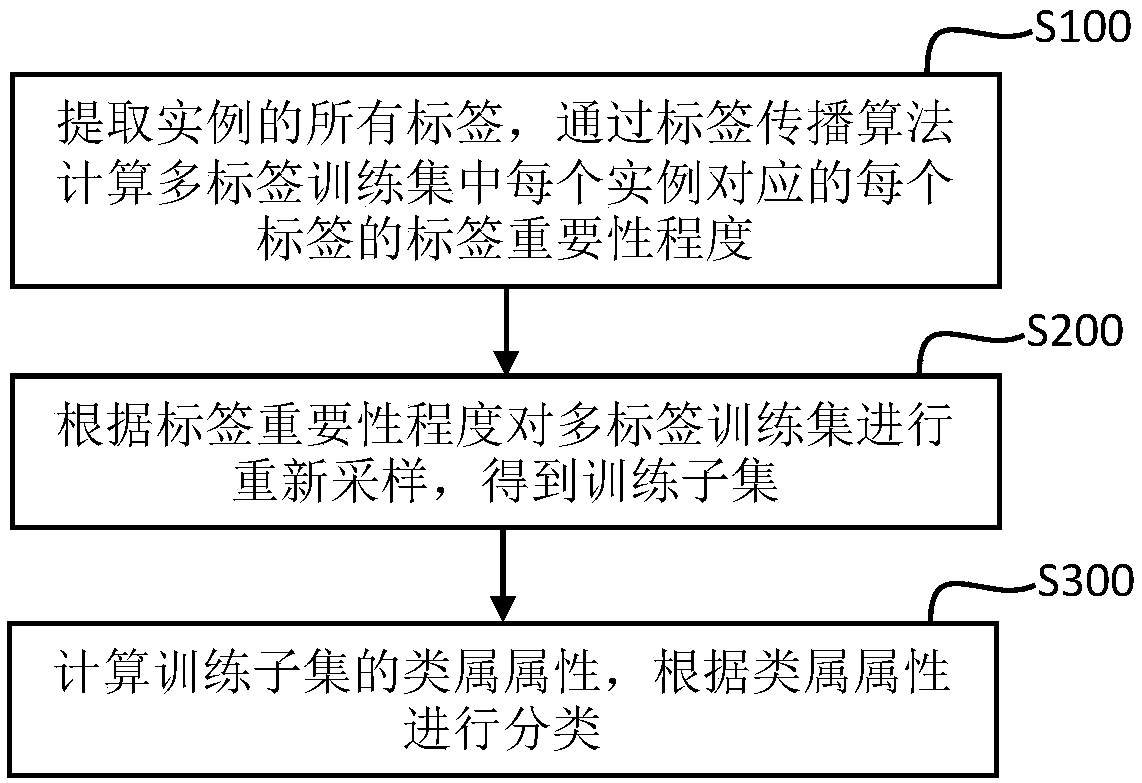
[0069] Such as figure 1 As shown, it is a schematic flow chart of the image labeling method based on multi-label learning described in Embodiment 1 of the present invention, and the method may include the following steps:
[0070] S100: Extract all the labels of the instance, and calculate the label importance degree of each label corresponding to each instance in the multi-label ...
Embodiment 2
[0150] The present invention also provides an image tagging terminal device based on multi-label learning, including a memory, a processor, and a computer program stored in the memory and operable on the processor, and the processor executes the computer program The steps in the above method embodiment of Embodiment 1 of the present invention are realized at the same time.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com