Satellite system and method for global coverage
A satellite system and satellite technology, which is applied in the field of satellite systems, can solve problems such as coverage impact and achieve the effect of graceful degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
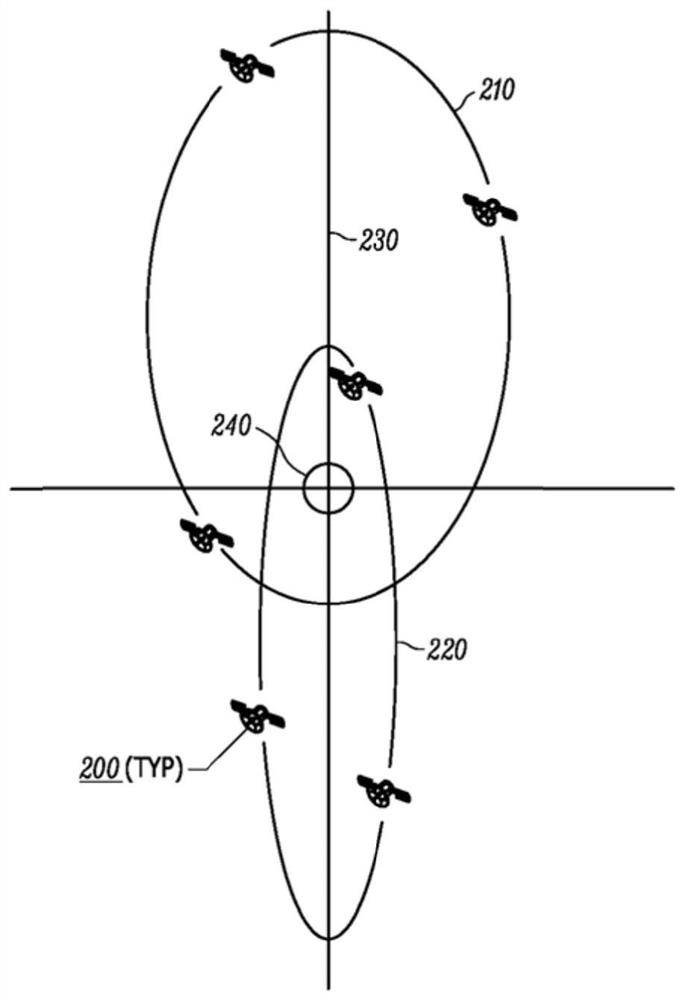
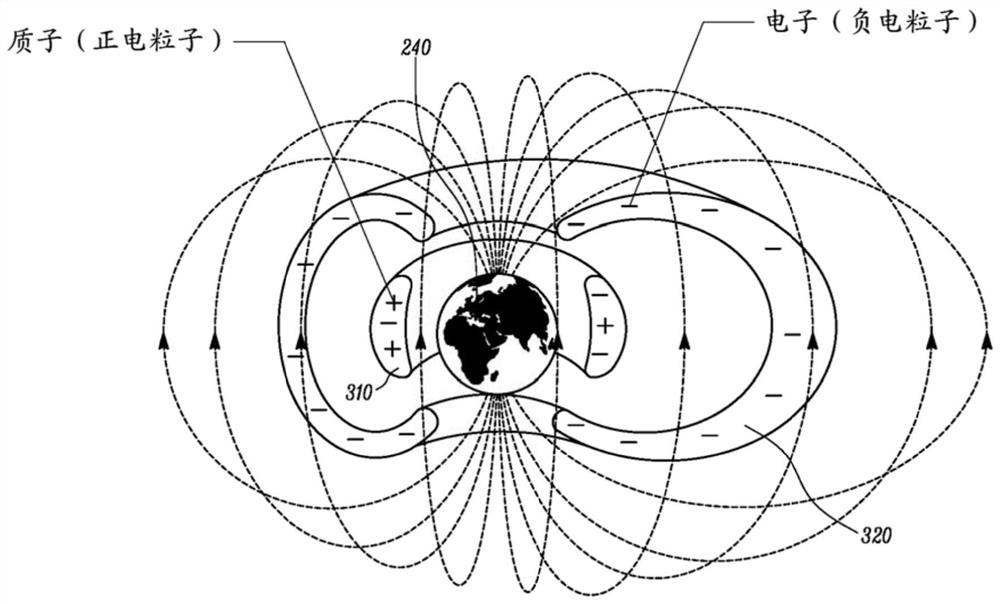
[0074] Example 2 uses the same orbital parameters as Example 1, except three satellites are used in a single plane instead of two. Of course, the three satellites are scheduled to be spaced 8 hours apart. As such, this embodiment provides continuous coverage north of latitude 21°, with an elevation angle of 10°. This represents a coverage of only 32% of the Earth. The constellation is represented in Figure 6A shown in the Figure 6B A simulation of the coverage it provides is shown. Of course, turning the orbit around would put the apogee above the South Pole, yielding complete coverage south of 21°S latitude, with an elevation angle of 10°.
Embodiment 3
[0075] Example 3 shows the effect of adding a fourth satellite to the single plane of Examples 1 and 2, otherwise using the same orbital parameters. The four satellites are very evenly spaced 6 hours apart from each other. The result is only a modest improvement in coverage relative to Example 2, providing continuous coverage north of 18°N latitude, with an elevation angle of 10°. This represents a coverage of only 34% of the Earth. The constellation is represented in Figure 7A shown in the Figure 7B A simulation of the coverage it provides is shown. Of course, turning the orbit around would put the apogee above the South Pole, producing continuous coverage south of 18° south latitude, with an elevation angle of 10°.
Embodiment 4
[0076] Example 4 uses the same number of satellites as Example 3, but instead of placing the four satellites on the same orbital path, two coplanar orbital paths are used, one with the apogee above the North Pole and the other with the apogee above the North Pole. above Antarctica. Two satellites are placed in each orbital path, evenly spaced 12 hours apart. Relative to Example 3, global coverage is significantly improved, providing continuous coverage of 57% of the Earth with an elevation angle of 10°. The constellation is represented in Figure 8A shown in the Figure 8B A simulation of the global coverage it provides is shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com