A self-adaptive multi-way tree anti-collision method based on a collision tree
An adaptive, multi-tree technology, applied in the field of radio frequency identification, can solve problems such as long identification time, complex anti-collision algorithm, and increased idle time slots, so as to improve identification rate and throughput, avoid low search efficiency, and reduce total The effect of the number of slots
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] Below in conjunction with specific embodiment, further set forth the present invention, should be understood that these embodiments are only used to illustrate the present invention and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention, after having read the present invention, those skilled in the art will understand various equivalent forms of the present invention The modifications all fall within the scope defined by the requirements of this application.
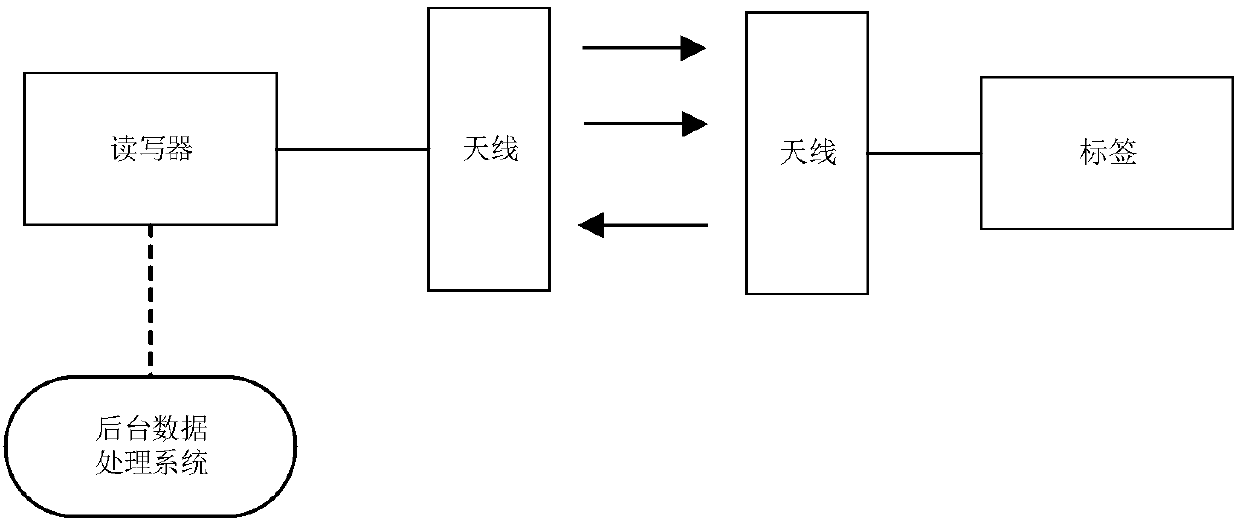
[0028] like figure 1 Shown is the working mode diagram of the RFID system. The tags interact with the reader through the antenna. When several tags respond to the reader at the same time, they will interfere with each other, making it difficult for the reader to correctly identify each tag. Since Manchester encoding is usually used in RFID systems, this feature makes it possible to obtain information on collision bits.
[0029] to solve figure 1 In the scene where multiple tags respond to the reader a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com