Simple finite element modeling method for composite stiffened skin-foam sandwich structure
A composite material and sandwich structure technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of poor stress transfer effect of model nodes, poor stress transfer effect between nodes, poor strain transfer effect, etc., to achieve Easy to master and use, improve stress transfer effect and strain transfer effect, easy to master effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
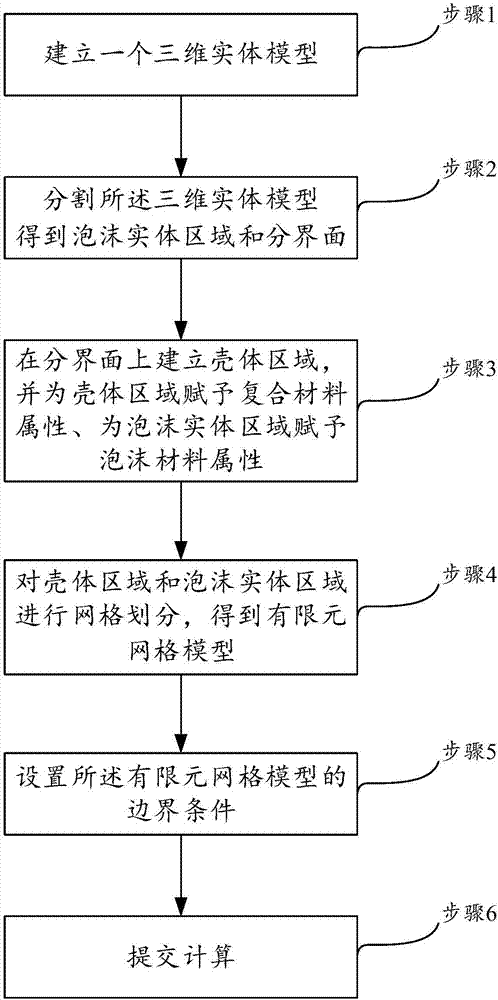
[0027] The simple finite element modeling method of the composite material reinforced skin-foam sandwich structure of the present invention will be explained and illustrated in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0028] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention innovatively discloses a simple finite element modeling method for a composite material reinforced skin-foam sandwich structure, which is an improvement and optimization of the traditional finite element modeling method. Specifically, the simple finite element modeling method of the composite material reinforced skin-foam sandwich structure provided by the present invention can be realized by Abaqus, and the composite material reinforced skin-foam sandwich structure is modeled under the Abaqus environment, but, in Based on the inspiration of the technical concept provided by the present invention, those skilled in the art may also consider implementing it on other three-dimensional model...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com