Organ preservation solution
A technology of organ preservation solution and compound, which is applied in the preservation, application, and animal husbandry of human or animal bodies. Effects of ischemia-reperfusion injury
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] (preparation of preservation solution)
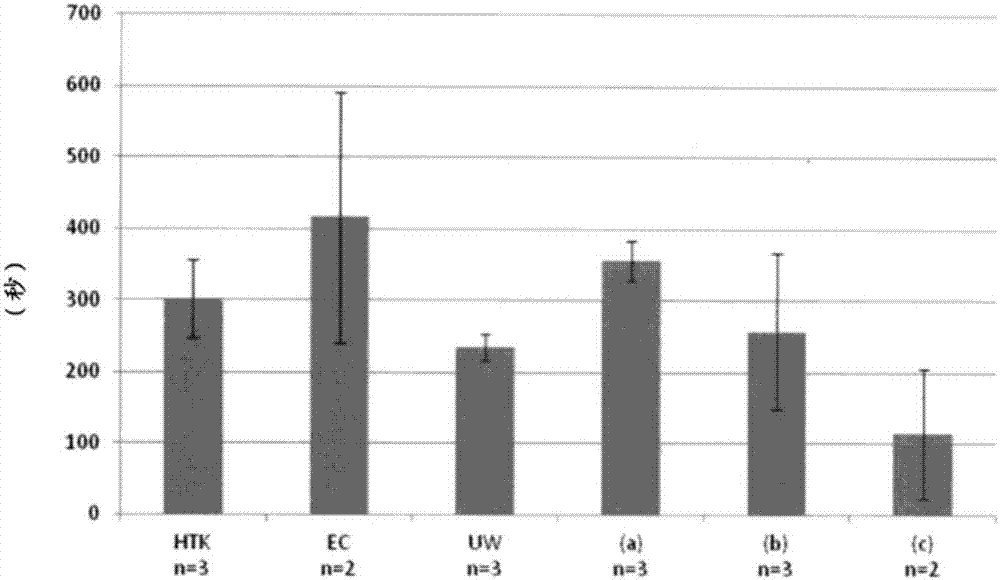
[0082] Three freshly prepared organ preservation solutions (preservation solution (a) to preservation solution (c)) were used as research objects. Details of components added and dissolved in distilled water are shown in Table 1 below. When an organ for transplantation is immersed in the above-mentioned preservation solution beyond the maximum allowable ischemia time specified for the conventional preservation solution product, it is examined whether the function of the organ can be maintained after transplantation. Specifically, when the hearts of donor mice immersed in the above three types of preservation solutions were transplanted into mice of the same strain, the time elapsed after the transplantation until the start of beating again was used as an index. In order to conduct a comparative study, three kinds of preservation solutions that are known as existing products, namely Euro-Collins solution (EC solution), histidine-...
Embodiment 2
[0096] (Mice Heterotopic Heart Transplantation 2)
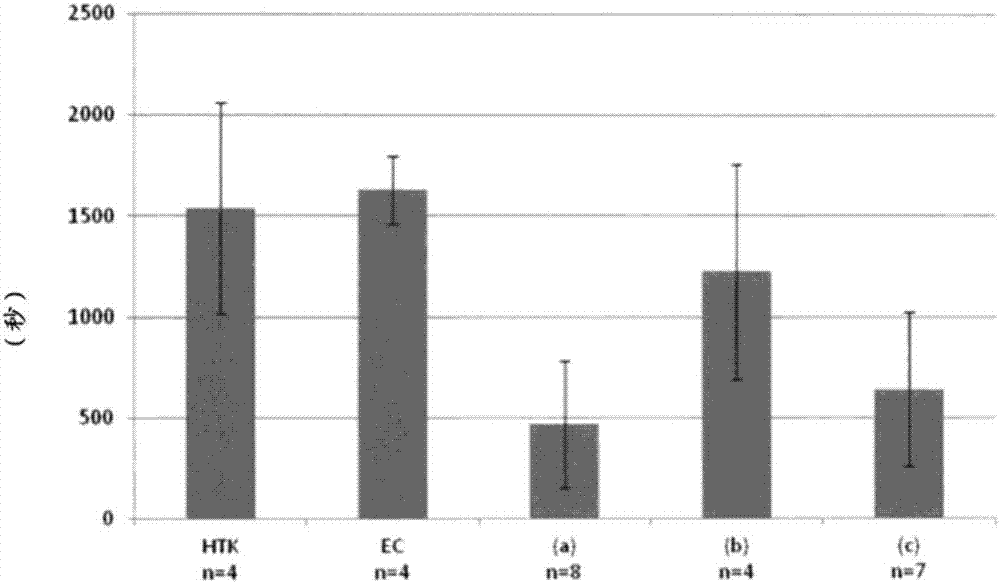
[0097] The immersion time in each preservation solution was set to 48 hours, and the existing products HTK solution and EC solution were used for comparative study, and the procedure of the above-mentioned Example 1 (heterotopic heart transplantation in mice 1) was followed. Heterotopic heart transplantation in mice was performed. The elapsed time until the transplanted heart started beating was measured for each individual mouse to which a heterotopic heart was transplanted. The results are shown in figure 2 middle.
[0098] (result 2)
[0099] Depend on figure 2 It can be seen that the re-beating start time of HTK solution and EC solution is more than 1500 seconds. On the other hand, the re-beating start time of preservation solution (a) is about 500 seconds, and the re-beating start time of preservation solution (b) is 1250 seconds. On the other hand, the re-beating start time of the preservation solution (c) was ab...
Embodiment 3
[0101] (Mice Heterotopic Heart Transplantation 3)
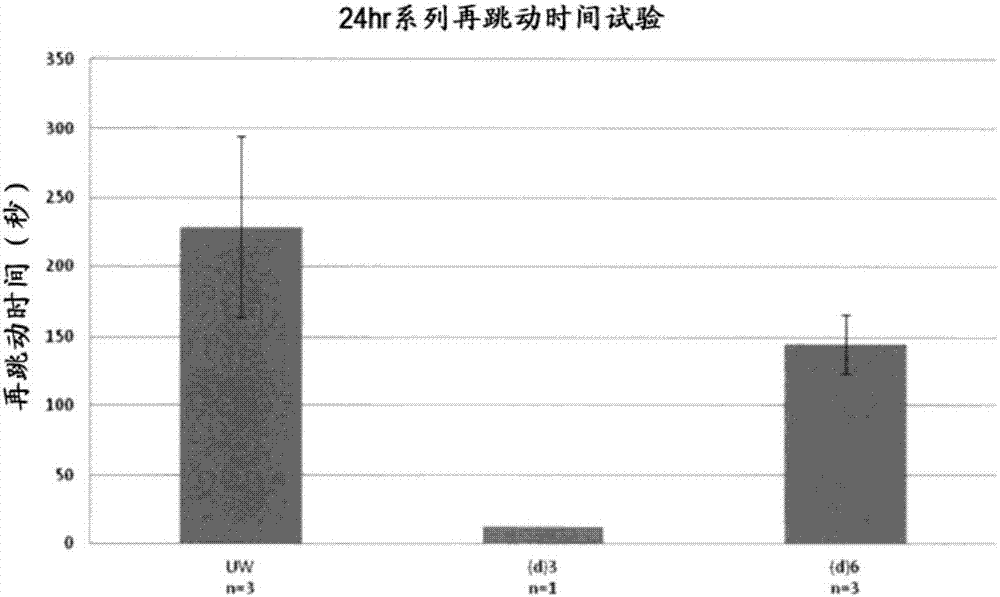
[0102] As a series of iron-added preservation solutions, a preservation solution (d) in which ferrous sulfate was added to the above-mentioned preservation solution (c) was further prepared, and research was continued. The details of the components of each preservation solution are shown in Table 3 below.
[0103] [table 3]
[0104]
[0105] As the iron-added series of preservation solutions, preservation solution (d) 3 and preservation solution (d) 6 were used, and the existing product UW solution was used for comparative research. The procedure of heart transplantation 1) performed heterotopic heart transplantation in mice. After immersion in the preservation solution for 24 hours, the time elapsed until the transplanted heart started beating was measured for each individual mouse to which the heterotopic heart was transplanted. The results are shown in image 3 middle.
[0106] Furthermore, after the heart transpla...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com