Bayes method for joint estimation of continuous traits and threshold traits based on genomic estimated breeding value
A technique for joint estimation and breeding value, applied in the Bayesian field, which can solve problems such as lack of joint analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
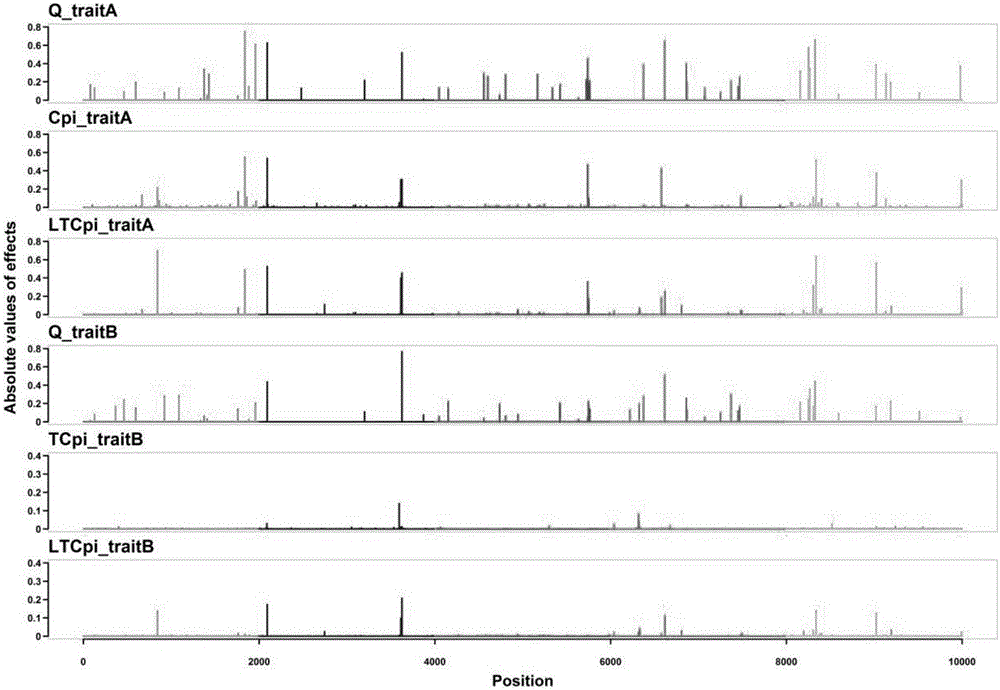
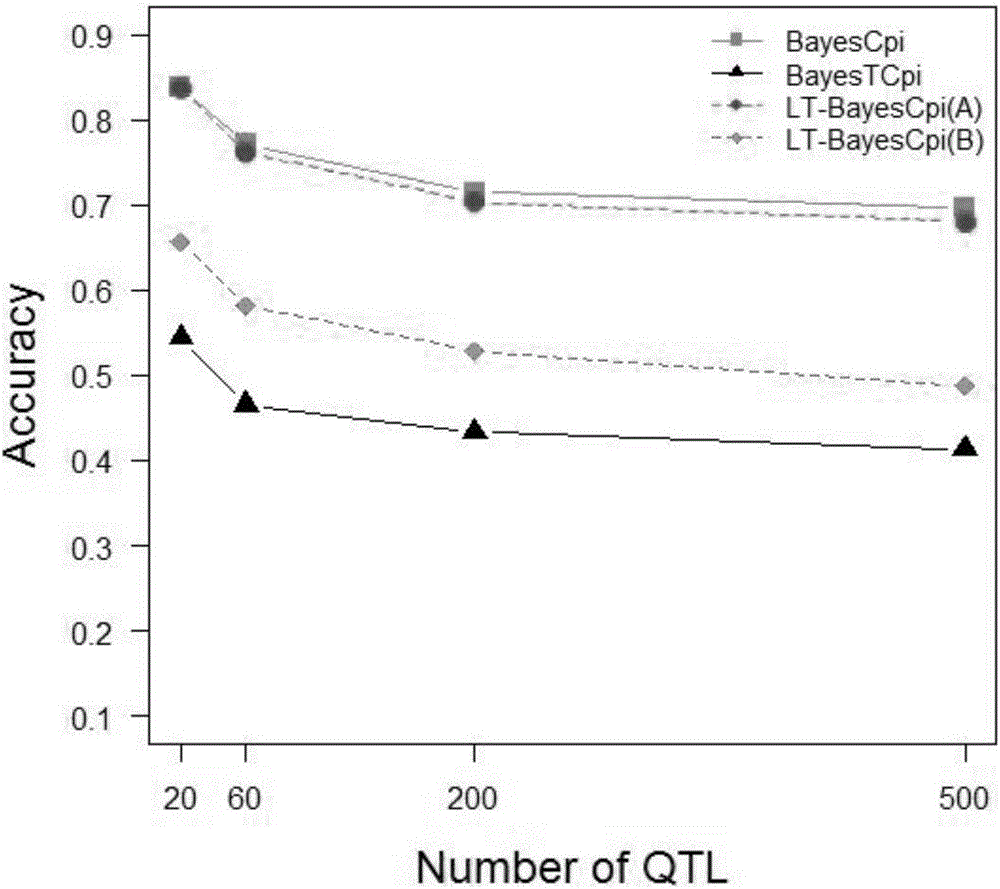
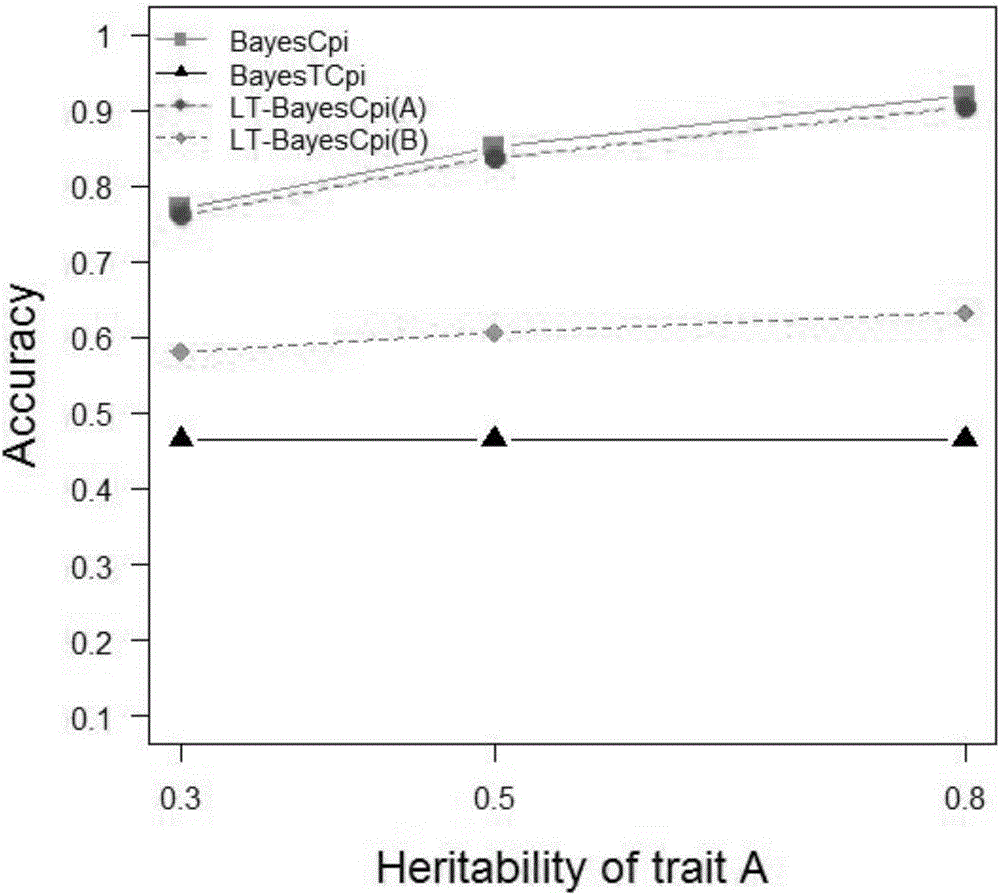
[0061] This example proposes a new Bayesian method based on the line-threshold model, called LT-BayesCπ, for joint analysis of continuous traits and threshold traits.
[0062] 1. Method
[0063] 1.1 Model
[0064] let y′ 1 ={y 1,i}(i=1,2,…,n) is the vector of observation values of continuous traits, y′ 2 ={y 2,i}(i=1,2,…,n) is the threshold trait observation value vector, l′={l i}(i=1,2,...,n) is the latent variable vector associated with the threshold trait. line-threshold model [15] for:
[0065] where β 1(2) is the fixed effect vector; g 1(2) is the SNP effect vector; e 1(2) is the random residual vector; X 1(2) for β 1(2) The correlation matrix of ; Z is the genotype indicator matrix (the assignments 0, 1, and 2 correspond to 11, 12, and 22 of the genotype, respectively). Let v'=[y' 1 , l′], given β and g, v obeys the following distribution:
[0066] v | β , g , R ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com