Fault diagnosis method through combination of nested iteration Fisher discriminant analysis and relative change
A technology of Fisher discrimination and relative change, which is applied to instruments, electrical test/monitoring, control/regulation systems, etc., and can solve problems such as bias and increased data fluctuations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0049] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific examples.
[0050] Take the Tennessee-Eastman process as an example. The Tennessee-Eastman process is a typical chemical process. The variables of this process include: 41 measured variables and 11 operational variables. The variables are listed in Table 1.
[0051] Table 1 Tennessee-Eastman Process Variable Table
[0052]
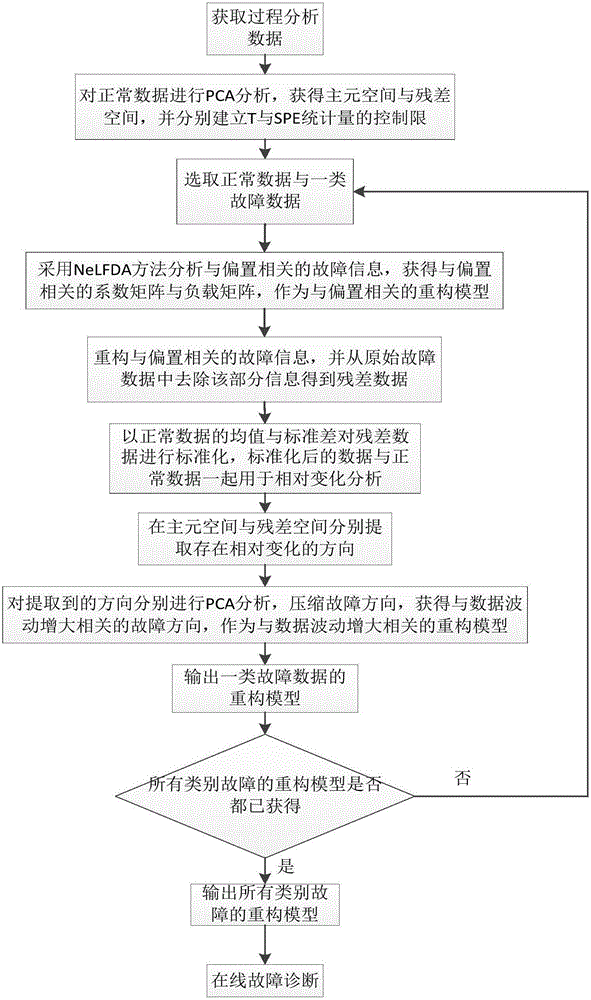
[0053] Such as figure 1 As shown, a fault diagnosis method combining nested iterative Fisher discriminant analysis and relative change analysis proposed by the present invention includes the following steps:
[0054] Step 1: Acquire data: For a chemical process with J variables, each sampling can obtain a 1×J vector, and the data obtained after sampling K times can be described as a two-dimensional matrix X(K×J). Get the normal data X respectively n (N n ×J) and fault data X f,m (N f,m ×J), where the subscript n repres...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com