A magneto-optical trap method and device for laser cooling and trapping
A technology of laser cooling and magneto-optical traps, which is applied in the direction of nanotechnology, instruments, and calculation models for information processing, and can solve problems such as insufficient utilization and complex optical paths
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
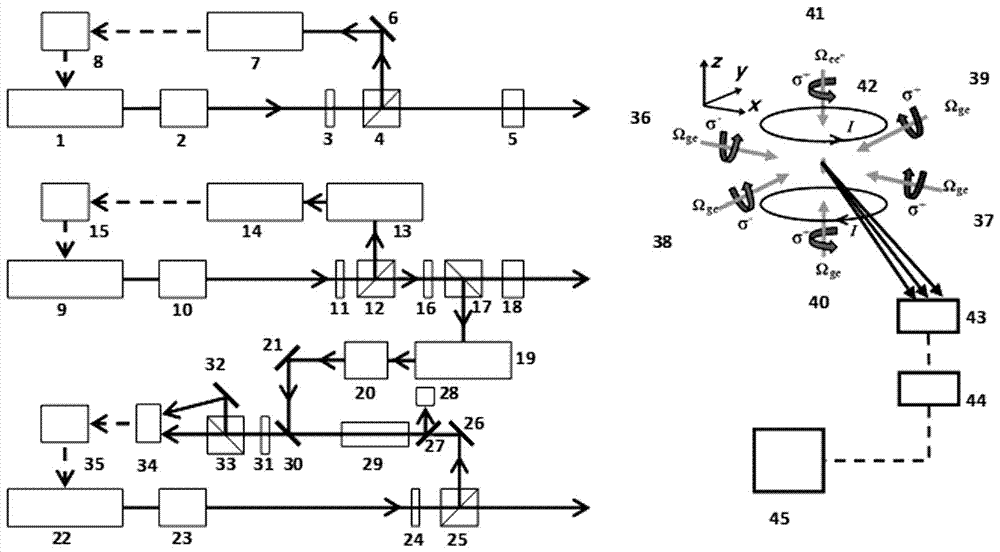
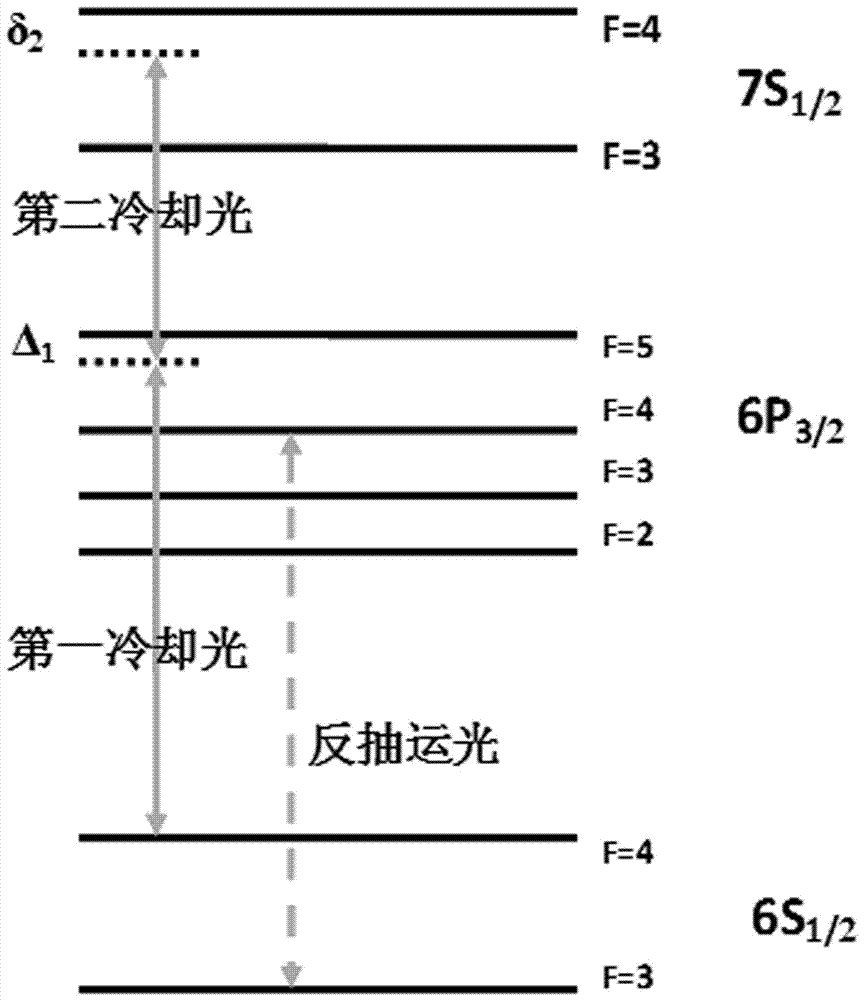
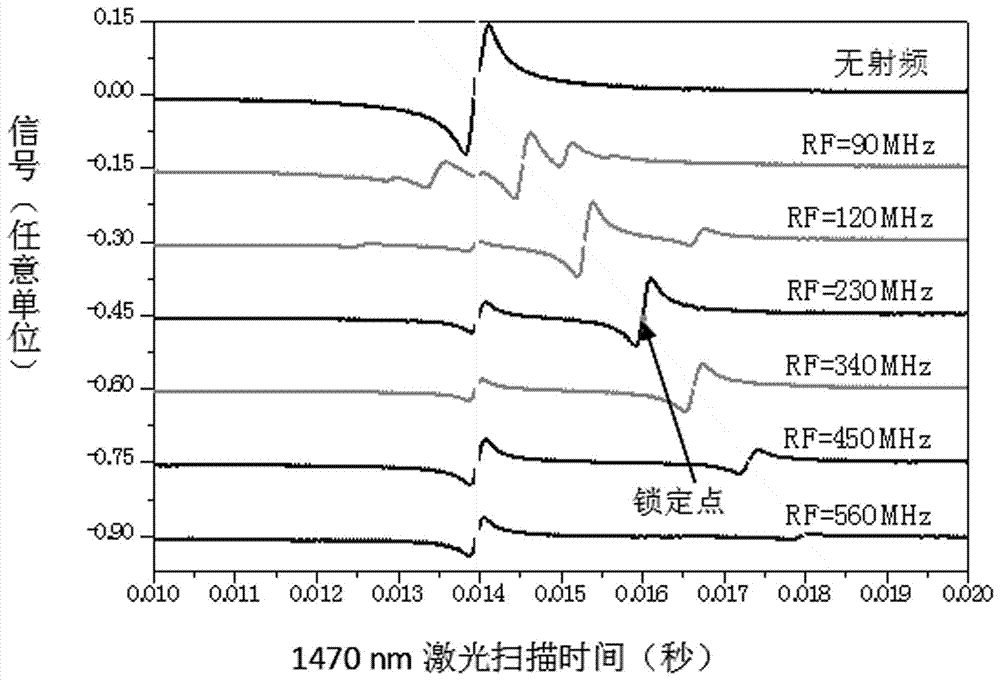
[0040] (4) According to figure 1 Build a magneto-optical trap optical path layout unit, wherein the cooling light in the z direction from 40 to 41 can be replaced or can be any of the following combinations (the first cooling laser is represented by L1, and the second cooling laser is represented by L2) : (a) (L2)+(L2); (b) (L1 L2)+(L2); (c) (L1 L2)+(L1 L2); (d) (L1)+(L1 L2); ( e) (L1) + (L2). Moreover, the optical path arrangement corresponding to the x, y, and z axes can be exchanged arbitrarily to meet the requirements of different experimental parameters. In the case of insufficient power of the second cooling laser, an appropriate optical path arrangement can also be selected to achieve cooling. The variation of the peak fluorescence signal of the atomic group with the two-photon detuning under different combinations is as follows: Figure 5 shown.
[0041] (5) According to figure 1 Build an atomic fluorescence collection unit, aim the lens of the CCD black and white ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com