Generation of pancreatic endoderm from pluripotent stem cells using small molecules
An endoderm, definitive endoderm technology, applied in non-embryonic pluripotent stem cells, artificially induced pluripotent cells, embryonic cells, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0088] 1. A method of producing pancreatic cells or pancreatic cell precursors, wherein at least 5% of the cells co-express PDX1 and NKX6.1, comprising exposing embryonic stem cells to an effective amount of at least one compound from the group consisting of:
[0089] a. BMP inhibitors
[0090] b. Kinase inhibitors
[0091] c. Retinoic acid receptor agonists,
[0092] To differentiate human embryonic stem cells into pancreatic cells or pancreatic cell precursors.
[0093] 2. The method of embodiment 1, wherein the compound is listed in Table 1 or 2.
[0094] 3. The method of embodiment 1 or 2, wherein the kinase inhibitor is an isomer of 1,9-pyrazoloanthrone with or without N-alkylation.
[0095] 4. The method of embodiments 1-3, wherein the kinase inhibitor is JNK inhibitor II.
[0096] 5. The method of embodiments 1-2, wherein the retinoic acid receptor agonist is AM580.
[0097] 6. The method of embodiments 1-5, wherein the JNK inhibitor II is combined with AM580.
[00...
Embodiment 1
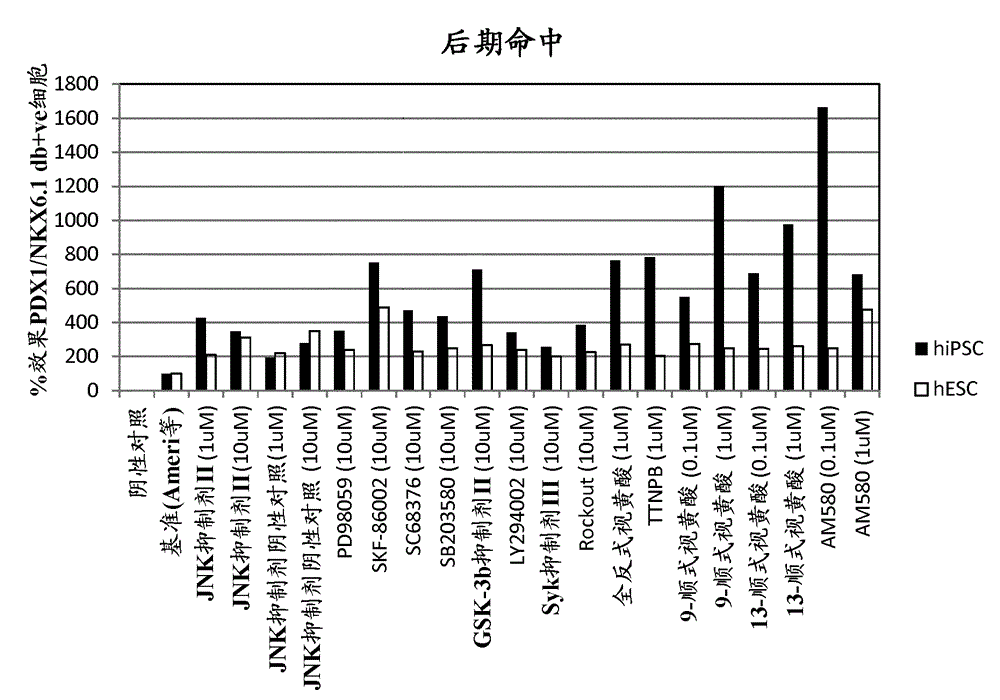
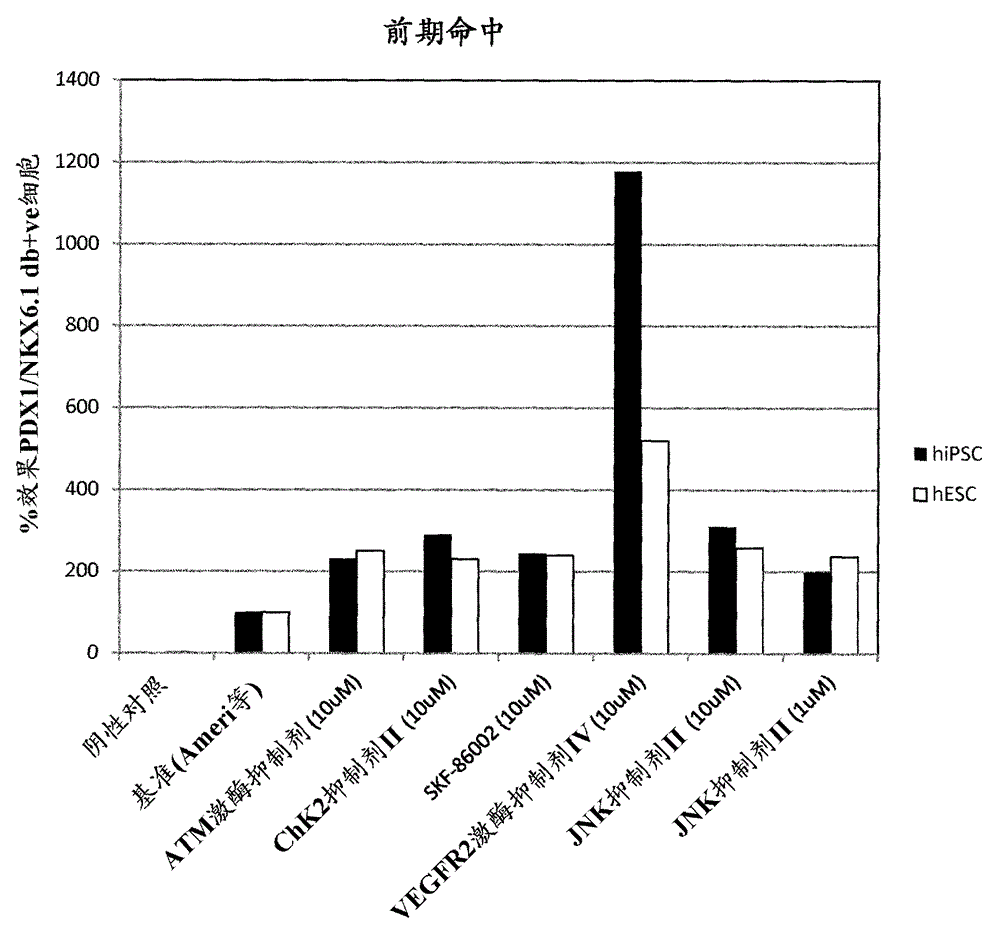
[0175] Example 1 – Screening of small molecules that induce NKX6.1 / PDX1 co-expression
[0176] Small molecule
[0177] Four different libraries were included in this screen: Kinase Inhibitor Library (Calbiochem #539743), Bioactive Lipid Library (Enzo Life Sciences #BML-2800), Nuclear Receptor Ligand Library (Enzo Life Sciences #BML-2802) and phosphatase inhibitor library (Enzo Life Sciences #BML-2834). Compounds within the biologically active library were detected at 1 μM and 0.1 μM. Compounds from other libraries were tested at 10 μM and 1 μM. In a second candidate-based screening approach, small molecules targeting major signaling pathways involved in pancreatic development were included.
[0178] NKX6.1 / PDX1 Screening
[0179] Library compounds in a bFGF-based media formulation (Ameri et al. 2010) (RPMI1640 Gibco #61870, 12% KOSR Gibco #10828, 0.1% PEST Gibco #15140, 64ng / mL bFGF Peprotech #100-18B) for preparation of PE to filter.
[0180] Library PE screening ...
Embodiment 2
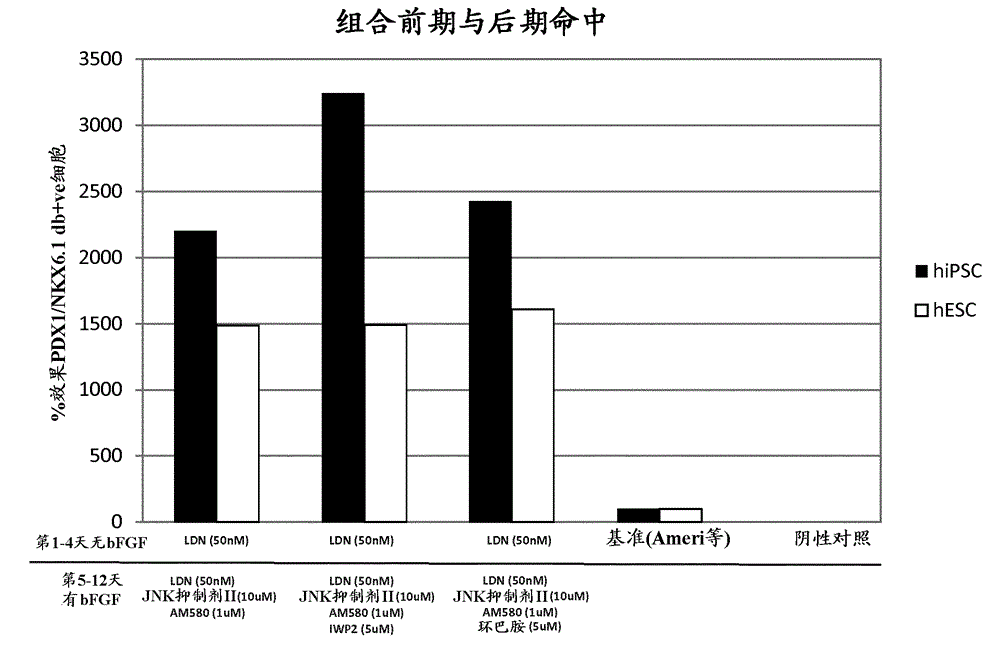
[0189] Example 2 - Combination of small molecule hits that induce NKX6.1 / PDX1 co-expression
[0190] Combining hits from candidate screening methods with hits from library methods
[0191] DE cells were exposed to 50nM LDN-193189 for 4 days, followed by AM580 (AH Diagnostics, BML GF104 0025), JNK inhibitor II (Calbiochem, 420119), 50nM LDN-193189 and 64ng / ml FGF2, or AM580, JNK inhibitor II, 50nM LDN-193189, 64ng / ml FGF2 and IWP2, or AM580, JNK inhibitor II, 50nM LDN-193189, 64ng / ml FGF2 and cyclopamine for 8 days ( Image 6 ). Media changes were performed daily.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com