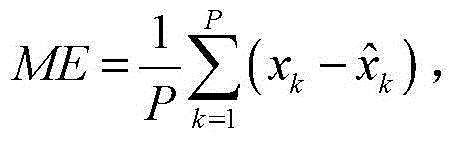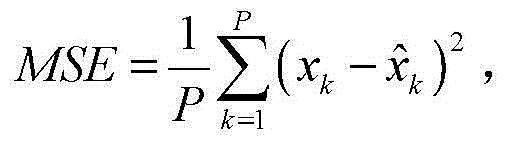Prediction model selection method based on applicability quantification of time series prediction model
A forecasting model, time series technology, applied in forecasting, data processing applications, computing, etc., can solve problems such as single forecasting angle and poor forecasting effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0009] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the prediction model selection method based on the applicability quantification of time series prediction model described in this embodiment, described method is realized based on m prediction models, and it comprises the following steps:
[0010] Step 1: According to the prediction step size P of each prediction model, the actual value x k and predictive model output Obtain the error and prediction efficiency of each prediction model, where the error includes overall error, local error, dimensionless criterion error and multiple test performance error, and the prediction efficiency is the time taken from inputting the time series of the prediction model to the output result of the prediction model. The shorter the time, the higher the efficiency of the prediction model;
[0011] Step 2: According to the forecast demand, among the m forecast models, combine the error and forecast efficiency ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0012] Specific embodiment 2: This embodiment is to further explain the prediction model selection method based on the quantification of the applicability of time series prediction models described in specific embodiment 1. In this embodiment, in step 2, multiple prediction models are paired The process of conducting the difference test of predictive ability:
[0013] The difference test Diebold-Mariano is used to test the difference in predictive ability of the two prediction models, and two results are output, which are the Diebold-Mariano statistics and the assumed probability p-value, respectively.
[0014] Suppose the two prediction models are the first prediction model and the second prediction model, when the Diebold-Mariano statistic is negative, the prediction ability of the first prediction model is stronger than that of the second prediction model; when the Diebold-Mariano statistic is positive, the predictive ability of the second predictive model is stronger than ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0018] Specific embodiment three: This embodiment is to further explain the forecasting model selection method based on quantification of the applicability of time series forecasting models described in specific embodiment one. In this embodiment, the overall error includes signed absolute error, unsigned absolute error, signed relative error and unsigned relative error,
[0019] The signed absolute error consists of the mean error ME,
[0020] The average error ME is used to predict the average degree that the output of the forecasting model is larger or smaller than the true value,
[0021] In step 1, according to the prediction step size P of each prediction model, the actual value x k and predictive model output The process of obtaining the average error ME of each prediction model is:
[0022] According to the formula:
[0023] ME = 1 P Σ k = ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com