Calculation method for remaining shelf life of fruits and vegetables
A calculation method and a technology for shelf life, which are applied in the calculation field of determining the remaining shelf life of fruits and vegetables by hardness index, can solve the problems of economic loss, reduction of the storage period of fruits and vegetables, fluctuation of storage temperature, etc., so as to reduce waste, improve storage and transportation value, and improve economic effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and by taking the calculation of the remaining shelf life of strawberries under the ambient temperature of 19°C as a specific example.
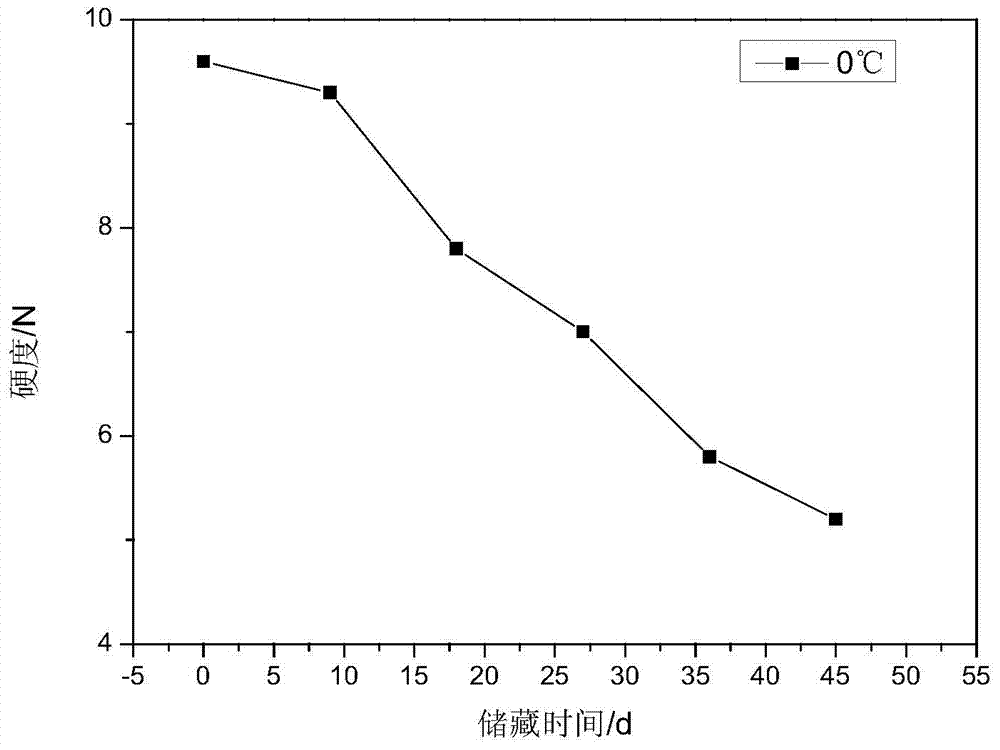
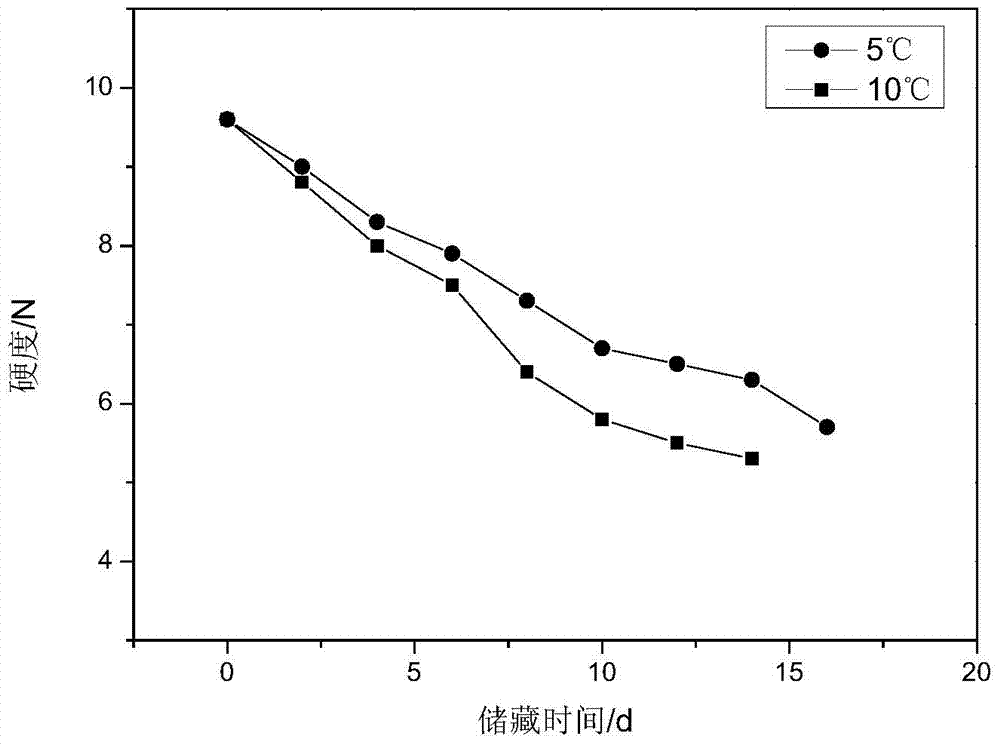
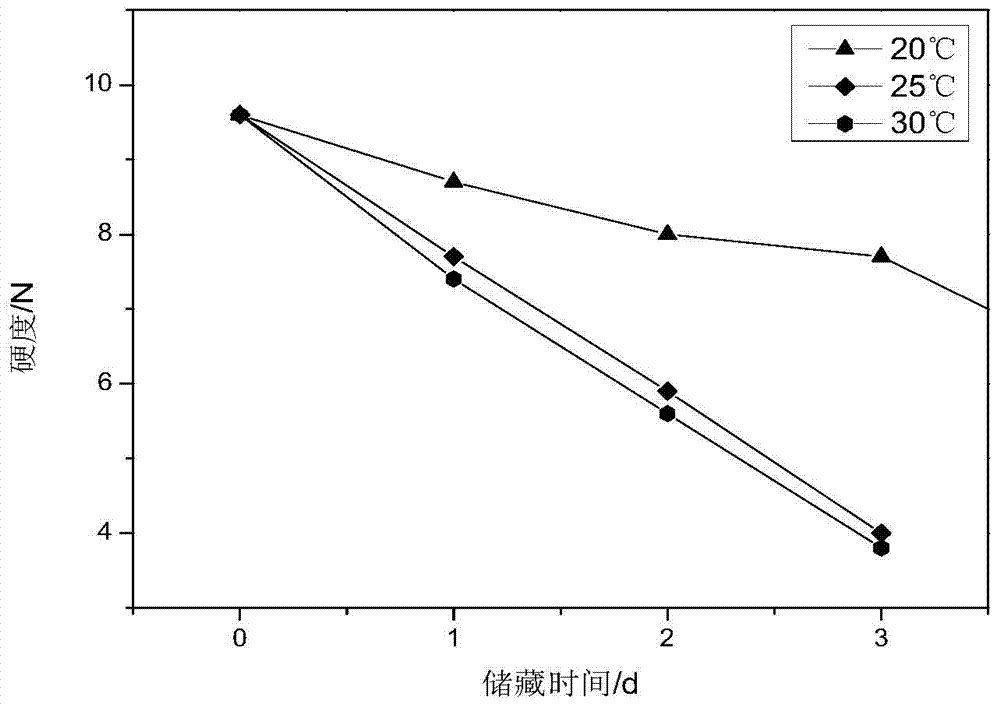
[0019] (1) The initial hardness value Q of strawberries was measured to be 9.6, and the hardness was used as the test index to test the relationship between the hardness of strawberries and the time change at different temperatures of 0°C, 5°C, 10°C, 20°C, 25°C, and 30°C , arrange the data, the result is as follows figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3 shown.
[0020] (2) Establish a kinetic model, using the first-order chemical reaction kinetic equation lnA t =lnA 0 -kt, yes figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3 Linear regression fitting was performed on the relationship between hardness and time at different temperatures in the medium, and six sets of fitting lines were obtained at 0°C, 5°C, 10°C, 20°C, 25°C, and 30°C, as shown below: ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com