Control circuit and method for buck-boost power converter
A technology of power converters and control circuits, which is applied in the direction of output power conversion devices, conversion equipment without intermediate conversion to AC, electrical components, etc., and can solve problems such as large output ripples, short working cycles, and discontinuous working cycles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0210] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with embodiment and accompanying drawing.
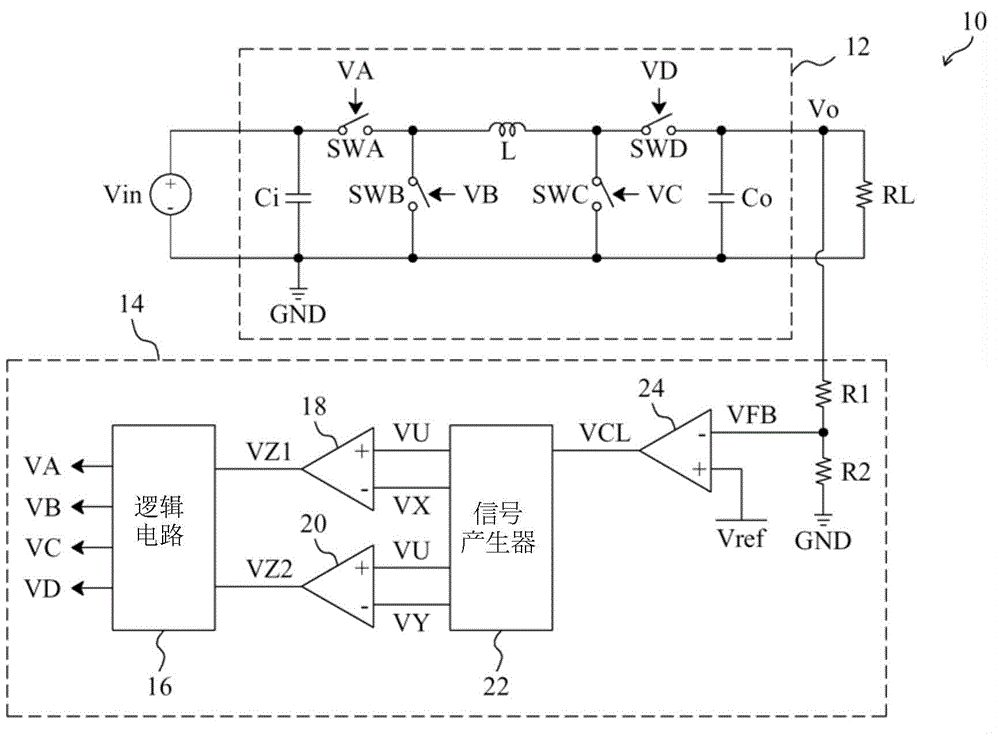
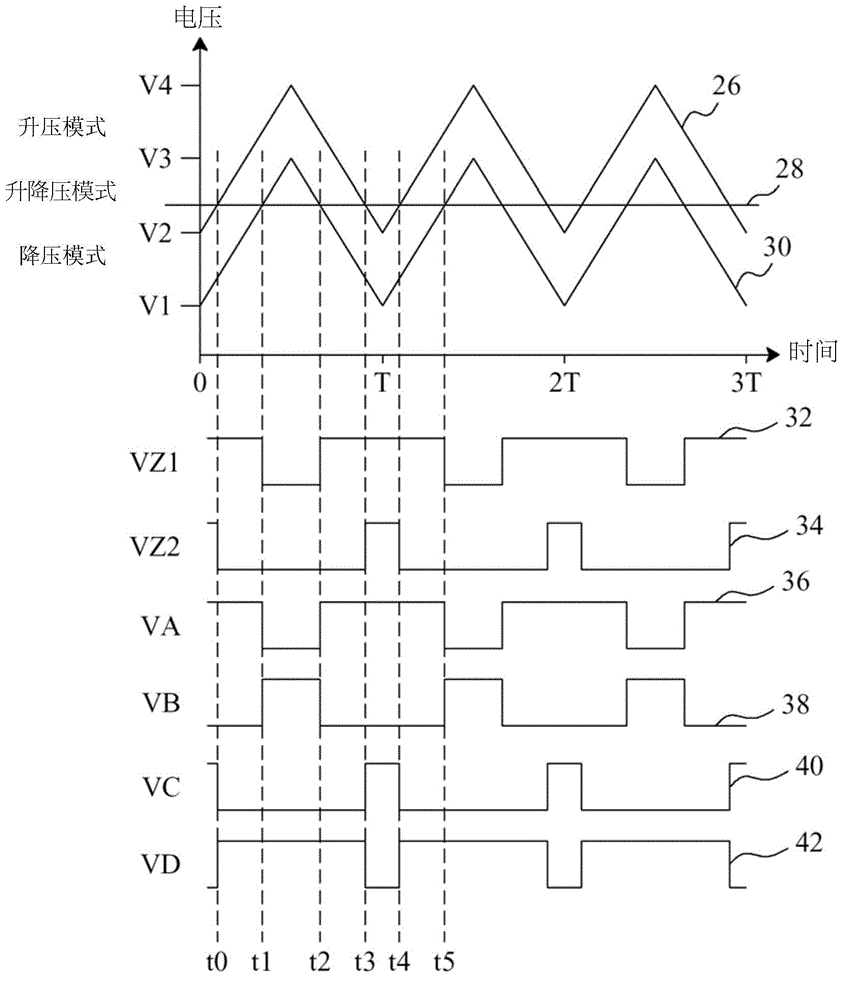
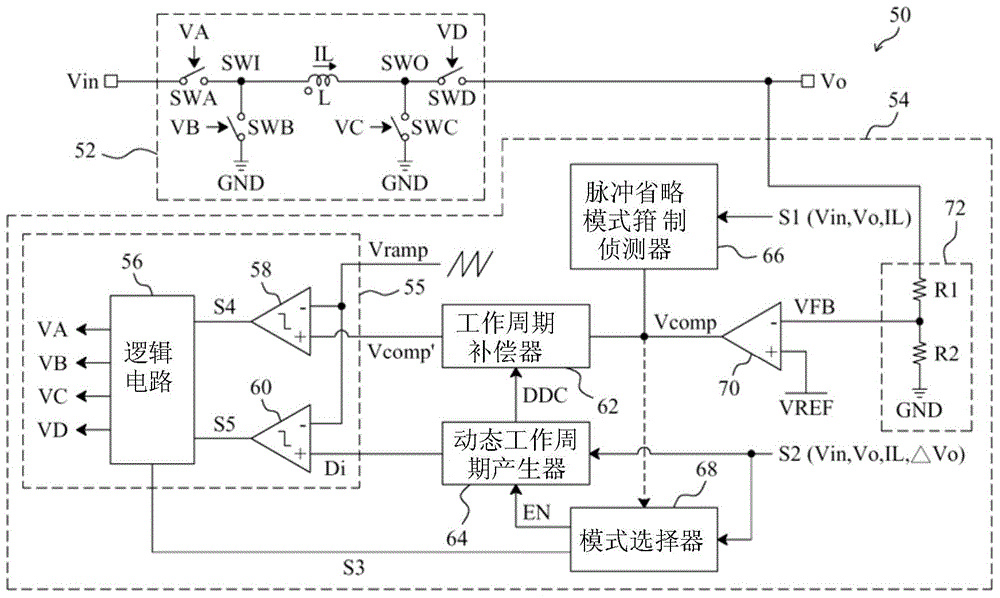
[0211] see now image 3 , image 3 A schematic diagram of an embodiment of the invention is shown. As shown in the figure, in the buck-boost power converter 50, the control circuit 54 provides control signals VA, VB, VC and VD to switch the switches SWA, SWB, and SWC and SWD are used to convert the input voltage Vin to the output voltage Vo. In the control circuit 54, the feedback circuit 72 detects the output voltage Vo to generate a feedback signal VFB, the error amplifier 70 amplifies the difference between the feedback signal VFB and the reference voltage VREF to generate an error signal Vcomp, and the pulse omission mode clamps the detector 66 clamps the level of the error signal Vcomp according to the detection signal S1, wherein the detection signal S1 is related to at least one of the input voltage Vin, the output voltage Vo and the inductor curren...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com