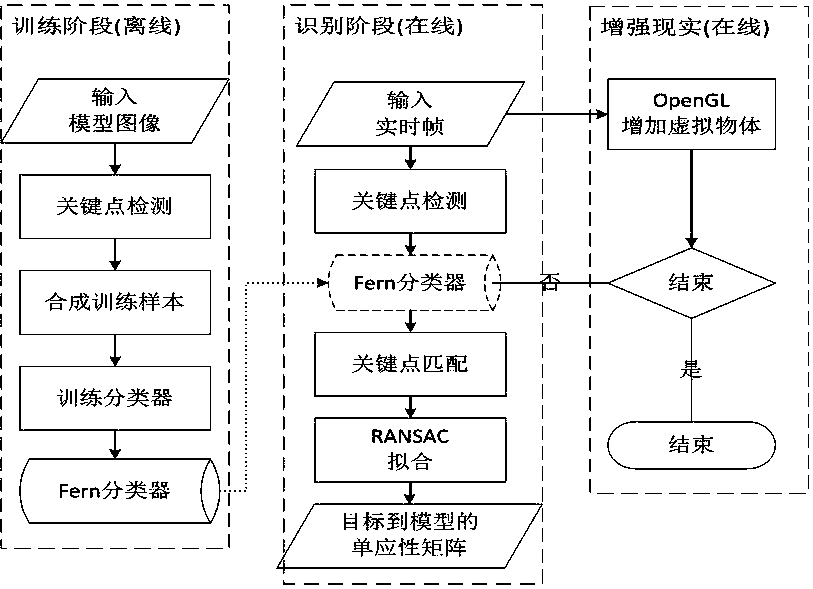
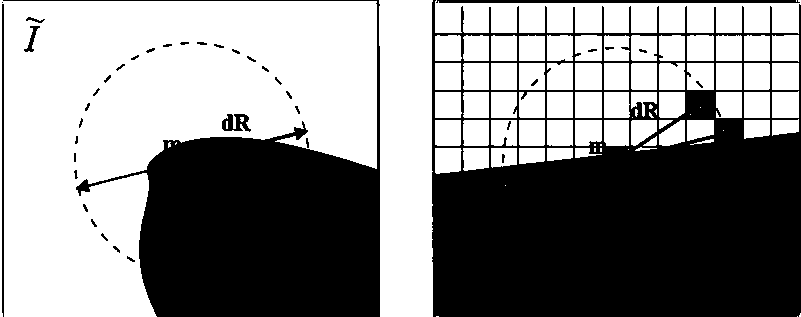
Optimization algorithm of unmarked flat object recognition
A technology of plane objects and optimization algorithms, applied in character and pattern recognition, calculation, computer parts and other directions, can solve the problems of inability to meet real-time requirements, high cost, and inability to reduce the amount of calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0065] Use the test video of the author of the baseline algorithm to do multiple comparison experiments. The test video has a total of 499 frames and a resolution of 640*480. The video has all the wide-baseline matching issues and even motion blur issues.
[0066] In order to study the influence degree of the optimization at different stages proposed by the present invention on the results, a total of 6 groups of comparative experiments were done, among which ① is the key point of the screening model in Section 3.2, ② is the key point of screening the target frame in Section 4.1, and ③ is ARANSAC.6 in Section 4.2 Group comparison experiments are: (1) Baseline method; (2) Baseline method + ①; (3) Baseline method + ③; (4) Baseline method + ① + ③; (5) Baseline method + ② + ③; (6) ) Baseline method + ① + ② + ③.
[0067] Table 1 Performance reference table for various aspects of comparative experiments
[0068] Performance\Comparative Experiment Number
(1)
(2) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com