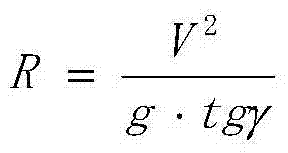Method for simulating flight process of aircraft
A flight process and aircraft technology, applied in the field of air traffic management and general aviation, can solve problems such as the inability to achieve high-level simulation, high information density, and direct flight algorithms that cannot adapt to flight simulators.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
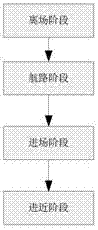
[0080] Based on the above-mentioned basic idea, the present invention takes the following comparatively specific steps to carry out flight simulation according to the different flight characteristics of the aircraft in the four stages of departure stage, route stage, approach stage and approach stage. For these four stages, the specific steps of the method are:
[0081] Step 1. Taking the center point of the aircraft runway as the starting point and taking the first point of the route as the end point, divide the departure phase of the aircraft. The departure phase is the process of the spacecraft climbing while accelerating:
[0082] Obtain the aircraft's departure speed and various passing points during the departure phase;
[0083] At each passing point of the departure phase, obtain the flight information of the aircraft once: speed, acceleration, climb rate, and turning slope; use the selected extrapolation algorithm to perform extrapolation according to the flight inform...
Embodiment 2
[0112] For the scheme recorded in embodiment 1, there are multiple methods for judging the direct flight and turning,
[0113] One is to judge whether a turn is necessary at this stage according to the standard route or the planned route;
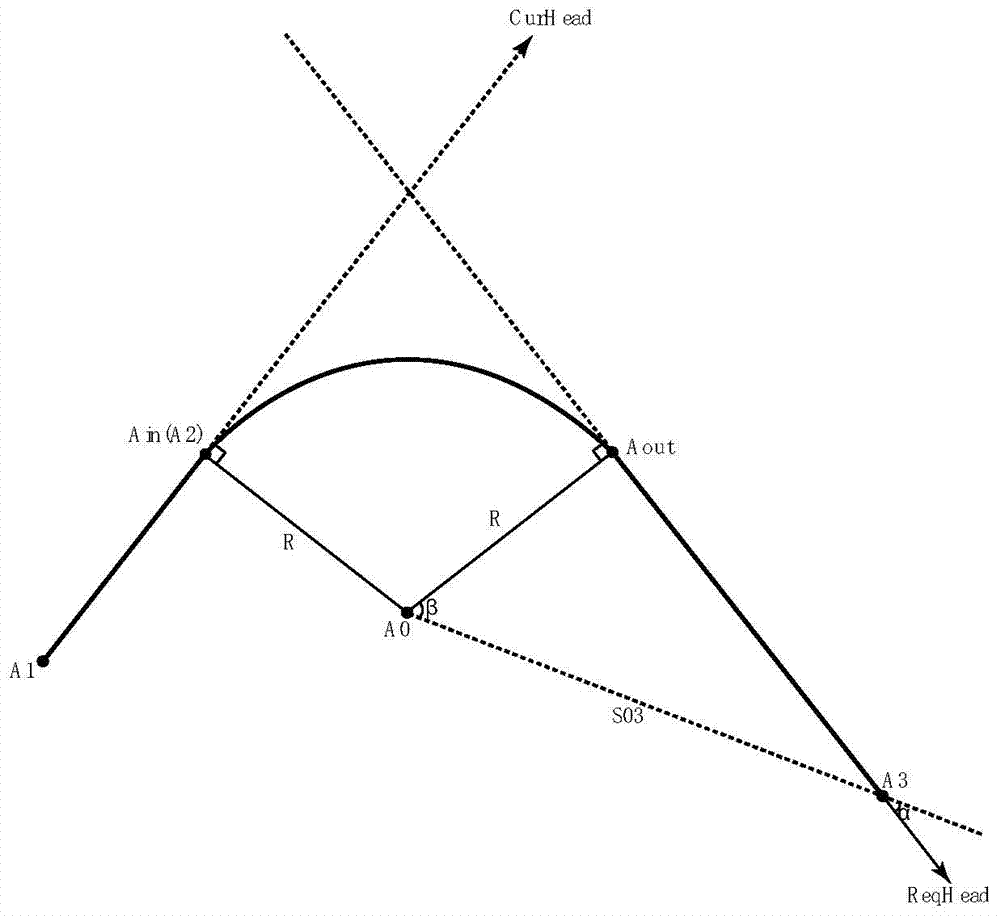
[0114] The second is to assume that the current passing point is A 2 location, such as figure 2 As shown, if the controller gives an instruction to turn or not at this time, it is directly judged whether to turn or not;
[0115] Second, if the controller does not give an instruction to turn or not, then obtain the previous passing point A of the current passing point 1 and the next passing point position A 3 , calculate the straight line |A 1 A 2 |and|A 3 A 2 The angle between |, judge whether to turn or not according to the range of the angle.
Embodiment 3
[0117] The turning extrapolation algorithm used in Embodiment 1 of the present invention is specifically:
[0118] Step 1. Determine the turning start point A in :
[0119] If at the current position A 2 When , the controller does not give a turn position instruction, then let A 2 for A in ;Otherwise determine A with the turning position specified by the turning position instruction in ;
[0120] Step 2: Calculate the turning radius R:
[0121] R = V 2 g · tgγ
[0122] Where g is the acceleration of gravity, V is the airspeed, and γ is the turning slope; the turning slope is a specified value;
[0123] Step 3: Determine the direction of the turn:
[0124] A in The heading at is the current heading curHead, that is, the straight line|A 1 A in The connection of |;
[0125] Calculate curHead and |A in A 3 |The angle θ of the con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com