Anti-adhesion material
An anti-adhesion and covering layer technology, applied in thin material processing, medical science, surgical medicine, etc., can solve the problems of poor operability and achieve the effects of improved adhesion, excellent anti-adhesion performance, and full decomposability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
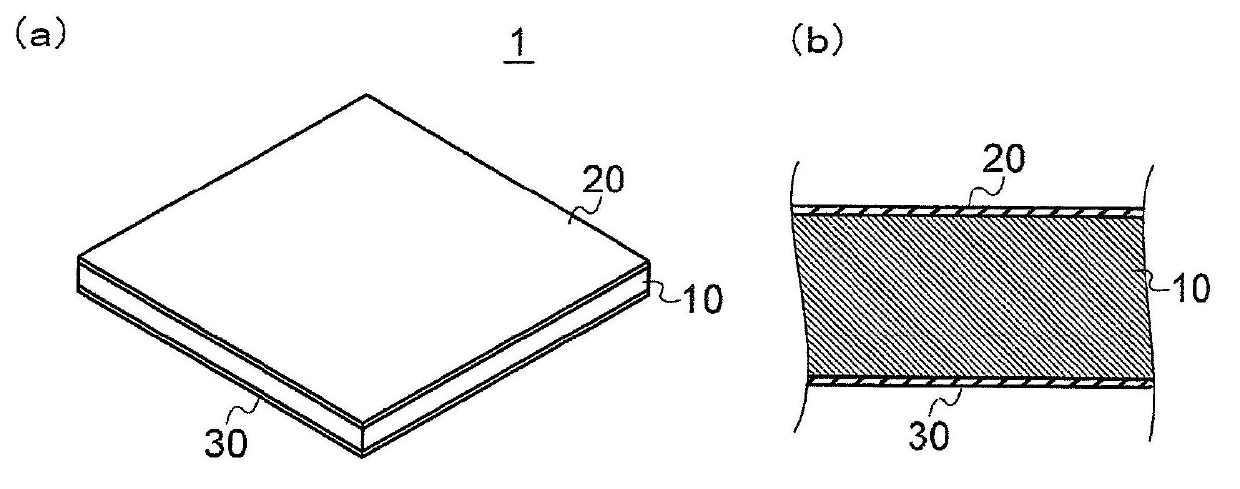
[0058] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram for explaining the anti-adhesion material 1 of the first embodiment, figure 1 (a) is a perspective view of the anti-adhesion material 1, figure 1 (b) Its partial enlarged cross-sectional view. In addition, for easy understanding of the invention, in figure 1 (a) and figure 1 In (b), the layer thickness of the base layer 10 and the layer thicknesses of the first covering layer 20 and the second covering layer 30 relative to the base layer 10 are shown with a certain degree of exaggeration.
[0059] Such as figure 1 As shown, the anti-adhesion material 1 of the first embodiment includes a sheet-shaped base layer 10, a first covering layer 20 disposed on one side of the base layer 10, and a second covering layer 20 disposed on the other side of the base layer 10. Layer 30.
[0060] The base layer 10 is made of a water-soluble polymer. As the water-soluble polymer, polysaccharides, proteins, or synthetic polymers can be preferably u...
no. 2 approach
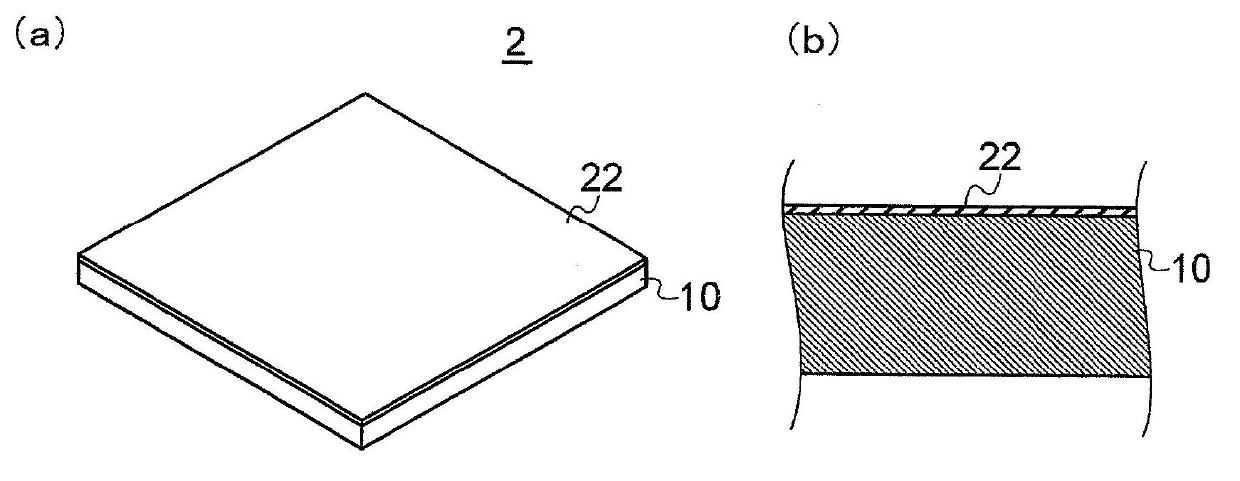
[0083] figure 2 It is a schematic diagram for demonstrating the anti-adhesion material 2 of 2nd Embodiment. figure 2 (a) is a perspective view of the anti-adhesion material 2, figure 2 (b) is a partially enlarged cross-sectional view of the anti-adhesion material 2 . In addition, for easy understanding of the invention, in figure 2 (a) and figure 2 In (b), the layer thickness of the base layer 10 and the layer thickness of the covering layer 22 with respect to the base layer 10 are shown with some degree of exaggeration. In addition, in figure 2 in, with figure 1 The same symbols are used for the same components, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
[0084] The anti-adhesion material 2 of the second embodiment basically has a structure very similar to that of the anti-adhesion material 1 of the first embodiment, but differs from the anti-adhesion material 1 of the first embodiment in that the covering layer is arranged only on one side of the base lay...
no. 3 approach
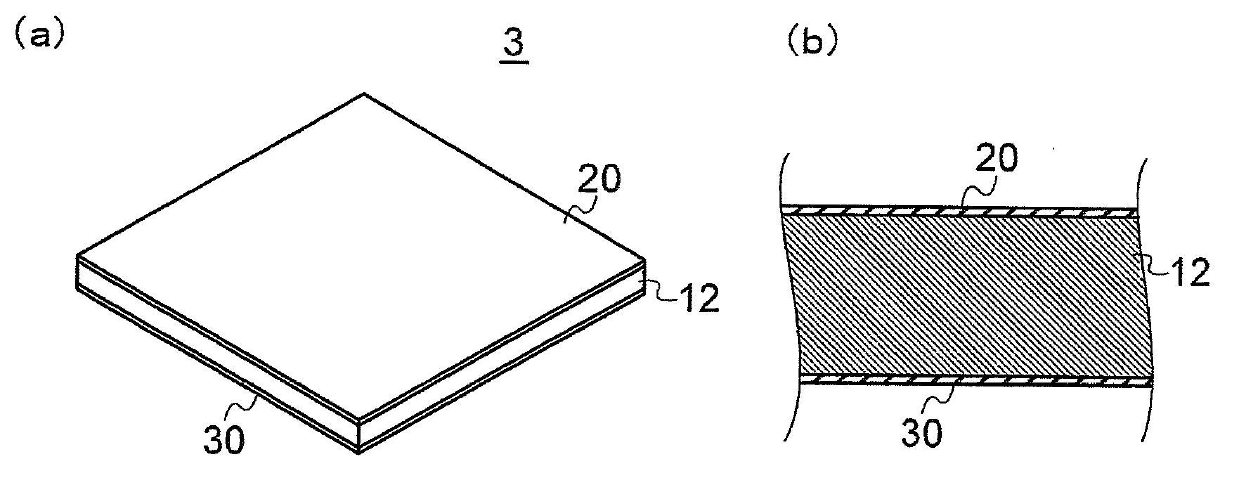
[0093] image 3 It is a schematic diagram for demonstrating the anti-adhesion material 3 of 3rd Embodiment. image 3 (a) is a perspective view of the anti-adhesion material 3, image 3 (b) is a partially enlarged cross-sectional view of the anti-adhesion material 3 . In addition, for easy understanding of the invention, in image 3 (a) and image 3 In (b), the layer thickness of the base layer 12 and the layer thicknesses of the first covering layer 20 and the second covering layer 30 relative to the base layer 12 are shown with a certain degree of exaggeration. In addition, in image 3 in, with figure 1 The same symbols are used for the same components, and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
[0094] The anti-adhesion material 3 of the third embodiment basically has a structure very similar to that of the anti-adhesion material 1 of the first embodiment, but differs from the anti-adhesion material 1 of the first embodiment in that an antibacterial agent is ad...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com