Blade grid for improving pneumatic stability of gas compressor
A technology of stability and compressor, applied in the direction of machines/engines, parts of pumping devices for elastic fluids, mechanical equipment, etc., to achieve the effects of reduced flow loss, improved aerodynamic stability, and enhanced effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Embodiment two
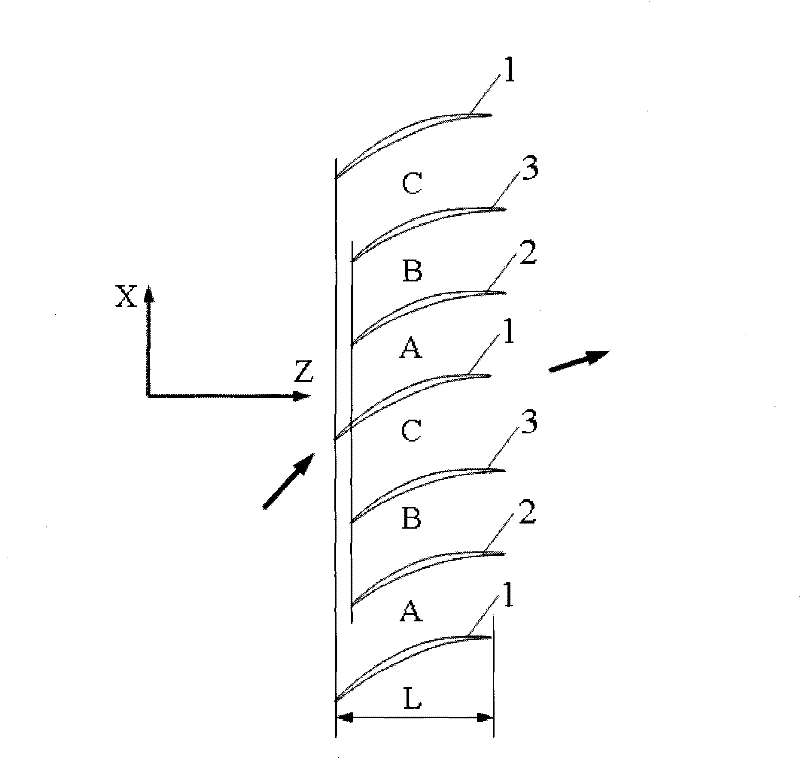
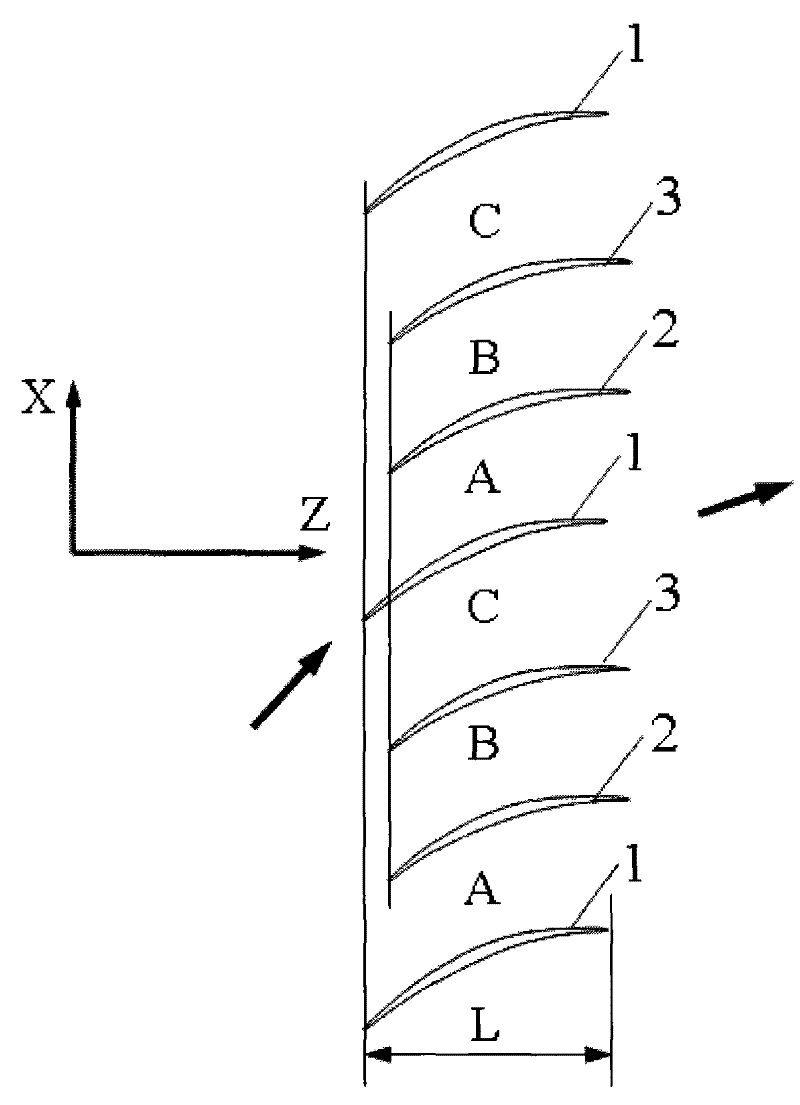
[0023] In this embodiment, the front edges of blades in the same row along the tangential direction of the cascade, that is, the X direction, are arranged differently in front and rear of the cascade axial direction, that is, in the Z direction. Wherein, the leading edge of blade 2 moves back a certain distance relative to the leading edge of blade 1 along the axial direction of the cascade, and the moving distance is 7% of the axial chord length L of blade 1; blade 3 adopts the same blade shape as blade 2, and The distance of the leading edge moving back along the axial direction of the cascade is the same as that of the blade 2 , that is, the moving distance is 7% of the axial chord length L of the blade 1 .
Embodiment 2
[0025] In this embodiment, the front edges of blades in the same row along the tangential direction of the cascade, that is, the X direction, are arranged differently in front and rear of the cascade axial direction, that is, in the Z direction. Wherein, the leading edge of blade 2 moves back for a distance relative to the leading edge of blade 1 along the axial direction of the cascade, and the moving distance is 15% of the axial chord length L of blade 1; blade 3 adopts the same blade shape as blade 2, and The distance of the leading edge moving back along the axial direction of the cascade is the same as that of the blade 2 , that is, the moving distance is 15% of the axial chord length L of the blade 1 .
Embodiment 3
[0027] In this embodiment, the front edges of blades in the same row along the tangential direction of the cascade, that is, the X direction, are arranged differently in front and rear of the cascade axial direction, that is, in the Z direction. Wherein, the leading edge of blade 2 moves back a certain distance relative to the leading edge of blade 1 along the axial direction of the cascade, and the moving distance is 12% of the axial chord length L of blade 1; blade 3 adopts the same blade shape as blade 2, and The backward moving distance of the leading edge along the axis of the cascade is the same as that of the blade 2 , that is, the moving distance is 12% of the axial chord length L of the blade 1 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com