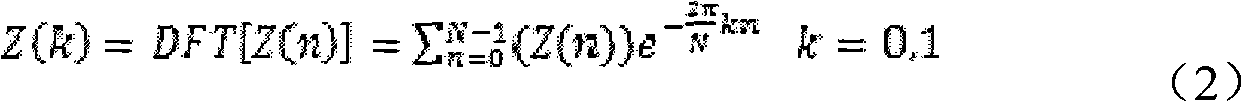Magnetizing inrush current discrimination method based on equivalent excitation impedance frequency domain character of transformer
A technology of excitation impedance and excitation inrush current, which is applied in the direction of instruments, measuring electrical variables, and measuring devices, can solve problems such as difficult to accurately measure transformer parameters or system parameters, misoperation of transformer differential protection, and unsatisfactory identification effects, etc., to achieve Simple and reliable discrimination, good recognition performance, reliable locking effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
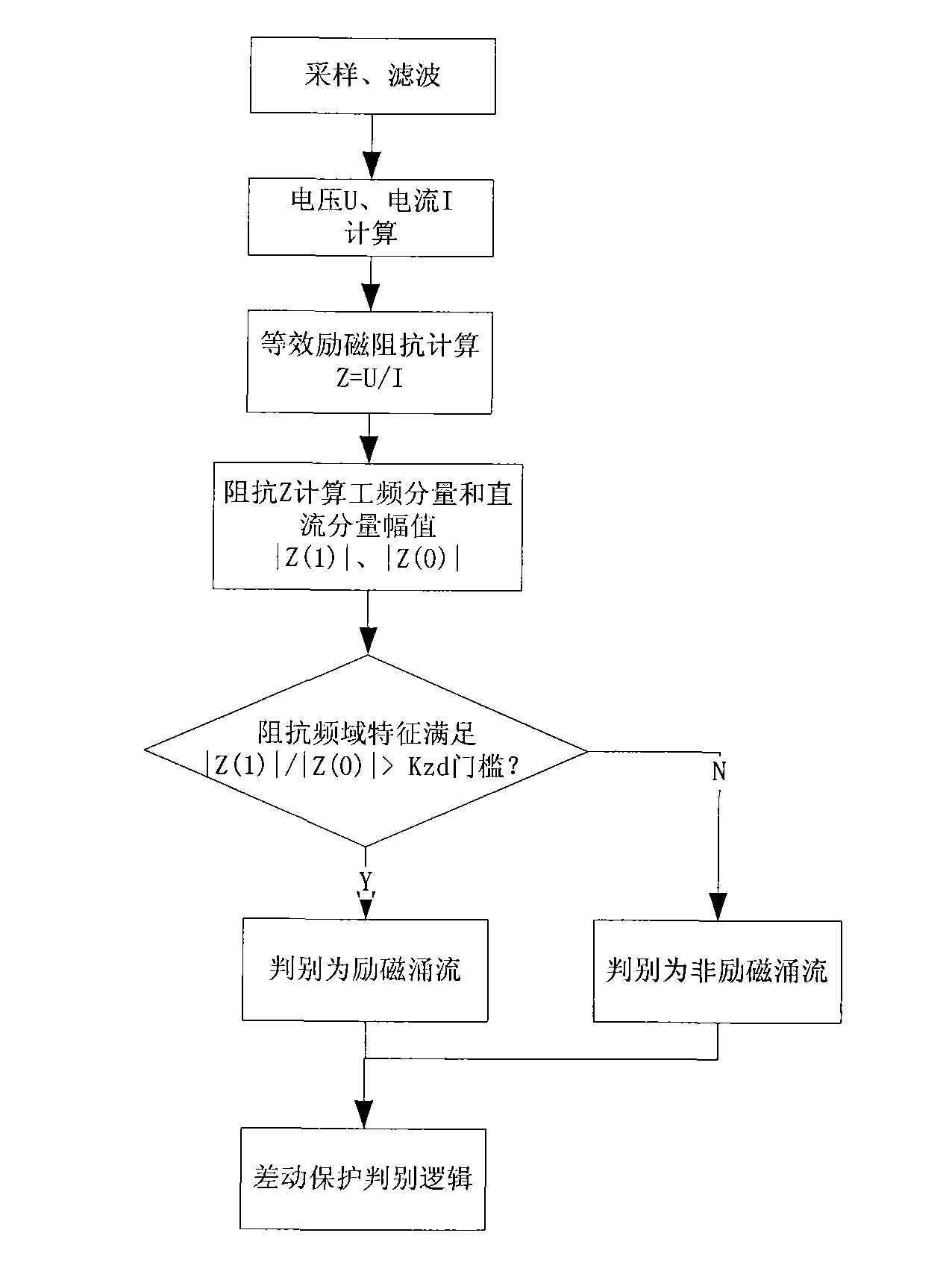
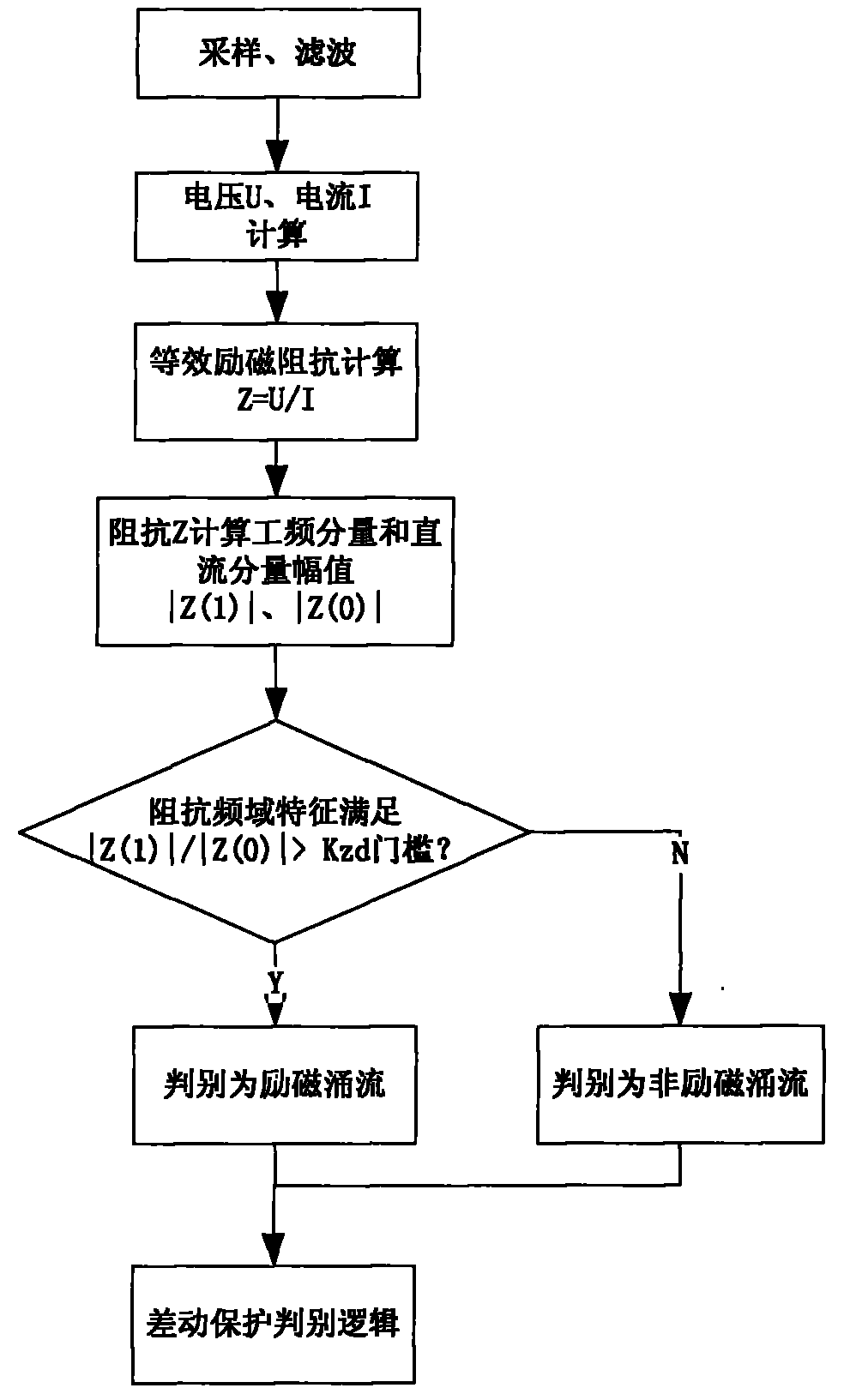
[0020] figure 1 This is the flow chart of the present invention. The transformer judges whether there is an inrush current in the transformer through the frequency domain characteristics of the equivalent excitation impedance, specifically:
[0021] First, the protection device performs real-time sampling and filtering calculations on the current and voltage of the transformer. The voltage and current are collected at the installation location of the device, and the amplitude of the collected and filtered voltage and current is calculated to obtain the transformer equivalent excitation impedance:
[0022] Z=U / I (1)
[0023] In formula (1), U and I are the calculated amplitudes of the voltage and current at a certain moment obtained by the filtering algorithm, Z changes with time, expressed by Z(t), after 1 power frequency cycle N point sampling discretization Denoted as Z(n);
[0024] Perform frequency domain analysis on Z(n), and extract the amplitude of its DC component and power f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com