Actuator for optical scanning
A technology for actuators and optical scanning, applied in optics, instruments, optical components, etc., can solve problems such as poor flexibility, inability to adjust the movable range, and inability to adjust the movable range of movable parts, etc., to achieve the effect of flexible adjustment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
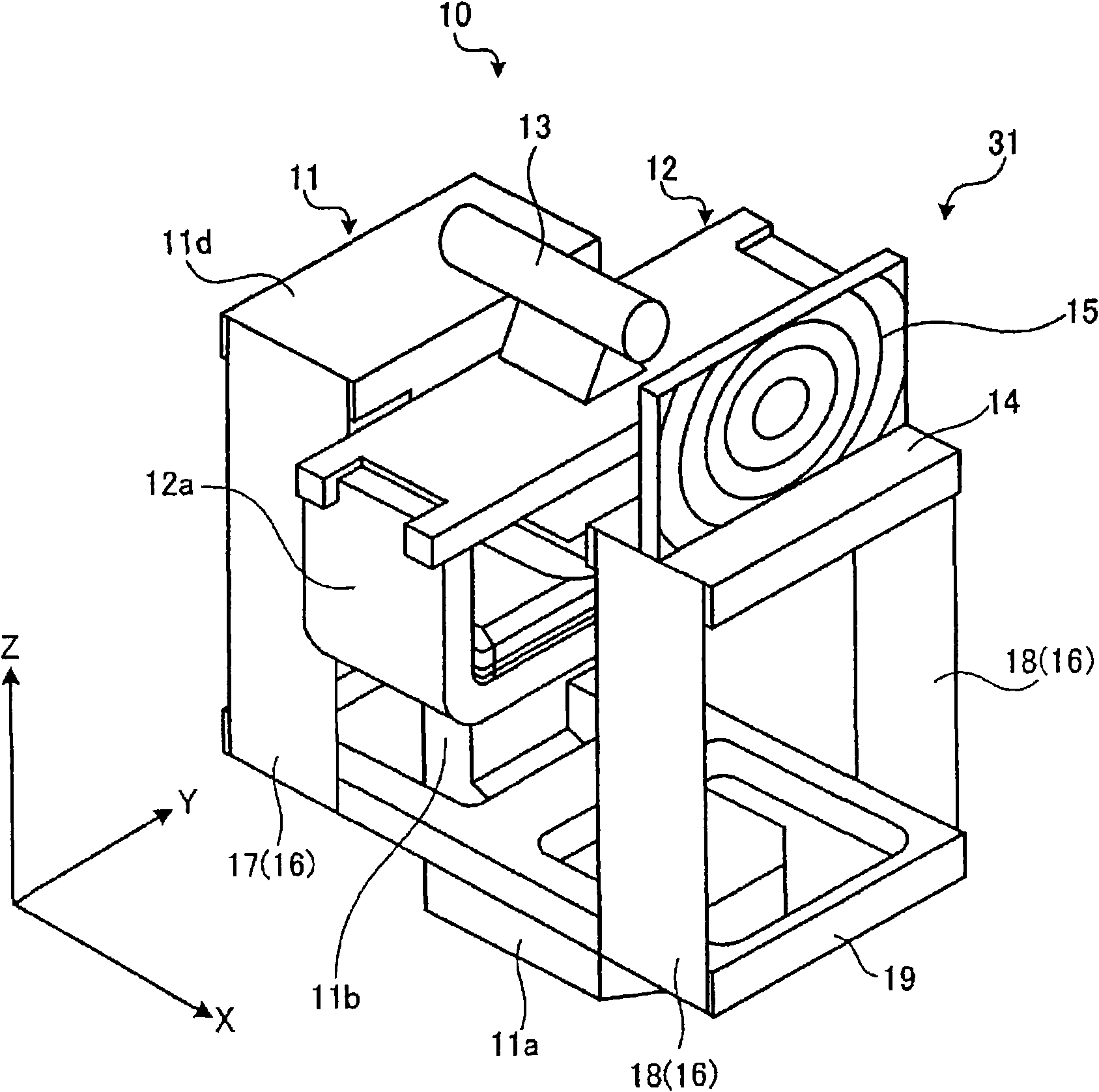
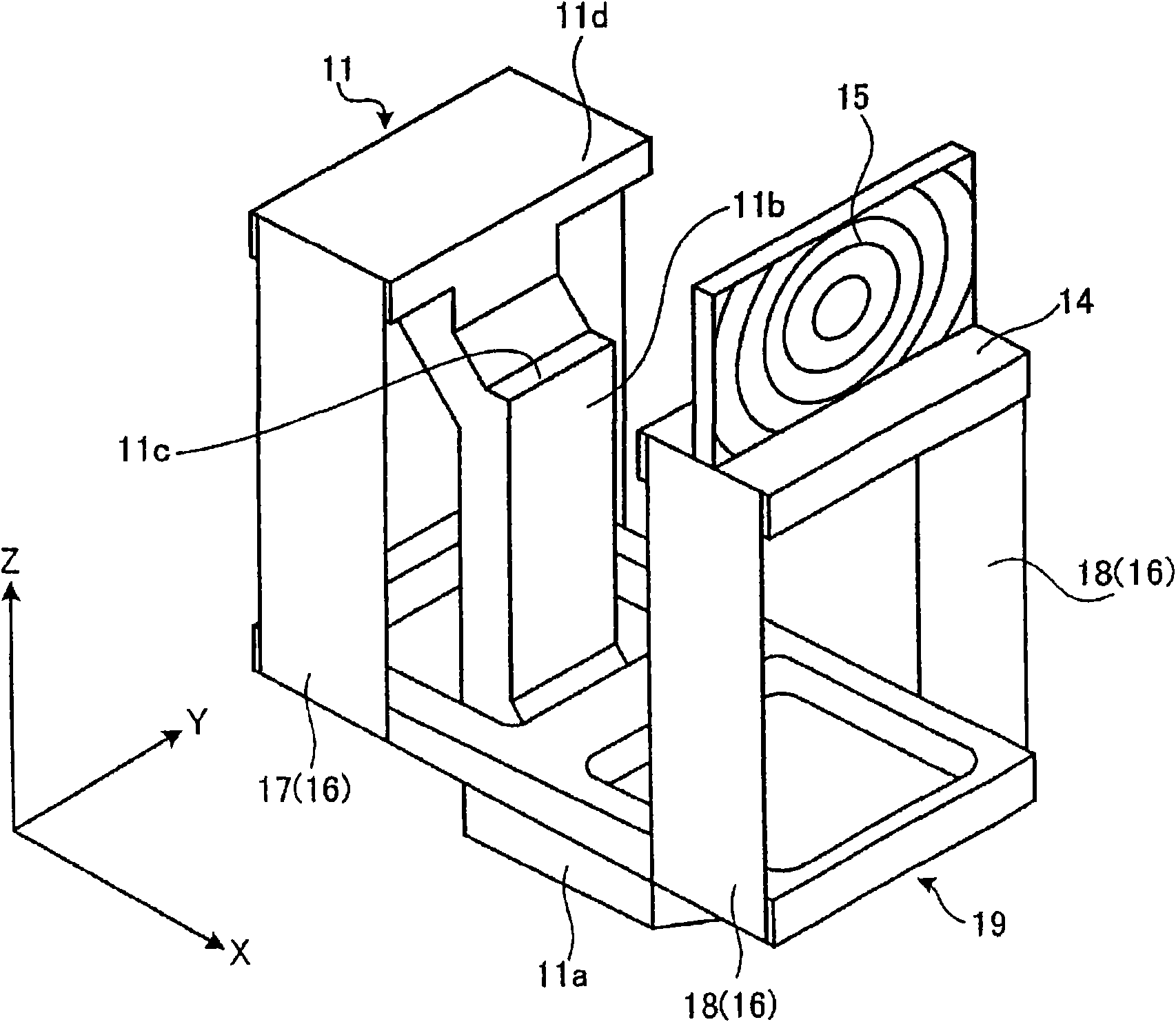
[0050] Next, Embodiment 1 according to the optical scanning actuator of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. figure 1 It is a perspective view showing the optical scanning actuator according to the first embodiment. figure 2It is a perspective view of the optical scanning actuator with the drive unit removed.
[0051] Such as figure 1 As shown, the optical scanning actuator 10 includes a main body 11 , a movable member 14 , a connecting member 16 , and a deformation relaxing member 19 .
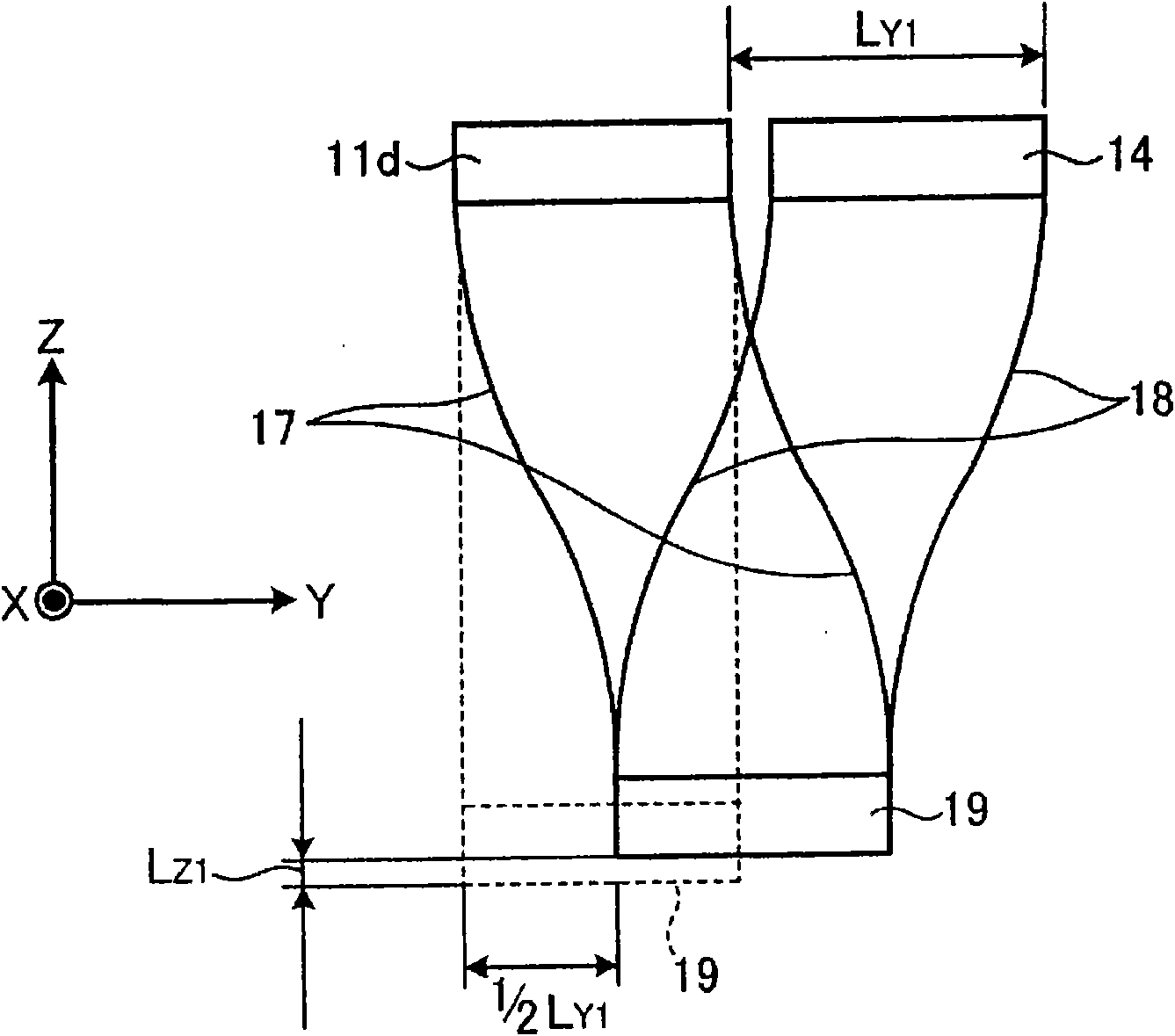
[0052] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the main body 11 is erected on the base 11a with a pillar 11b, and a workbench 11d is formed on the upper part of the pillar 11b through a stepped setting part 11c, and a fixing member of the driving part 12 is set on the setting part 11c. The driving unit 12 is provided with a scanning light source 13 on the upper surface, and like the driving unit 6 of the conventional optical scanning actua...
Embodiment approach 2
[0073] Next, Embodiment 2 of the optical scanning actuator of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. In contrast to the optical scanning actuator according to Embodiment 1, which has fixed side leaf springs and movable side leaf springs arranged front and rear, the optical scanning actuator according to Embodiment 2 has fixed side leaf springs and movable side leaf springs arranged side to side. Figure 11 It is a perspective view showing the actuator for optical scanning according to the second embodiment. Figure 12 It is a schematic diagram schematically showing the positional relationship of the fixed member, the movable member, the deformation relieving member, the fixed-side leaf spring, and the movable-side leaf spring when the movable member swings to the right.
[0074] Such as Figure 11 As shown, the optical scanning actuator 30 includes a main body 31 , a movable member 34 , a connecting member 36 , and a deformation rela...
Embodiment approach 3
[0090] Next, Embodiment 3 of the optical scanning actuator of the present invention will be described in detail with reference to the drawings. In the optical scanning actuator of Embodiment 1, the fixed-side leaf spring and the movable-side leaf spring are arranged in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis of light emitted from the scanning light source, whereas the optical scanning actuator of Embodiment 3 The device arranges the fixed-side leaf spring and the movable-side leaf spring in the direction of the optical axis of light emitted from the scanning light source. Figure 14 It is a perspective view showing an optical scanning actuator according to Embodiment 3. FIG. Here, components of the optical scanning actuator according to the third embodiment and the optical scanning actuator according to the first embodiment are assigned the same reference numerals.
[0091] The actuator 40 for optical scanning is provided with a driving part 12 on the main body 11, and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com