Cipher key replacing method, system and device
A key and key group technology, applied in electrical components, wireless communications, security devices, etc., can solve problems such as confusion in integrity verification, user data errors, and failure of UP data to be decrypted correctly.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
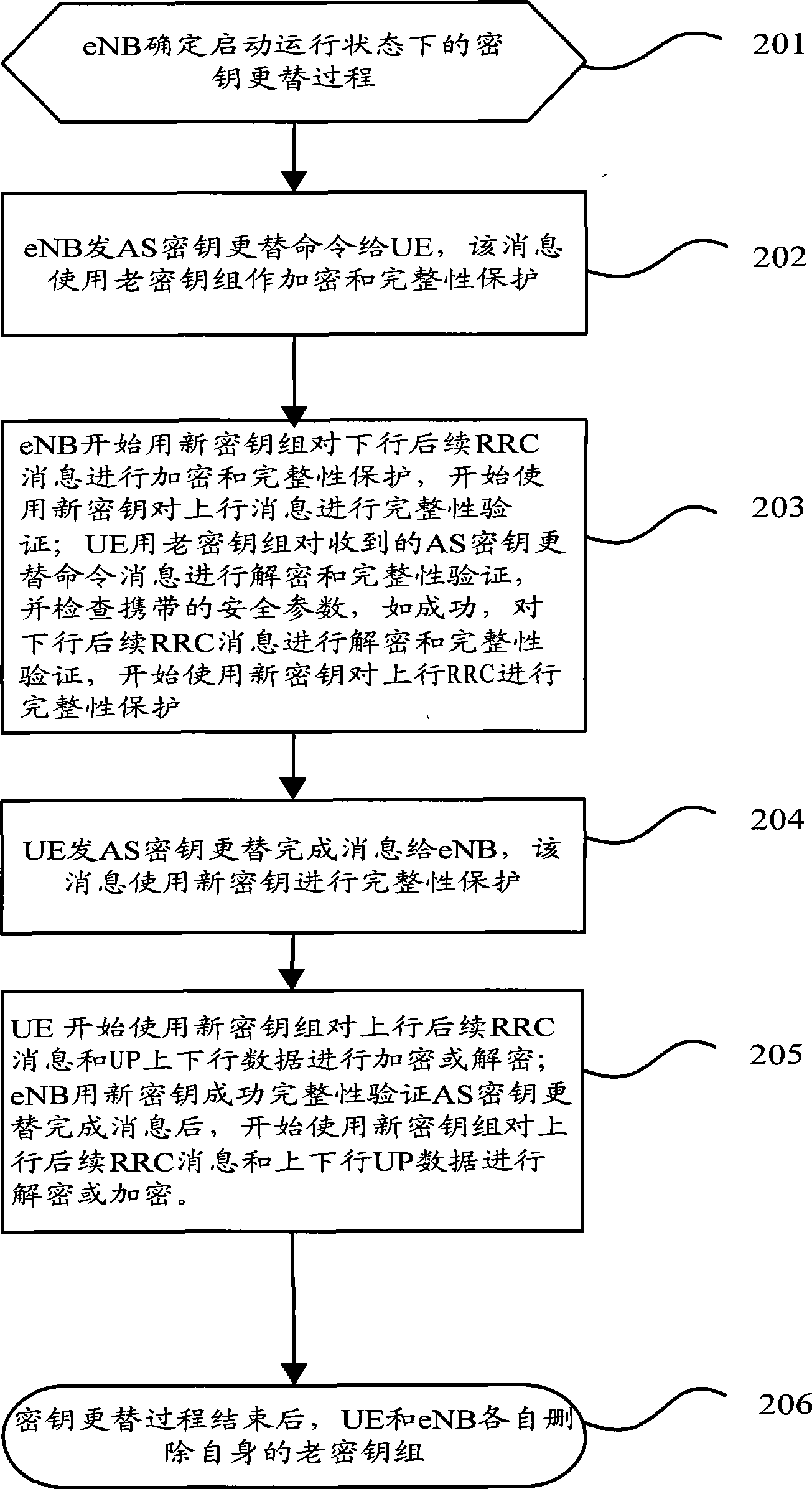
[0062]In this embodiment, the AS key replacement command message uses the old key group for integrity protection and encryption, the AS key replacement completion message uses the new key for integrity protection or further encryption, and the uplink and downlink UP data and uplink subsequent RRC messages After the AS key replacement complete message, the new key group is used for encryption and decryption. After the AS key replacement command message, the downlink subsequent RRC message starts to use the new key group for encryption and integrity protection. Downlink RRC messages and downlink UP data The time to enable the new key for encryption is different. The encryption of uplink UP data and subsequent uplink RRC messages is after the AS key replacement command is completed.
[0063] figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the implementation flow of Embodiment 1 of the key replacement method in the running state of the present invention, including the following steps:
[...
Embodiment 2
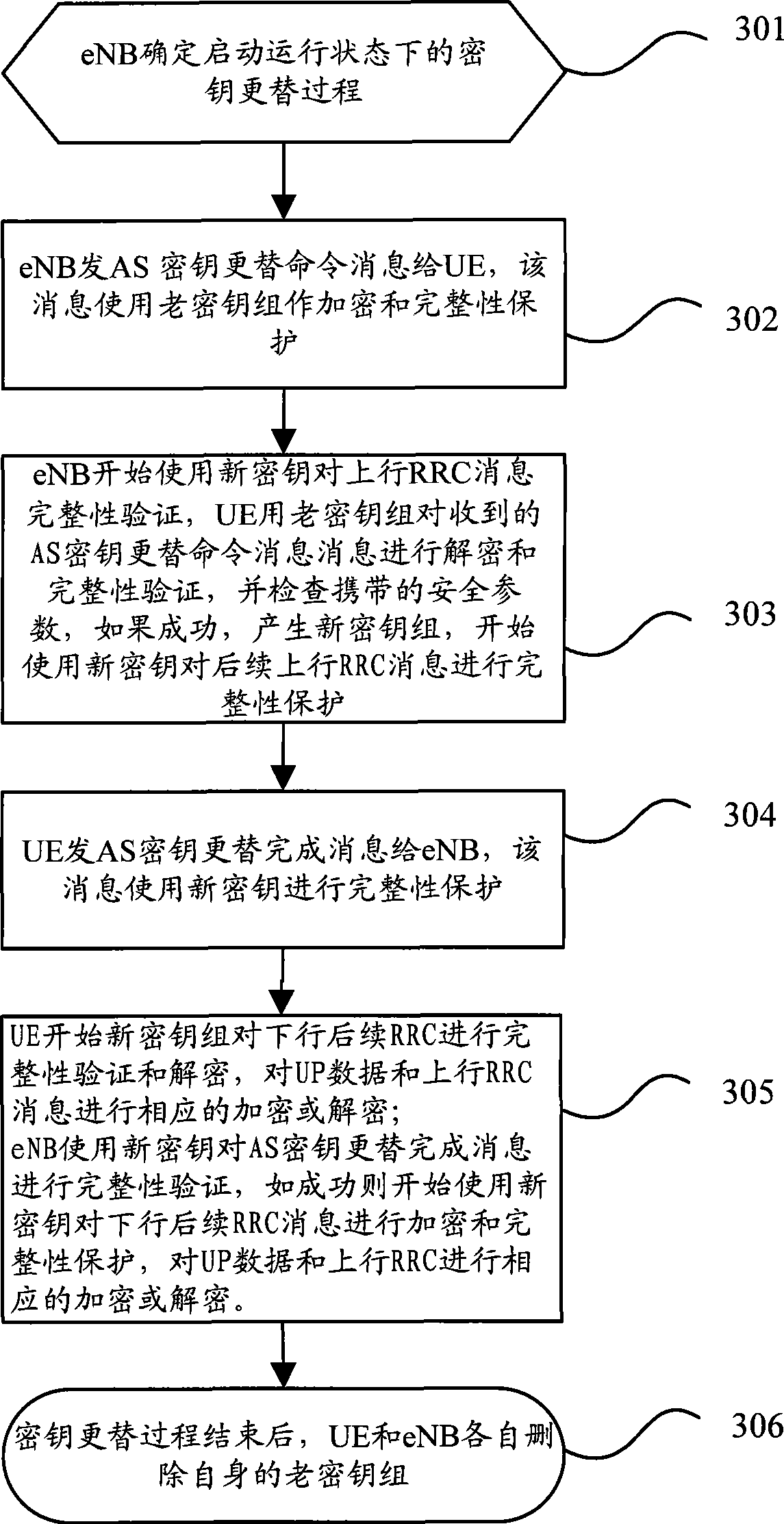
[0081] In this embodiment, the AS key replacement command message uses the integrity protection and encryption of the old key group, the AS key replacement completion message uses the new key for integrity protection, and the uplink and downlink UP data and subsequent uplink and downlink RRC Encryption with the new key set begins after the Key Replacement Complete message.
[0082] image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the implementation flow of Embodiment 2 of the key replacement method in the running state of the present invention, including the following steps:
[0083] Step 301: the eNB determines to start the key replacement process in the running state;
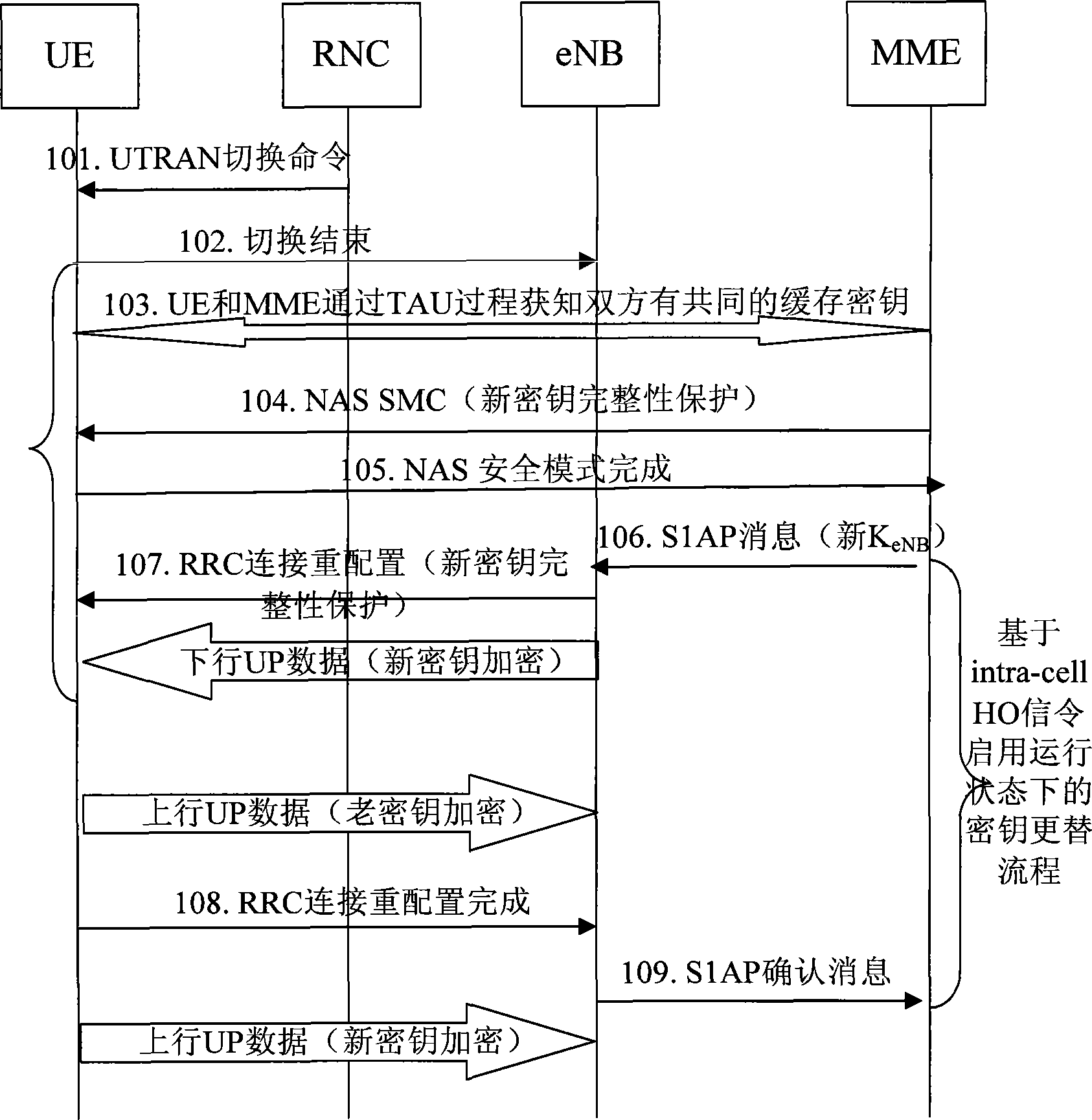
[0084] Generally, there are three situations that can trigger the key replacement mechanism: ①The PDCP counter reaches the threshold value; ②MME generates a new AKA and changes the root key; ③When the UE switches from other networks to the LTE / SAE network, the MME finds that it and the UE have a common cache key. Amo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com