The Potential of 5G UC in Revolutionizing the Art Industry
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
5G UC in Art: Background and Objectives
The advent of 5G Ultra-Capacity (UC) technology marks a significant milestone in the evolution of wireless communication, promising to revolutionize various industries, including the art world. This technological leap builds upon the foundations laid by previous generations of mobile networks, offering unprecedented speeds, reduced latency, and enhanced connectivity.
The art industry has long been at the forefront of adopting new technologies to push creative boundaries and enhance audience engagement. From the early days of digital art to the recent explosion of NFTs, technology has consistently played a pivotal role in shaping artistic expression and distribution. The introduction of 5G UC presents a new frontier for artists, curators, and art institutions to explore and exploit.
The primary objective of integrating 5G UC into the art industry is to transform the creation, presentation, and consumption of art. This technology aims to enable more immersive and interactive experiences, breaking down geographical barriers and democratizing access to art. By leveraging the high-speed, low-latency capabilities of 5G UC, artists can create and share complex, data-intensive works in real-time, opening up new possibilities for collaborative and participatory art.
Furthermore, 5G UC has the potential to revolutionize the museum and gallery experience. Virtual and augmented reality applications, powered by 5G, can offer visitors personalized, information-rich tours and allow remote audiences to explore exhibitions from anywhere in the world. This technology also promises to enhance art conservation and research efforts by facilitating the rapid transfer of high-resolution images and 3D scans of artworks.
In the realm of art commerce, 5G UC could significantly impact the way art is bought and sold. Online auctions and virtual art fairs could become more sophisticated and engaging, with real-time bidding and immersive previews of artworks. The technology could also enable new forms of digital art ownership and provenance tracking, building upon the current blockchain and NFT trends.
As we explore the potential of 5G UC in the art industry, it is crucial to consider both the opportunities and challenges it presents. While the technology offers exciting possibilities for creativity and accessibility, it also raises questions about digital divide, data privacy, and the preservation of traditional art forms. The goal is to harness the power of 5G UC to enhance and expand the art world, rather than replace existing practices entirely.
The art industry has long been at the forefront of adopting new technologies to push creative boundaries and enhance audience engagement. From the early days of digital art to the recent explosion of NFTs, technology has consistently played a pivotal role in shaping artistic expression and distribution. The introduction of 5G UC presents a new frontier for artists, curators, and art institutions to explore and exploit.
The primary objective of integrating 5G UC into the art industry is to transform the creation, presentation, and consumption of art. This technology aims to enable more immersive and interactive experiences, breaking down geographical barriers and democratizing access to art. By leveraging the high-speed, low-latency capabilities of 5G UC, artists can create and share complex, data-intensive works in real-time, opening up new possibilities for collaborative and participatory art.
Furthermore, 5G UC has the potential to revolutionize the museum and gallery experience. Virtual and augmented reality applications, powered by 5G, can offer visitors personalized, information-rich tours and allow remote audiences to explore exhibitions from anywhere in the world. This technology also promises to enhance art conservation and research efforts by facilitating the rapid transfer of high-resolution images and 3D scans of artworks.
In the realm of art commerce, 5G UC could significantly impact the way art is bought and sold. Online auctions and virtual art fairs could become more sophisticated and engaging, with real-time bidding and immersive previews of artworks. The technology could also enable new forms of digital art ownership and provenance tracking, building upon the current blockchain and NFT trends.
As we explore the potential of 5G UC in the art industry, it is crucial to consider both the opportunities and challenges it presents. While the technology offers exciting possibilities for creativity and accessibility, it also raises questions about digital divide, data privacy, and the preservation of traditional art forms. The goal is to harness the power of 5G UC to enhance and expand the art world, rather than replace existing practices entirely.
Market Demand Analysis for 5G UC in Art
The integration of 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) technology into the art industry has sparked significant market interest and demand. This advanced connectivity solution offers unprecedented opportunities for artists, galleries, museums, and art enthusiasts to engage with and experience art in revolutionary ways.
The global art market, valued at over $65 billion in 2021, is poised for substantial growth with the adoption of 5G UC technology. Market research indicates that art institutions and collectors are increasingly seeking immersive, high-quality digital experiences, driving demand for 5G-enabled solutions. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated this trend, with virtual exhibitions and online art sales becoming more prevalent.
One of the primary drivers of market demand is the potential for ultra-high-definition streaming and virtual reality (VR) experiences in art galleries and museums. 5G UC's low latency and high bandwidth capabilities enable real-time, interactive tours of art collections, allowing visitors to explore artworks in unprecedented detail from anywhere in the world. This has led to a surge in demand for 5G-enabled devices and applications specifically designed for the art sector.
The art auction market is another area experiencing increased demand for 5G UC technology. Online auctions have grown significantly in recent years, and 5G's capabilities can enhance the bidding experience through seamless live streaming and real-time interaction. This has prompted auction houses to invest in 5G infrastructure to improve their digital offerings and reach a broader audience.
Artists themselves are driving market demand for 5G UC by exploring new forms of digital art creation and distribution. The technology's high-speed data transfer capabilities enable artists to collaborate remotely in real-time, opening up new possibilities for cross-border artistic partnerships. Additionally, the growing popularity of digital art and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) has created a need for robust networks capable of handling large file transfers and complex blockchain transactions.
Educational institutions specializing in art are also contributing to the market demand for 5G UC. Art schools and universities are incorporating advanced technologies into their curricula, requiring high-speed, low-latency networks to support virtual classrooms, remote art critiques, and collaborative projects. This educational shift is creating a new generation of tech-savvy artists and art professionals who expect 5G capabilities in their future workplaces.
The market analysis reveals a growing ecosystem of startups and established tech companies developing 5G-enabled solutions specifically for the art industry. These range from augmented reality (AR) applications for enhancing gallery experiences to AI-powered art authentication tools that require 5G's advanced connectivity. This burgeoning market segment is attracting significant investment, further driving the demand for 5G UC infrastructure in art-related venues and institutions.
The global art market, valued at over $65 billion in 2021, is poised for substantial growth with the adoption of 5G UC technology. Market research indicates that art institutions and collectors are increasingly seeking immersive, high-quality digital experiences, driving demand for 5G-enabled solutions. The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated this trend, with virtual exhibitions and online art sales becoming more prevalent.
One of the primary drivers of market demand is the potential for ultra-high-definition streaming and virtual reality (VR) experiences in art galleries and museums. 5G UC's low latency and high bandwidth capabilities enable real-time, interactive tours of art collections, allowing visitors to explore artworks in unprecedented detail from anywhere in the world. This has led to a surge in demand for 5G-enabled devices and applications specifically designed for the art sector.
The art auction market is another area experiencing increased demand for 5G UC technology. Online auctions have grown significantly in recent years, and 5G's capabilities can enhance the bidding experience through seamless live streaming and real-time interaction. This has prompted auction houses to invest in 5G infrastructure to improve their digital offerings and reach a broader audience.
Artists themselves are driving market demand for 5G UC by exploring new forms of digital art creation and distribution. The technology's high-speed data transfer capabilities enable artists to collaborate remotely in real-time, opening up new possibilities for cross-border artistic partnerships. Additionally, the growing popularity of digital art and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) has created a need for robust networks capable of handling large file transfers and complex blockchain transactions.
Educational institutions specializing in art are also contributing to the market demand for 5G UC. Art schools and universities are incorporating advanced technologies into their curricula, requiring high-speed, low-latency networks to support virtual classrooms, remote art critiques, and collaborative projects. This educational shift is creating a new generation of tech-savvy artists and art professionals who expect 5G capabilities in their future workplaces.
The market analysis reveals a growing ecosystem of startups and established tech companies developing 5G-enabled solutions specifically for the art industry. These range from augmented reality (AR) applications for enhancing gallery experiences to AI-powered art authentication tools that require 5G's advanced connectivity. This burgeoning market segment is attracting significant investment, further driving the demand for 5G UC infrastructure in art-related venues and institutions.
5G UC Technology: Current State and Challenges
The current state of 5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) technology in the art industry is characterized by both significant advancements and notable challenges. 5G UC, with its ultra-high bandwidth and low latency, has the potential to revolutionize various aspects of art creation, distribution, and consumption. However, its implementation in the art sector is still in its early stages, with several hurdles to overcome.
One of the primary advantages of 5G UC in the art industry is its ability to support high-quality, real-time streaming of immersive art experiences. This technology enables artists to create and share virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) artworks with unprecedented detail and interactivity. Museums and galleries can leverage 5G UC to offer virtual tours and interactive exhibits, allowing art enthusiasts to engage with collections remotely.
Despite these promising applications, the widespread adoption of 5G UC in the art industry faces several challenges. Infrastructure development remains a significant obstacle, as the deployment of 5G UC networks requires substantial investment in hardware and spectrum allocation. Many art institutions, especially smaller galleries and museums, may find it difficult to justify the costs associated with upgrading their facilities to support 5G UC technology.
Another challenge lies in the development of user-friendly interfaces and applications that can fully utilize the capabilities of 5G UC. While the technology itself is powerful, creating intuitive and engaging art experiences that leverage its potential requires specialized skills and resources. This gap between technological capability and practical implementation presents a hurdle for many artists and institutions.
Data security and privacy concerns also pose challenges in the adoption of 5G UC in the art industry. As more art experiences become digital and interconnected, protecting sensitive information and intellectual property becomes increasingly important. Ensuring robust security measures without compromising the seamless experience promised by 5G UC is a delicate balance that needs to be addressed.
The integration of 5G UC with existing art practices and workflows presents another challenge. Many artists and institutions have established methods of creating and displaying art, and transitioning to new technologies can be disruptive. Developing strategies to seamlessly incorporate 5G UC into existing artistic processes while preserving traditional techniques is crucial for widespread acceptance in the art community.
Lastly, the digital divide remains a significant concern. While 5G UC has the potential to democratize access to art, it may also exacerbate existing inequalities if not implemented thoughtfully. Ensuring equitable access to 5G UC-enabled art experiences across different socioeconomic groups and geographical locations is a challenge that needs to be addressed to fully realize the technology's potential in revolutionizing the art industry.
One of the primary advantages of 5G UC in the art industry is its ability to support high-quality, real-time streaming of immersive art experiences. This technology enables artists to create and share virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) artworks with unprecedented detail and interactivity. Museums and galleries can leverage 5G UC to offer virtual tours and interactive exhibits, allowing art enthusiasts to engage with collections remotely.
Despite these promising applications, the widespread adoption of 5G UC in the art industry faces several challenges. Infrastructure development remains a significant obstacle, as the deployment of 5G UC networks requires substantial investment in hardware and spectrum allocation. Many art institutions, especially smaller galleries and museums, may find it difficult to justify the costs associated with upgrading their facilities to support 5G UC technology.
Another challenge lies in the development of user-friendly interfaces and applications that can fully utilize the capabilities of 5G UC. While the technology itself is powerful, creating intuitive and engaging art experiences that leverage its potential requires specialized skills and resources. This gap between technological capability and practical implementation presents a hurdle for many artists and institutions.
Data security and privacy concerns also pose challenges in the adoption of 5G UC in the art industry. As more art experiences become digital and interconnected, protecting sensitive information and intellectual property becomes increasingly important. Ensuring robust security measures without compromising the seamless experience promised by 5G UC is a delicate balance that needs to be addressed.
The integration of 5G UC with existing art practices and workflows presents another challenge. Many artists and institutions have established methods of creating and displaying art, and transitioning to new technologies can be disruptive. Developing strategies to seamlessly incorporate 5G UC into existing artistic processes while preserving traditional techniques is crucial for widespread acceptance in the art community.
Lastly, the digital divide remains a significant concern. While 5G UC has the potential to democratize access to art, it may also exacerbate existing inequalities if not implemented thoughtfully. Ensuring equitable access to 5G UC-enabled art experiences across different socioeconomic groups and geographical locations is a challenge that needs to be addressed to fully realize the technology's potential in revolutionizing the art industry.
Current 5G UC Solutions for Art Industry
01 5G Ultra-Capacity Network Architecture
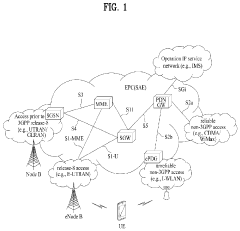
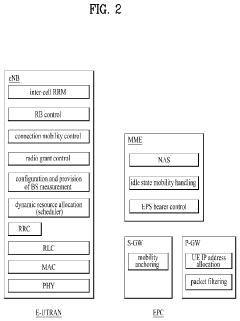
5G UC refers to an advanced network architecture that provides enhanced capacity and performance in 5G networks. It utilizes a combination of mid-band and high-band spectrum to deliver faster speeds, lower latency, and increased network capacity compared to standard 5G implementations.- 5G Ultra-Capacity network architecture: 5G UC refers to an advanced network architecture that provides enhanced capacity and performance in 5G networks. It utilizes a combination of mid-band and high-band spectrum to deliver faster speeds, lower latency, and increased network capacity compared to standard 5G deployments.
- Spectrum management for 5G UC: Efficient spectrum management is crucial for 5G UC networks. This involves techniques for dynamic spectrum allocation, carrier aggregation, and advanced beamforming to maximize the use of available frequency bands and improve overall network performance.
- 5G UC device capabilities and compatibility: Devices supporting 5G UC require specific hardware and software capabilities to fully utilize the enhanced network features. This includes advanced antenna designs, improved signal processing, and compatibility with multiple frequency bands used in UC deployments.
- Network optimization for 5G UC: Optimizing 5G UC networks involves advanced techniques such as AI-driven network management, self-organizing networks (SON), and intelligent traffic steering. These approaches help maximize network efficiency, reduce interference, and improve overall user experience in high-capacity scenarios.
- Integration of 5G UC with existing infrastructure: Seamless integration of 5G UC with existing 4G LTE and early 5G networks is essential for widespread adoption. This involves developing interoperability solutions, hybrid network architectures, and efficient handover mechanisms between different network technologies.
02 Spectrum Utilization in 5G UC
5G Ultra-Capacity networks leverage a wide range of spectrum bands, including mid-band (2.5 GHz to 6 GHz) and millimeter-wave frequencies (24 GHz and above). This multi-band approach allows for improved coverage, capacity, and data throughput in urban and high-density areas.Expand Specific Solutions03 Advanced Antenna Technologies for 5G UC
5G UC implementations often incorporate advanced antenna technologies such as Massive MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) and beamforming. These technologies enable more efficient use of spectrum, improved signal quality, and increased network capacity to support a higher number of connected devices.Expand Specific Solutions04 Network Slicing and Virtualization in 5G UC
5G Ultra-Capacity networks utilize network slicing and virtualization techniques to create multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure. This allows for optimized resource allocation and tailored services for different use cases, such as enhanced mobile broadband, massive IoT, and ultra-reliable low-latency communications.Expand Specific Solutions05 Edge Computing Integration with 5G UC
5G Ultra-Capacity networks often integrate edge computing capabilities to bring processing power closer to end-users and devices. This integration reduces latency, improves application performance, and enables new use cases in areas such as augmented reality, autonomous vehicles, and industrial IoT.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in 5G UC and Art Tech
The 5G UC technology in the art industry is in its early development stage, with significant potential for growth. The market size is expanding as more artists and institutions explore innovative applications. While the technology is not yet fully mature, several key players are driving advancements. Companies like Samsung Electronics, Huawei Technologies, and Nokia are leading in 5G infrastructure development, which is crucial for enabling UC applications in art. LG Electronics and IBM are focusing on integrating 5G UC into consumer devices and cloud services, respectively, potentially revolutionizing art creation and consumption. As the technology evolves, we can expect increased collaboration between tech giants and art institutions to unlock new possibilities in digital art experiences and interactive exhibitions.
Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
Technical Solution: Ericsson's 5G UC solution for the art industry focuses on creating a seamless ecosystem for artists, curators, and art enthusiasts. Their platform leverages network slicing to allocate dedicated resources for different art applications, ensuring optimal performance. Ericsson's approach includes a cloud-native core network that supports dynamic scaling of resources based on demand. They've developed specific use cases such as haptic feedback-enabled virtual sculpting and AI-assisted art restoration using high-resolution imaging. Ericsson's 5G UC technology achieves an impressive uplink capacity of up to 100 Mbps[5], enabling real-time 3D scanning and uploading of artworks. Their solution also incorporates advanced security features to protect valuable digital art assets and intellectual property.
Strengths: Strong focus on specific art industry use cases, scalable cloud-native architecture. Weaknesses: May require significant investment in network infrastructure for full implementation.
Nokia Solutions & Networks Oy
Technical Solution: Nokia's 5G UC solution for the art industry emphasizes creating immersive and interactive experiences. Their technology enables "smart museums" with location-based services and personalized content delivery. Nokia's approach includes the use of small cells and Massive MIMO to ensure consistent high-bandwidth coverage in complex indoor environments like galleries. They've developed a platform that supports real-time holographic projections of artworks, allowing for virtual exhibitions with ultra-low latency. Nokia's 5G UC technology achieves a connection density of up to 1 million devices per square kilometer[7], enabling IoT-based art installations and interactive exhibits at scale. Their solution also incorporates edge computing capabilities to process and render complex 3D art models locally, reducing strain on the core network.
Strengths: Expertise in indoor coverage solutions, high connection density for IoT art installations. Weaknesses: May face challenges in markets where competitors have stronger 5G presence.
Core Innovations in 5G UC for Art
Method and device for reader to transmit signal in wireless communication system
PatentActiveUS20210326542A1
Innovation
- A method where the transmission timing of signals from RFID readers is determined using an offset value based on the unique ID of each reader, allowing them to transmit signals at different times to avoid collisions, with the offset value being determined by the reader's location, ID, or GNSS information, ensuring precise positioning.
Method for transmitting and receiving signals related to QOS prediction in a wireless communication system and apparatus therefor
PatentActiveUS20200045559A1
Innovation
- A method involving a server that transmits a QoS prediction request to a Network Data Analytics Function (NWDAF), which includes specific requirements such as packet delay budget, packet error rate, and guaranteed bit rate, and receives notifications about QoS changes based on geographical and temporal information, enabling proactive management of QoS.
Regulatory Framework for 5G UC in Art
The regulatory framework for 5G UC in the art industry is a complex and evolving landscape that requires careful consideration. As 5G Ultra-Capacity (UC) technology continues to revolutionize various sectors, including the art world, it is crucial to establish a comprehensive regulatory structure that addresses the unique challenges and opportunities presented by this advanced connectivity.
One of the primary concerns in developing a regulatory framework for 5G UC in art is ensuring the protection of intellectual property rights. With the increased capacity for high-quality streaming and real-time collaboration, there is a need for robust copyright laws that safeguard artists' creations in the digital realm. This includes addressing issues such as unauthorized reproduction, distribution, and modification of digital artworks facilitated by 5G UC technology.
Data privacy and security regulations are also paramount in the context of 5G UC applications in art. As artists and institutions leverage the technology for immersive experiences and interactive installations, there is a need for clear guidelines on the collection, storage, and use of user data. Regulatory bodies must work to establish standards that protect individuals' privacy while allowing for innovative artistic expressions.
The deployment of 5G UC infrastructure in cultural spaces and art institutions raises questions about spectrum allocation and management. Regulatory frameworks should address the fair distribution of 5G UC frequencies, ensuring that art organizations have access to the necessary bandwidth for their projects. This may involve collaboration between telecommunications authorities and cultural policymakers to create dedicated spectrum allocations for artistic and cultural purposes.
Another critical aspect of the regulatory framework is the establishment of technical standards for 5G UC-enabled art installations and experiences. These standards should cover aspects such as interoperability, quality of service, and accessibility to ensure that 5G UC technology can be seamlessly integrated into diverse artistic contexts. Regulatory bodies may need to work closely with industry stakeholders and artists to develop guidelines that balance innovation with reliability and user experience.
As 5G UC technology enables new forms of artistic expression and audience engagement, there is a need for updated regulations regarding content moderation and curation. This includes addressing issues such as age-appropriate content, cultural sensitivity, and the potential for misinformation in immersive art experiences. Regulatory frameworks should provide clear guidelines for content creators and platform operators while preserving artistic freedom and expression.
The global nature of 5G UC technology necessitates international cooperation in developing regulatory frameworks for its application in art. Cross-border collaborations and agreements will be essential to address issues such as data transfer, content licensing, and the protection of artists' rights across different jurisdictions. Regulatory bodies should work towards harmonizing standards and creating mechanisms for international dispute resolution in the context of 5G UC-enabled art projects.
One of the primary concerns in developing a regulatory framework for 5G UC in art is ensuring the protection of intellectual property rights. With the increased capacity for high-quality streaming and real-time collaboration, there is a need for robust copyright laws that safeguard artists' creations in the digital realm. This includes addressing issues such as unauthorized reproduction, distribution, and modification of digital artworks facilitated by 5G UC technology.
Data privacy and security regulations are also paramount in the context of 5G UC applications in art. As artists and institutions leverage the technology for immersive experiences and interactive installations, there is a need for clear guidelines on the collection, storage, and use of user data. Regulatory bodies must work to establish standards that protect individuals' privacy while allowing for innovative artistic expressions.
The deployment of 5G UC infrastructure in cultural spaces and art institutions raises questions about spectrum allocation and management. Regulatory frameworks should address the fair distribution of 5G UC frequencies, ensuring that art organizations have access to the necessary bandwidth for their projects. This may involve collaboration between telecommunications authorities and cultural policymakers to create dedicated spectrum allocations for artistic and cultural purposes.
Another critical aspect of the regulatory framework is the establishment of technical standards for 5G UC-enabled art installations and experiences. These standards should cover aspects such as interoperability, quality of service, and accessibility to ensure that 5G UC technology can be seamlessly integrated into diverse artistic contexts. Regulatory bodies may need to work closely with industry stakeholders and artists to develop guidelines that balance innovation with reliability and user experience.
As 5G UC technology enables new forms of artistic expression and audience engagement, there is a need for updated regulations regarding content moderation and curation. This includes addressing issues such as age-appropriate content, cultural sensitivity, and the potential for misinformation in immersive art experiences. Regulatory frameworks should provide clear guidelines for content creators and platform operators while preserving artistic freedom and expression.
The global nature of 5G UC technology necessitates international cooperation in developing regulatory frameworks for its application in art. Cross-border collaborations and agreements will be essential to address issues such as data transfer, content licensing, and the protection of artists' rights across different jurisdictions. Regulatory bodies should work towards harmonizing standards and creating mechanisms for international dispute resolution in the context of 5G UC-enabled art projects.
Economic Impact of 5G UC on Art Market
The integration of 5G UC technology into the art industry is poised to have a significant economic impact on the art market. This advanced connectivity solution is expected to revolutionize various aspects of the art ecosystem, from creation and distribution to consumption and monetization.
One of the primary economic benefits of 5G UC in the art market is the potential for increased sales and revenue generation. The ultra-fast, low-latency network enables seamless streaming of high-resolution digital art, virtual exhibitions, and immersive experiences. This enhanced accessibility and engagement can attract a broader audience, potentially leading to higher sales volumes and increased market participation.
The technology also opens up new revenue streams for artists and galleries through innovative digital art forms and experiences. For instance, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) art installations, enabled by 5G UC's high bandwidth and low latency, can command premium prices and attract tech-savvy collectors. This diversification of art forms can expand the overall market size and create new economic opportunities within the industry.
Furthermore, 5G UC can significantly reduce operational costs for art institutions and galleries. Virtual exhibitions and remote curation capabilities enabled by high-speed, reliable connectivity can decrease the need for physical spaces and associated overhead expenses. This cost reduction can lead to improved profit margins and potentially lower barriers to entry for emerging artists and smaller galleries.
The technology's impact on art authentication and provenance tracking is another crucial economic factor. 5G UC can facilitate real-time, secure data transfer for blockchain-based art registries and smart contracts. This enhanced transparency and security in art transactions can increase buyer confidence, potentially driving up values and reducing fraud-related losses in the art market.
Lastly, 5G UC's ability to support advanced data analytics and AI-driven insights can lead to more efficient market operations. Galleries and auction houses can leverage real-time market data and predictive analytics to optimize pricing strategies and identify emerging trends, potentially increasing overall market efficiency and profitability.
In conclusion, the economic impact of 5G UC on the art market is multifaceted, promising increased revenue generation, cost reduction, and improved market efficiency. As the technology continues to evolve and integrate into the art ecosystem, it has the potential to reshape the economic landscape of the industry significantly.
One of the primary economic benefits of 5G UC in the art market is the potential for increased sales and revenue generation. The ultra-fast, low-latency network enables seamless streaming of high-resolution digital art, virtual exhibitions, and immersive experiences. This enhanced accessibility and engagement can attract a broader audience, potentially leading to higher sales volumes and increased market participation.
The technology also opens up new revenue streams for artists and galleries through innovative digital art forms and experiences. For instance, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) art installations, enabled by 5G UC's high bandwidth and low latency, can command premium prices and attract tech-savvy collectors. This diversification of art forms can expand the overall market size and create new economic opportunities within the industry.
Furthermore, 5G UC can significantly reduce operational costs for art institutions and galleries. Virtual exhibitions and remote curation capabilities enabled by high-speed, reliable connectivity can decrease the need for physical spaces and associated overhead expenses. This cost reduction can lead to improved profit margins and potentially lower barriers to entry for emerging artists and smaller galleries.
The technology's impact on art authentication and provenance tracking is another crucial economic factor. 5G UC can facilitate real-time, secure data transfer for blockchain-based art registries and smart contracts. This enhanced transparency and security in art transactions can increase buyer confidence, potentially driving up values and reducing fraud-related losses in the art market.
Lastly, 5G UC's ability to support advanced data analytics and AI-driven insights can lead to more efficient market operations. Galleries and auction houses can leverage real-time market data and predictive analytics to optimize pricing strategies and identify emerging trends, potentially increasing overall market efficiency and profitability.
In conclusion, the economic impact of 5G UC on the art market is multifaceted, promising increased revenue generation, cost reduction, and improved market efficiency. As the technology continues to evolve and integrate into the art ecosystem, it has the potential to reshape the economic landscape of the industry significantly.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!