Exploring the Role of 5G UC in Advancing Real-Time Language Translation
JUL 18, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
5G UC and Translation: Background and Objectives
The convergence of 5G Ultra-Capacity (UC) technology and real-time language translation represents a significant leap forward in global communication. 5G UC, characterized by its high-speed, low-latency, and massive connectivity capabilities, provides the necessary infrastructure to support advanced language translation services. This technological synergy aims to break down language barriers and facilitate seamless communication across diverse linguistic landscapes.
The evolution of language translation technology has been marked by continuous advancements, from early rule-based systems to statistical methods and, more recently, neural machine translation. However, these solutions have been limited by processing power, network speed, and the ability to handle real-time conversations effectively. The introduction of 5G UC presents an opportunity to overcome these limitations and usher in a new era of instantaneous, accurate, and context-aware translation services.
The primary objective of integrating 5G UC with language translation is to enable real-time, high-quality translation across multiple modalities, including speech, text, and even augmented reality applications. This integration aims to support a wide range of use cases, from international business negotiations and global education initiatives to tourism and emergency response scenarios where immediate, accurate communication is crucial.
Another key goal is to leverage the enhanced network capabilities of 5G UC to improve the accuracy and contextual understanding of translations. By utilizing edge computing and distributed AI models, translation systems can process vast amounts of data locally, reducing latency and improving the ability to capture nuances and cultural context in real-time conversations.
Furthermore, the development of 5G UC-powered translation services seeks to democratize access to multilingual communication. By reducing the need for specialized hardware and leveraging the ubiquity of smartphones and other connected devices, this technology aims to make real-time translation accessible to a broader audience, potentially revolutionizing how people interact across language barriers in both personal and professional settings.
The technical trajectory of this field is expected to focus on optimizing AI models for mobile and edge devices, developing more efficient compression algorithms for audio and video streams, and creating seamless integration between translation services and various communication platforms. As 5G UC networks continue to expand and evolve, the potential for innovative translation applications grows, promising a future where language differences no longer impede global communication and collaboration.
The evolution of language translation technology has been marked by continuous advancements, from early rule-based systems to statistical methods and, more recently, neural machine translation. However, these solutions have been limited by processing power, network speed, and the ability to handle real-time conversations effectively. The introduction of 5G UC presents an opportunity to overcome these limitations and usher in a new era of instantaneous, accurate, and context-aware translation services.
The primary objective of integrating 5G UC with language translation is to enable real-time, high-quality translation across multiple modalities, including speech, text, and even augmented reality applications. This integration aims to support a wide range of use cases, from international business negotiations and global education initiatives to tourism and emergency response scenarios where immediate, accurate communication is crucial.
Another key goal is to leverage the enhanced network capabilities of 5G UC to improve the accuracy and contextual understanding of translations. By utilizing edge computing and distributed AI models, translation systems can process vast amounts of data locally, reducing latency and improving the ability to capture nuances and cultural context in real-time conversations.
Furthermore, the development of 5G UC-powered translation services seeks to democratize access to multilingual communication. By reducing the need for specialized hardware and leveraging the ubiquity of smartphones and other connected devices, this technology aims to make real-time translation accessible to a broader audience, potentially revolutionizing how people interact across language barriers in both personal and professional settings.
The technical trajectory of this field is expected to focus on optimizing AI models for mobile and edge devices, developing more efficient compression algorithms for audio and video streams, and creating seamless integration between translation services and various communication platforms. As 5G UC networks continue to expand and evolve, the potential for innovative translation applications grows, promising a future where language differences no longer impede global communication and collaboration.
Market Demand for Real-Time Translation Services
The demand for real-time language translation services has been growing exponentially in recent years, driven by globalization, increased international travel, and the rise of remote work. This trend has been further accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, which has highlighted the need for effective communication across language barriers in various sectors, including healthcare, education, and business.
In the business sector, multinational corporations are increasingly seeking real-time translation solutions to facilitate seamless communication among global teams and with international clients. The ability to conduct meetings, negotiations, and collaborations without language barriers is becoming a crucial competitive advantage in the global marketplace.
The tourism industry, despite recent setbacks due to travel restrictions, is expected to rebound strongly and continue driving demand for real-time translation services. Travelers are seeking more immersive and authentic experiences, which often involve interacting with locals in their native languages. Real-time translation technology can significantly enhance these experiences and open up new destinations to a broader range of tourists.
Education is another sector experiencing a surge in demand for real-time translation services. With the rise of online learning platforms and international educational collaborations, there is a growing need for tools that can facilitate cross-cultural communication and learning. Real-time translation can enable students from different countries to participate in joint classes, discussions, and projects without language barriers.
The healthcare industry has also recognized the critical importance of accurate and immediate language translation, particularly in emergency situations and telemedicine consultations. The ability to provide timely and precise medical information across language barriers can significantly improve patient outcomes and healthcare delivery efficiency.
E-commerce and digital content platforms are increasingly looking to implement real-time translation features to expand their global reach. This includes not only product descriptions and customer service interactions but also user-generated content such as reviews and comments, which can greatly influence purchasing decisions across different markets.
As artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies continue to advance, there is a growing expectation for more sophisticated and context-aware translation services. Users are demanding not just word-for-word translations, but solutions that can accurately convey nuances, idioms, and cultural context in real-time across various communication channels.
The integration of real-time translation capabilities into everyday devices and applications is becoming increasingly important. From smartphones and smart speakers to augmented reality glasses, consumers are seeking seamless language translation experiences that can be accessed effortlessly in their daily lives.
In the business sector, multinational corporations are increasingly seeking real-time translation solutions to facilitate seamless communication among global teams and with international clients. The ability to conduct meetings, negotiations, and collaborations without language barriers is becoming a crucial competitive advantage in the global marketplace.
The tourism industry, despite recent setbacks due to travel restrictions, is expected to rebound strongly and continue driving demand for real-time translation services. Travelers are seeking more immersive and authentic experiences, which often involve interacting with locals in their native languages. Real-time translation technology can significantly enhance these experiences and open up new destinations to a broader range of tourists.
Education is another sector experiencing a surge in demand for real-time translation services. With the rise of online learning platforms and international educational collaborations, there is a growing need for tools that can facilitate cross-cultural communication and learning. Real-time translation can enable students from different countries to participate in joint classes, discussions, and projects without language barriers.
The healthcare industry has also recognized the critical importance of accurate and immediate language translation, particularly in emergency situations and telemedicine consultations. The ability to provide timely and precise medical information across language barriers can significantly improve patient outcomes and healthcare delivery efficiency.
E-commerce and digital content platforms are increasingly looking to implement real-time translation features to expand their global reach. This includes not only product descriptions and customer service interactions but also user-generated content such as reviews and comments, which can greatly influence purchasing decisions across different markets.
As artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies continue to advance, there is a growing expectation for more sophisticated and context-aware translation services. Users are demanding not just word-for-word translations, but solutions that can accurately convey nuances, idioms, and cultural context in real-time across various communication channels.
The integration of real-time translation capabilities into everyday devices and applications is becoming increasingly important. From smartphones and smart speakers to augmented reality glasses, consumers are seeking seamless language translation experiences that can be accessed effortlessly in their daily lives.
5G UC Technology: Current State and Challenges
5G UC (Ultra-Capacity) technology represents a significant advancement in mobile network capabilities, offering enhanced speed, capacity, and reliability. However, its application in real-time language translation faces several challenges and limitations in its current state.
The primary advantage of 5G UC is its ability to provide ultra-fast data speeds and low latency, which are crucial for real-time applications like language translation. With theoretical peak speeds of up to 20 Gbps and latency as low as 1 millisecond, 5G UC has the potential to revolutionize the way we communicate across language barriers.
Despite these promising capabilities, the current state of 5G UC deployment is still limited. While many major cities and urban areas have begun rolling out 5G networks, coverage remains inconsistent and often restricted to specific locations. This patchy availability poses a significant challenge for widespread adoption of real-time translation services that rely on consistent, high-speed connectivity.
Another challenge lies in the processing power required for real-time language translation. While 5G UC can transmit data quickly, the actual translation process still requires substantial computational resources. Current mobile devices may struggle to handle complex translation algorithms in real-time, necessitating a balance between on-device processing and cloud-based solutions.
Power consumption is another concern with 5G UC technology. The high-speed data transmission and increased processing demands can quickly drain device batteries, potentially limiting the practical use of real-time translation services in mobile scenarios.
Compatibility issues also present a challenge. Not all devices are 5G-enabled, and even among those that are, there may be variations in supported frequency bands and technologies. This fragmentation can lead to inconsistent user experiences and complicate the development of universally accessible translation services.
Security and privacy concerns are paramount when dealing with real-time communication and translation. The increased data transmission rates of 5G UC also increase the potential attack surface for malicious actors. Ensuring robust encryption and data protection measures without compromising the speed and efficiency of translation services remains a significant challenge.
Lastly, the cost associated with 5G UC infrastructure and compatible devices presents an economic barrier to widespread adoption. While prices are expected to decrease over time, the current high costs may limit access to advanced real-time translation services, particularly in developing regions or among lower-income populations.
The primary advantage of 5G UC is its ability to provide ultra-fast data speeds and low latency, which are crucial for real-time applications like language translation. With theoretical peak speeds of up to 20 Gbps and latency as low as 1 millisecond, 5G UC has the potential to revolutionize the way we communicate across language barriers.
Despite these promising capabilities, the current state of 5G UC deployment is still limited. While many major cities and urban areas have begun rolling out 5G networks, coverage remains inconsistent and often restricted to specific locations. This patchy availability poses a significant challenge for widespread adoption of real-time translation services that rely on consistent, high-speed connectivity.
Another challenge lies in the processing power required for real-time language translation. While 5G UC can transmit data quickly, the actual translation process still requires substantial computational resources. Current mobile devices may struggle to handle complex translation algorithms in real-time, necessitating a balance between on-device processing and cloud-based solutions.
Power consumption is another concern with 5G UC technology. The high-speed data transmission and increased processing demands can quickly drain device batteries, potentially limiting the practical use of real-time translation services in mobile scenarios.
Compatibility issues also present a challenge. Not all devices are 5G-enabled, and even among those that are, there may be variations in supported frequency bands and technologies. This fragmentation can lead to inconsistent user experiences and complicate the development of universally accessible translation services.
Security and privacy concerns are paramount when dealing with real-time communication and translation. The increased data transmission rates of 5G UC also increase the potential attack surface for malicious actors. Ensuring robust encryption and data protection measures without compromising the speed and efficiency of translation services remains a significant challenge.
Lastly, the cost associated with 5G UC infrastructure and compatible devices presents an economic barrier to widespread adoption. While prices are expected to decrease over time, the current high costs may limit access to advanced real-time translation services, particularly in developing regions or among lower-income populations.
Existing 5G-Enabled Translation Solutions
01 5G UC network infrastructure for real-time translation
5G Ultra Capacity networks provide the high-speed, low-latency infrastructure necessary for real-time language translation. This advanced network technology enables faster data transmission and processing, supporting seamless communication across language barriers in various applications such as international business meetings, global events, and cross-cultural interactions.- 5G UC network infrastructure for real-time translation: 5G Ultra Capacity networks provide the necessary high-speed, low-latency infrastructure to support real-time language translation services. This advanced network technology enables faster data transmission and processing, allowing for near-instantaneous translation of spoken or written content across multiple languages.
- AI-powered translation algorithms for 5G UC: Advanced artificial intelligence algorithms are utilized to perform real-time language translation on 5G UC networks. These AI models are optimized for speed and accuracy, leveraging the increased bandwidth and reduced latency of 5G UC to deliver high-quality translations with minimal delay.
- Edge computing for real-time translation in 5G UC: Edge computing technologies are integrated into 5G UC networks to process translation requests closer to the user, reducing latency and improving overall performance. This distributed computing approach allows for faster and more efficient real-time language translation services.
- Multi-modal translation support in 5G UC environments: 5G UC-based translation systems support multiple input and output modalities, including speech-to-speech, text-to-speech, and text-to-text translations. This versatility allows for seamless communication across different languages and formats, leveraging the high-capacity network for simultaneous processing of various data types.
- Context-aware translation optimization for 5G UC: Real-time translation systems on 5G UC networks incorporate context-aware algorithms that analyze surrounding information to improve translation accuracy. This includes considering factors such as user location, conversation history, and cultural nuances to provide more natural and precise translations in various scenarios.
02 AI-powered language translation algorithms
Advanced artificial intelligence algorithms are employed to enhance the accuracy and speed of real-time language translation. These algorithms utilize machine learning techniques to continuously improve translation quality, handle context-specific nuances, and adapt to various dialects and accents, ensuring more natural and precise communication.Expand Specific Solutions03 Edge computing for reduced latency in translation
Edge computing technology is integrated into the 5G UC infrastructure to process translation requests closer to the user. This approach significantly reduces latency, enabling near-instantaneous translation and improving the overall user experience in real-time communication scenarios.Expand Specific Solutions04 Multi-modal translation capabilities
5G UC-enabled translation systems incorporate multi-modal capabilities, allowing for real-time translation across various input and output formats. This includes speech-to-text, text-to-speech, and even visual translation, enabling more comprehensive and versatile communication solutions for diverse user needs.Expand Specific Solutions05 Secure and privacy-preserving translation services
Advanced encryption and privacy-preserving techniques are implemented to ensure the security and confidentiality of translated content. These measures protect sensitive information during transmission and processing, addressing concerns related to data privacy in real-time language translation services.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in 5G UC and Translation Industries
The development of 5G UC for real-time language translation is in its early stages, with the market showing significant growth potential. The technology's maturity is rapidly advancing, driven by major players in the telecommunications and technology sectors. Companies like Samsung Electronics, Ericsson, Qualcomm, and Huawei are at the forefront, leveraging their expertise in 5G infrastructure and AI to enhance translation capabilities. NTT Docomo and China Mobile are also making strides in this field, focusing on practical applications for their vast user bases. As the technology evolves, we can expect increased competition and innovation from both established tech giants like IBM and emerging specialized firms, leading to more sophisticated and seamless real-time translation solutions.
QUALCOMM, Inc.
Technical Solution: Qualcomm has developed a 5G-enabled real-time language translation solution that leverages its Snapdragon mobile platforms. The system utilizes on-device AI processing combined with 5G UC's low latency and high bandwidth capabilities to perform real-time speech recognition, translation, and text-to-speech conversion. Qualcomm's approach integrates advanced natural language processing models optimized for mobile devices, allowing for efficient translation even in areas with limited connectivity. The solution supports multiple languages and can adapt to different accents and speaking styles[1][3]. Qualcomm has also partnered with various telecom operators to showcase this technology in real-world 5G networks, demonstrating its practical applicability in diverse scenarios such as international business meetings and tourism[2].
Strengths: On-device processing reduces reliance on cloud services, enhancing privacy and reducing latency. Integration with Snapdragon platforms ensures wide compatibility with mobile devices. Weaknesses: May be limited to devices using Qualcomm chipsets, potentially restricting widespread adoption.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Huawei has developed a comprehensive 5G-powered real-time translation system that combines edge computing with cloud-based processing. Their solution utilizes 5G UC's network slicing capabilities to prioritize translation traffic, ensuring consistent low-latency performance. Huawei's approach incorporates advanced AI models for speech recognition and natural language processing, which are distributed across the edge and cloud infrastructure. This hybrid model allows for rapid processing of common phrases on-device while leveraging cloud resources for more complex translations. The system also features adaptive learning, improving translation accuracy over time based on user feedback and usage patterns[4][5]. Huawei has demonstrated this technology in various international events and smart city projects, showcasing its ability to handle multiple languages simultaneously in high-density environments[6].
Strengths: Hybrid edge-cloud architecture provides flexibility and scalability. Network slicing ensures reliable performance in congested networks. Weaknesses: Potential geopolitical concerns may limit adoption in some markets. Heavy reliance on cloud infrastructure could pose challenges in areas with limited connectivity.
Core Innovations in 5G UC for Translation
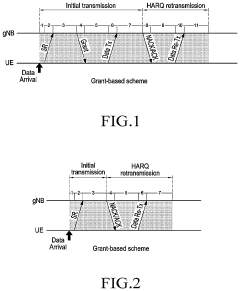
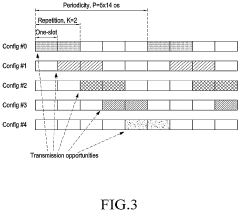
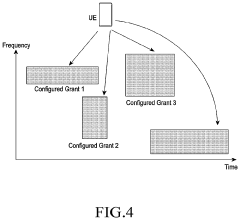
Resource selection for ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) uplink
PatentActiveUS11963165B2
Innovation
- A method for resource selection by user equipment (UE) and base stations to intelligently choose the best configured grant resources based on transmission parameters, such as transport block size, transmission power, latency, and reliability, using advanced algorithms like RBIR/EESM for link prediction, enabling precise selection of resources for URLLC uplink transmissions.
Data trasmission apparatus and control method thereof
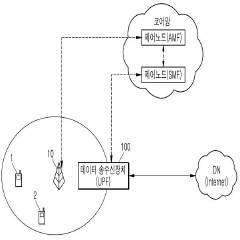
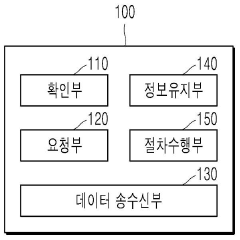
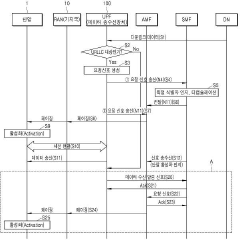
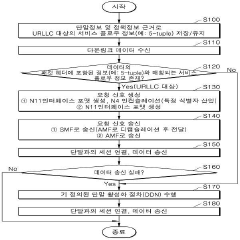
PatentActiveKR1020190045596A
Innovation
- A data transceiver apparatus and method that directly requests paging from the AMF without signaling with other control nodes, utilizing the N11 interface to minimize signaling delays by creating a session with the terminal for data transmission.
Regulatory Framework for 5G UC Applications
The regulatory framework for 5G UC applications in real-time language translation is a complex and evolving landscape. As 5G Ultra-Capacity (UC) networks continue to expand, governments and regulatory bodies are working to establish guidelines that balance innovation with public safety and privacy concerns.
One of the primary regulatory considerations for 5G UC in language translation is spectrum allocation. Regulatory agencies must ensure that sufficient bandwidth is available for these high-capacity applications while managing potential interference with other services. This often involves a delicate balancing act between different stakeholders and may require international coordination to harmonize spectrum usage across borders.
Data privacy and security regulations play a crucial role in shaping the development of real-time translation services. As these applications process vast amounts of personal conversations and potentially sensitive information, regulators are implementing strict data protection measures. For instance, the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets stringent requirements for data handling and user consent, which directly impact the design and deployment of 5G UC-powered translation services.
Telecommunications regulators are also addressing the quality of service (QoS) requirements for 5G UC applications. Real-time language translation demands ultra-low latency and high reliability, necessitating specific performance standards. Regulatory bodies are establishing minimum QoS benchmarks that network operators must meet to ensure seamless translation experiences.
Cross-border regulations present another layer of complexity for 5G UC translation services. As these applications often involve international communication, regulators must consider issues such as data localization requirements, cross-border data transfers, and compliance with varying national security laws. This necessitates collaboration between regulatory agencies in different countries to create a cohesive framework that facilitates global communication while respecting local laws.
Accessibility regulations are increasingly important in the context of 5G UC translation applications. Many countries are implementing laws that require digital services to be accessible to individuals with disabilities. This may include mandates for real-time captioning or sign language interpretation, which could be integrated into 5G UC translation platforms.
As artificial intelligence plays a significant role in advanced translation services, regulators are also grappling with the ethical implications of AI-powered language processing. This includes addressing potential biases in translation algorithms and ensuring transparency in how AI systems make decisions. Some jurisdictions are considering or implementing AI-specific regulations that would directly impact the development and deployment of 5G UC translation technologies.
One of the primary regulatory considerations for 5G UC in language translation is spectrum allocation. Regulatory agencies must ensure that sufficient bandwidth is available for these high-capacity applications while managing potential interference with other services. This often involves a delicate balancing act between different stakeholders and may require international coordination to harmonize spectrum usage across borders.
Data privacy and security regulations play a crucial role in shaping the development of real-time translation services. As these applications process vast amounts of personal conversations and potentially sensitive information, regulators are implementing strict data protection measures. For instance, the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets stringent requirements for data handling and user consent, which directly impact the design and deployment of 5G UC-powered translation services.
Telecommunications regulators are also addressing the quality of service (QoS) requirements for 5G UC applications. Real-time language translation demands ultra-low latency and high reliability, necessitating specific performance standards. Regulatory bodies are establishing minimum QoS benchmarks that network operators must meet to ensure seamless translation experiences.
Cross-border regulations present another layer of complexity for 5G UC translation services. As these applications often involve international communication, regulators must consider issues such as data localization requirements, cross-border data transfers, and compliance with varying national security laws. This necessitates collaboration between regulatory agencies in different countries to create a cohesive framework that facilitates global communication while respecting local laws.
Accessibility regulations are increasingly important in the context of 5G UC translation applications. Many countries are implementing laws that require digital services to be accessible to individuals with disabilities. This may include mandates for real-time captioning or sign language interpretation, which could be integrated into 5G UC translation platforms.
As artificial intelligence plays a significant role in advanced translation services, regulators are also grappling with the ethical implications of AI-powered language processing. This includes addressing potential biases in translation algorithms and ensuring transparency in how AI systems make decisions. Some jurisdictions are considering or implementing AI-specific regulations that would directly impact the development and deployment of 5G UC translation technologies.
Cross-Cultural Impact of Real-Time Translation
The advent of real-time language translation, powered by 5G UC technology, is poised to revolutionize cross-cultural communication and interaction on a global scale. This technological breakthrough has the potential to break down language barriers that have long hindered international collaboration, commerce, and cultural exchange.
One of the most significant impacts of real-time translation is its ability to foster greater understanding and empathy between diverse cultures. By enabling instant, accurate communication across language divides, this technology can help bridge cultural gaps and promote mutual respect. It allows individuals from different linguistic backgrounds to engage in meaningful conversations, share ideas, and gain insights into each other's perspectives without the need for intermediaries or time-consuming translation processes.
In the business world, real-time translation facilitated by 5G UC can dramatically enhance international trade and collaboration. Companies can conduct negotiations, form partnerships, and provide customer support across borders with unprecedented ease and efficiency. This technology has the potential to level the playing field for small and medium-sized enterprises, enabling them to compete in global markets previously dominated by larger, multilingual corporations.
The tourism industry stands to benefit significantly from this technological advancement. Travelers can navigate foreign countries with greater confidence, interact more authentically with locals, and immerse themselves in different cultures without the constraints of language barriers. This enhanced cultural exchange can lead to more enriching travel experiences and foster greater global understanding.
In the realm of education, real-time translation can revolutionize international academic collaboration and exchange programs. Students and researchers from different countries can participate in joint projects, attend lectures, and engage in discussions without language limitations. This can lead to a more diverse and inclusive global academic community, facilitating the exchange of knowledge and ideas across cultural and linguistic boundaries.
Moreover, the technology has the potential to preserve and revitalize endangered languages. By making it easier for speakers of minority languages to communicate with the wider world while maintaining their linguistic heritage, real-time translation can help prevent language extinction and promote linguistic diversity.
However, it is important to consider the potential drawbacks and challenges of widespread real-time translation. There is a risk that reliance on technology could discourage language learning, potentially leading to a homogenization of global culture. Additionally, nuances, idioms, and cultural context may be lost in translation, highlighting the continued importance of cultural competence and sensitivity in cross-cultural interactions.
One of the most significant impacts of real-time translation is its ability to foster greater understanding and empathy between diverse cultures. By enabling instant, accurate communication across language divides, this technology can help bridge cultural gaps and promote mutual respect. It allows individuals from different linguistic backgrounds to engage in meaningful conversations, share ideas, and gain insights into each other's perspectives without the need for intermediaries or time-consuming translation processes.
In the business world, real-time translation facilitated by 5G UC can dramatically enhance international trade and collaboration. Companies can conduct negotiations, form partnerships, and provide customer support across borders with unprecedented ease and efficiency. This technology has the potential to level the playing field for small and medium-sized enterprises, enabling them to compete in global markets previously dominated by larger, multilingual corporations.
The tourism industry stands to benefit significantly from this technological advancement. Travelers can navigate foreign countries with greater confidence, interact more authentically with locals, and immerse themselves in different cultures without the constraints of language barriers. This enhanced cultural exchange can lead to more enriching travel experiences and foster greater global understanding.
In the realm of education, real-time translation can revolutionize international academic collaboration and exchange programs. Students and researchers from different countries can participate in joint projects, attend lectures, and engage in discussions without language limitations. This can lead to a more diverse and inclusive global academic community, facilitating the exchange of knowledge and ideas across cultural and linguistic boundaries.
Moreover, the technology has the potential to preserve and revitalize endangered languages. By making it easier for speakers of minority languages to communicate with the wider world while maintaining their linguistic heritage, real-time translation can help prevent language extinction and promote linguistic diversity.
However, it is important to consider the potential drawbacks and challenges of widespread real-time translation. There is a risk that reliance on technology could discourage language learning, potentially leading to a homogenization of global culture. Additionally, nuances, idioms, and cultural context may be lost in translation, highlighting the continued importance of cultural competence and sensitivity in cross-cultural interactions.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!