System and method of calibrating a phase-locked loop while maintaining lock
a phase-locked loop and lock technology, applied in the field of phase-locked loop calibration, can solve the problems of jitter in the output signal, affecting the performance of the pll, and being sensitive to process, voltage and temperature variations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
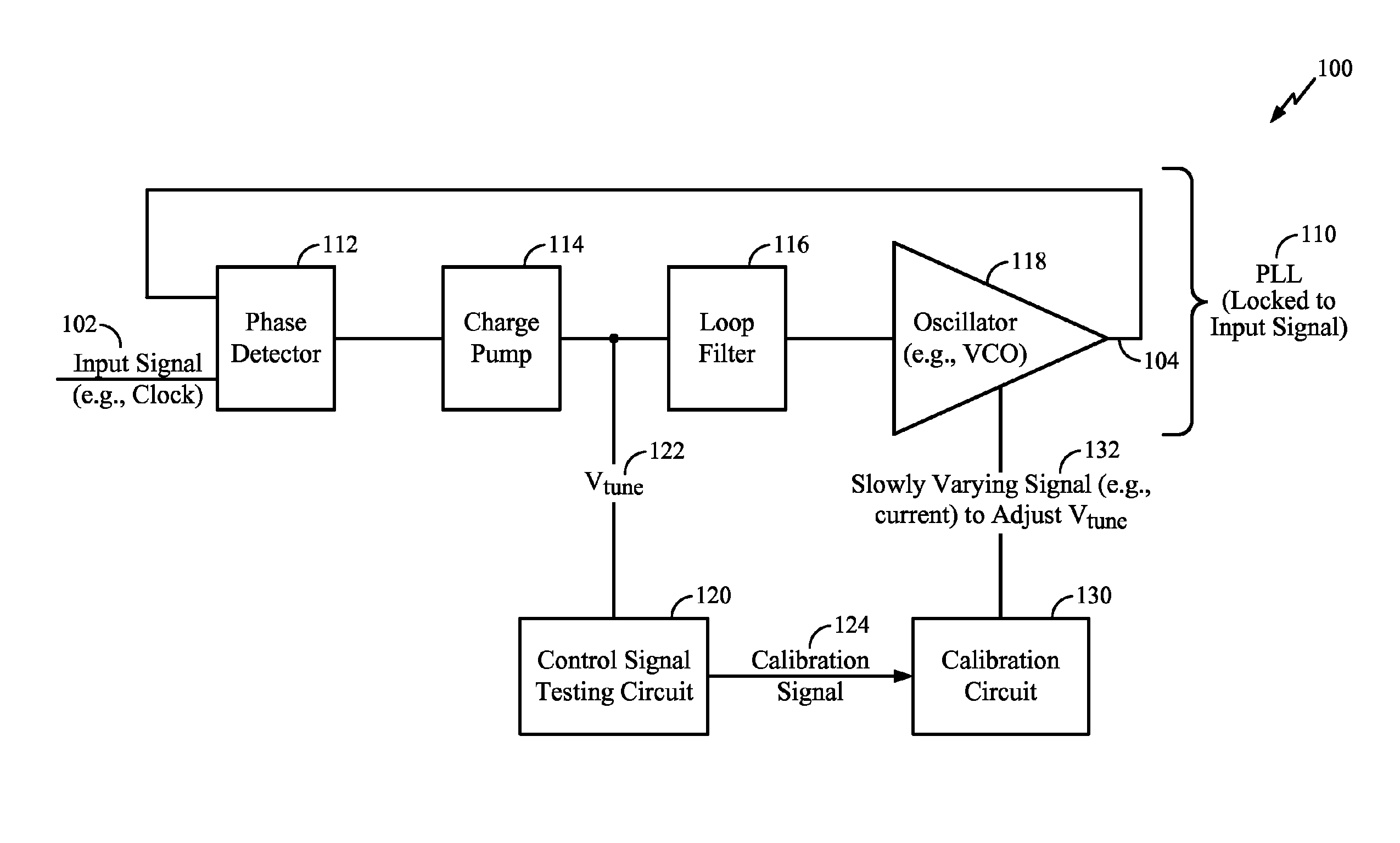
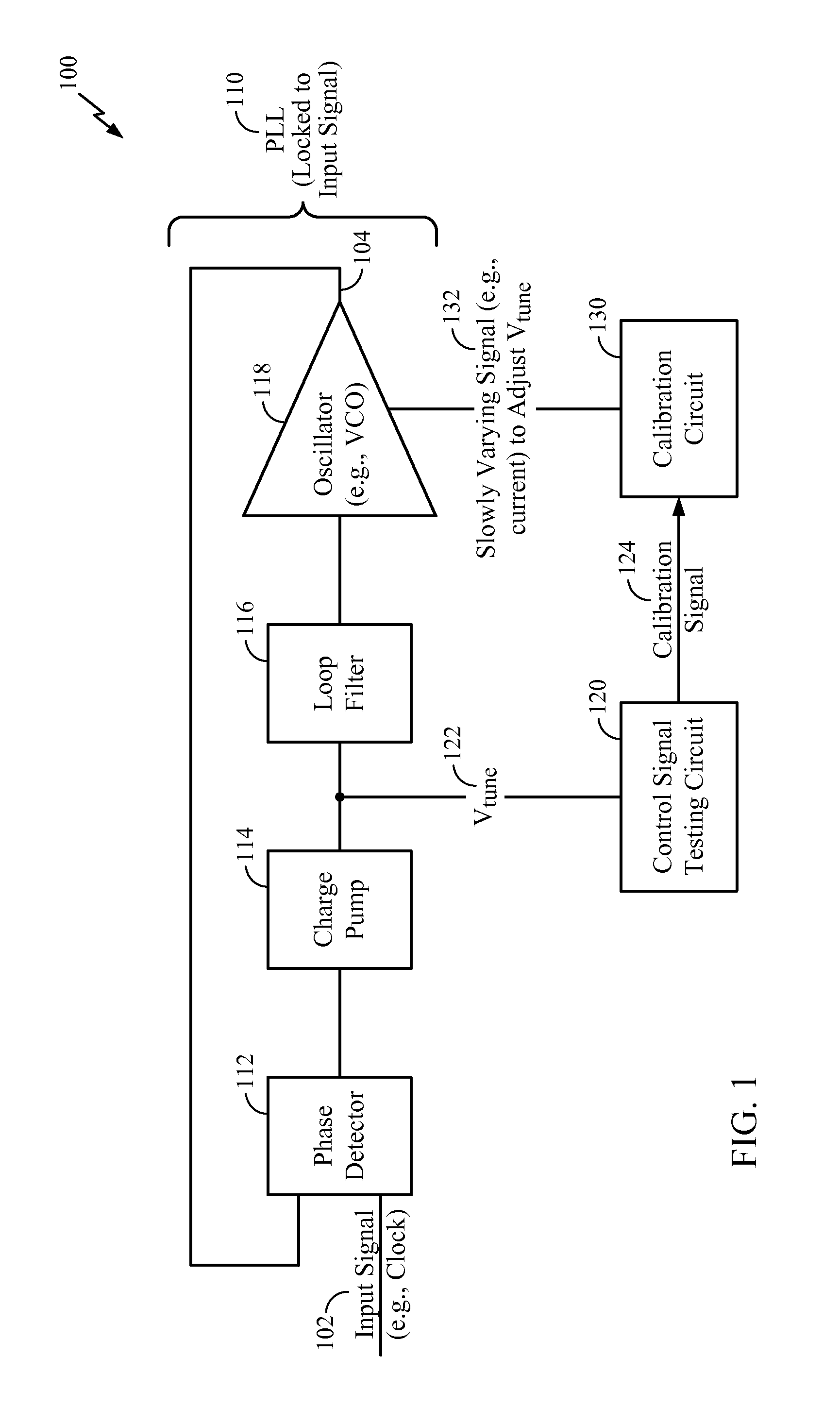
[0019]Referring to FIG. 1, a particular illustrative embodiment of a system of calibrating a phase-locked loop (PLL) while maintaining lock is disclosed and generally designated 100. The system 100 includes a PLL 110 coupled to a control signal testing circuit 120 and to a calibration circuit 130.
[0020]The PLL 110 may receive an input signal 102 and may produce an output signal 104. For example, the input signal 102 may be a clock signal (e.g., having a frequency of 100 Hz). When locked to the input signal 102, the output signal 104 produced by the PLL 110 may have the same frequency as the input signal 102 (e.g., 100 Hz) or may have a multiple of the frequency of the input signal 102 (e.g., 200 Hz, 500 Hz, 10 MHz, 1 GHz, etc.).
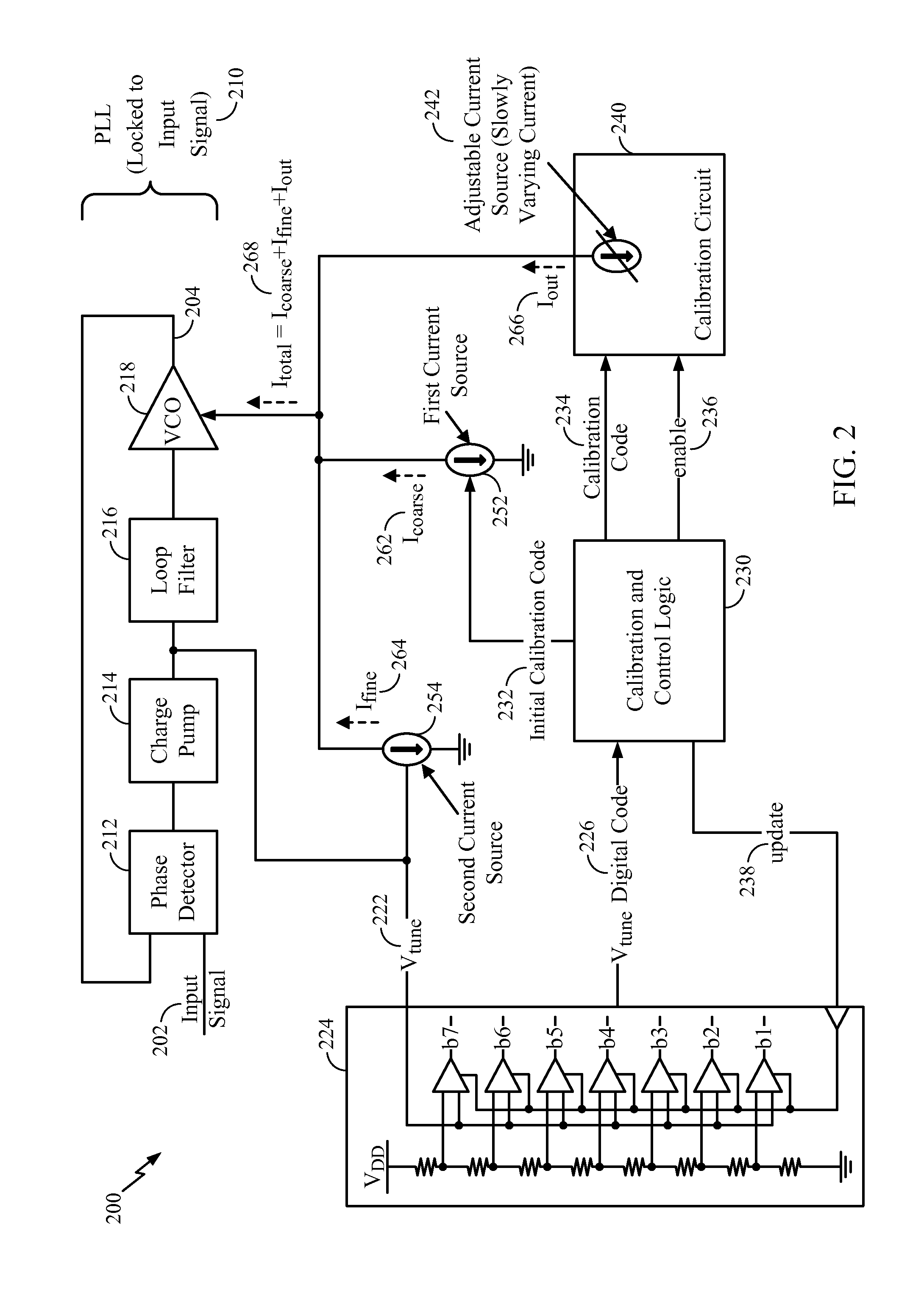
[0021]The PLL 110 may include a phase detector 112, a charge pump 114, a loop filter 116 (e.g., a low-pass filter), and an oscillator 118 (e.g., a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO)). When the frequency of the output signal 104 is a multiple of the frequency...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com