Inhibition of Angiogenesis and Destruction of Angiogenic Vessels with Extracts of Noni Juice (Morinda Citrifolia)
a technology of extracts of noni juice and angiogenesis, which is applied in the direction of biocide, cardiovascular disorder, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems that juice appeared to adversely affect the antiangiogenic component(s) in the juice, and achieve the effects of inhibiting angiogenesis, inhibiting angiogenesis, and degrading existing capillary networks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0038]Materials and Methods
[0039]The Human Placental Vein Angiogenesis Model: Discarded human placentas were obtained anonymously with prior approval of an Institutional Review Board. The placental veins were dissected free from the placenta and adventitial tissue. The trimmed vein segment was opened longitudinally to produce a flat film of venous tissue of full thickness. Vein discs (2 mm diameter) were created with a sterile skin punch (Miltex Instrument Company, Inc.; Lake Success, N.Y.). The discs were placed into wells of a standard 96-well plate (Corning Inc., Corning, N.Y.). The vein disc harvest was completed within three hours of delivery to optimize endothelial cell viability. Vein discs from a single placenta were distributed equally among all treatment groups to ensure randomization. Each well was preloaded with a human thrombin solution (0.05 IU in 2.0 μl), and allowed to evaporate to dryness before use. All chemicals were purchased from Sigma Chemical Company (St. Loui...
example 2
[0045]Inhibitory Effects of Noni Juice on Angiogenesis:
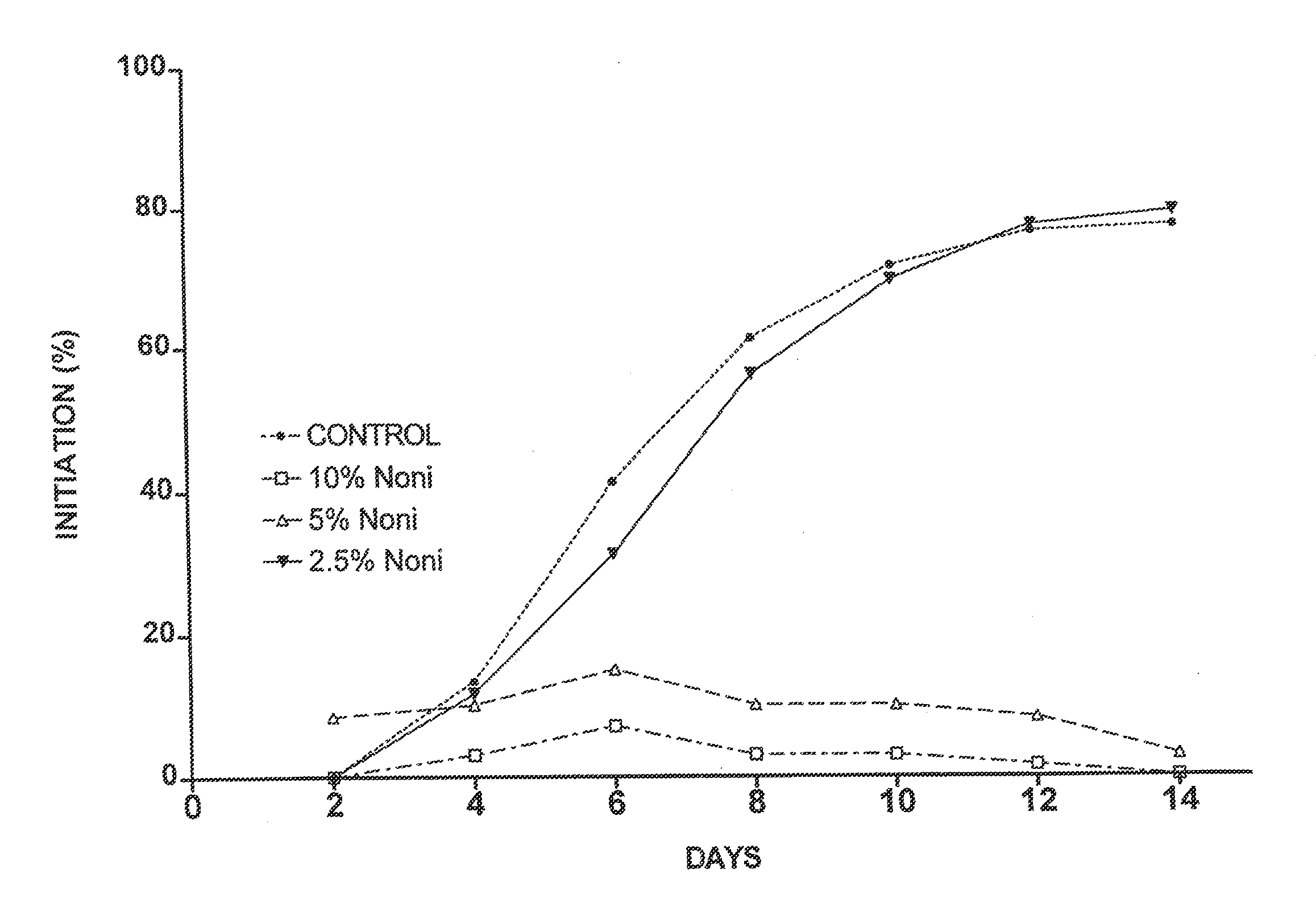
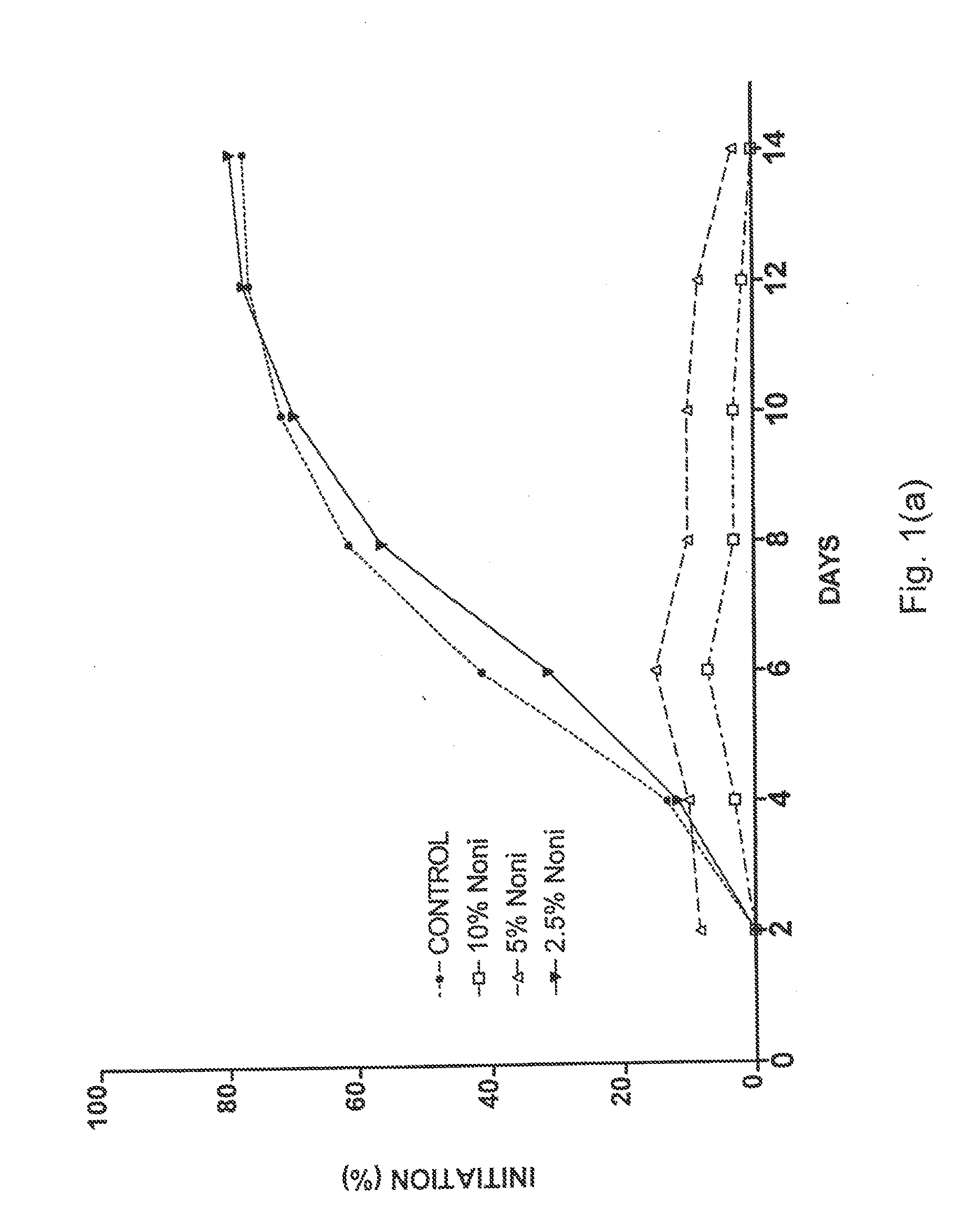
[0046]Four separate placentas were used as sources for placental vein discs (PVD) to test the effects of Noni juice on angiogenesis. HPVAM was supplemented with various dilutions of commercial Noni juice to yield four test groups: 33% Noni juice, n=60; 10% Noni, n=120; 5% Noni, n=120; and 2.5% Noni, n=60. The control medium was supplemented with matching concentrations of NaCl (i.e., 33%, 10%, 5%, and 2.5%) to ensure that the observed effects were not due to a difference in concentration of the medium ingredients. Every two days, the medium in each well was replaced, and each well was scored for both initiation of angiogenesis and angiogenic index.
[0047]As shown in FIG. 1a, the initiation of angiogenesis was reduced by all concentrations of Noni juice. However, the effect of 2.5% Noni juice was small as compared to that of 5% and 10% Noni juice. The data for 33% Noni juice were not plotted because these vein discs did not show a...
example 3
[0049]Effects of Noni Juice on Established Capillary Networks
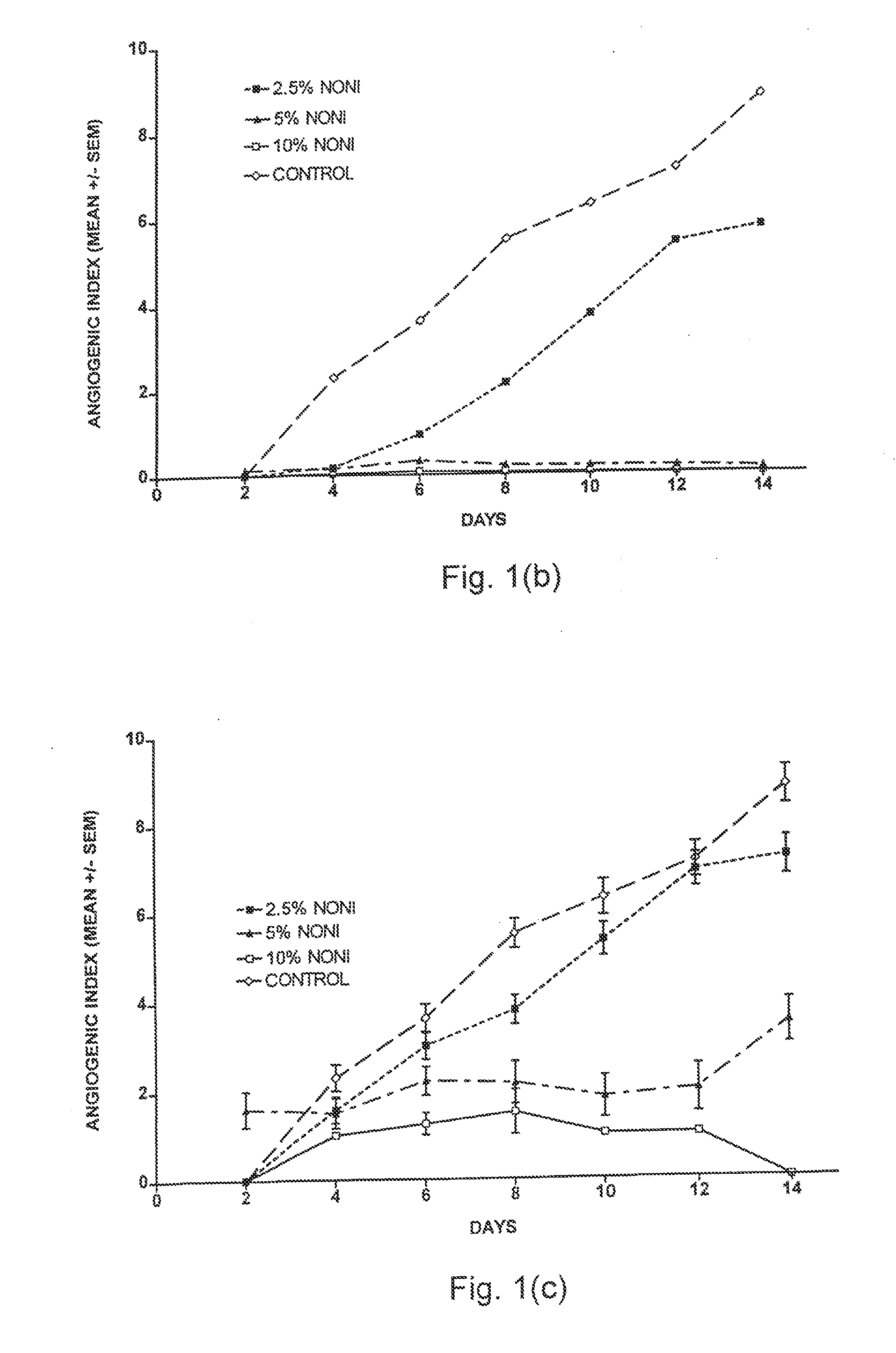
[0050]Placental vein discs were derived from two separate placentas to study the effects of Noni juice on established capillary networks. HPVAM was added to the wells and changed every two days. The PVD were allowed to grow for 6 days, at which time a mean AI=3.5 was reached. At this time, the experimental medium was supplemented with 10% Noni juice. Every two days after the addition of Noni juice, the PVD were scored, and the medium was changed as described in Example 1.
[0051]The number of wells with angiogenic vessels decreased upon addition of 10% Noni following six days of disc growth in standard medium. (FIG. 2a). In addition, both initiation and proliferation, measured as the mean AI, decreased after 10% Noni juice was added. (FIG. 2b). In both FIGS. 2a and 2b, the x-axis represents days following the initiation of the Noni treatment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com