Viewpoint-invariant image matching and generation of three-dimensional models from two-dimensional imagery
a two-dimensional imagery and viewpoint-invariant technology, applied in the field of object modeling and matching systems, can solve the problems of low degree of accuracy of viewpoint selection, so as to achieve the effect of progressively reducing the errors of inaccurate viewpoint selection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
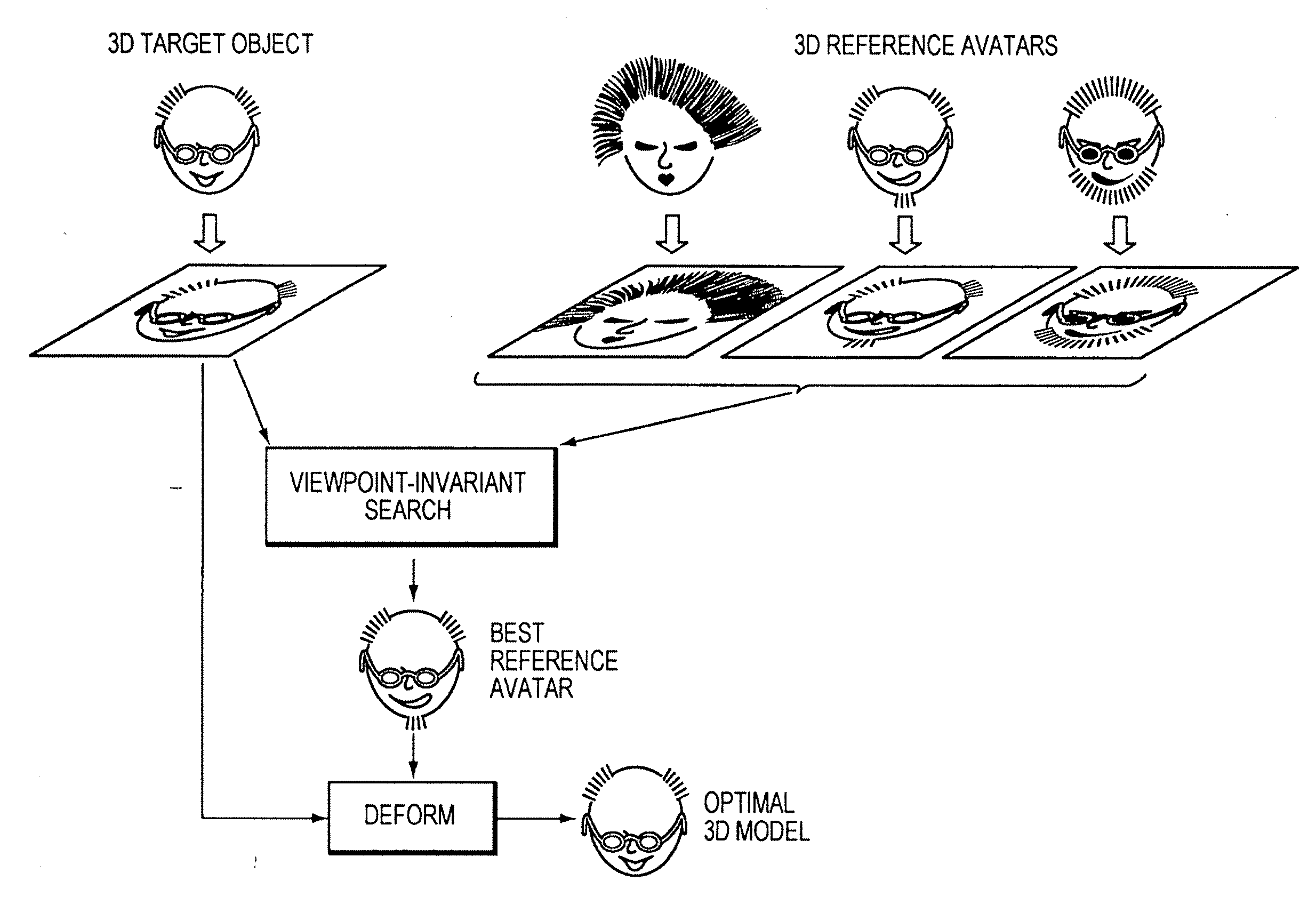
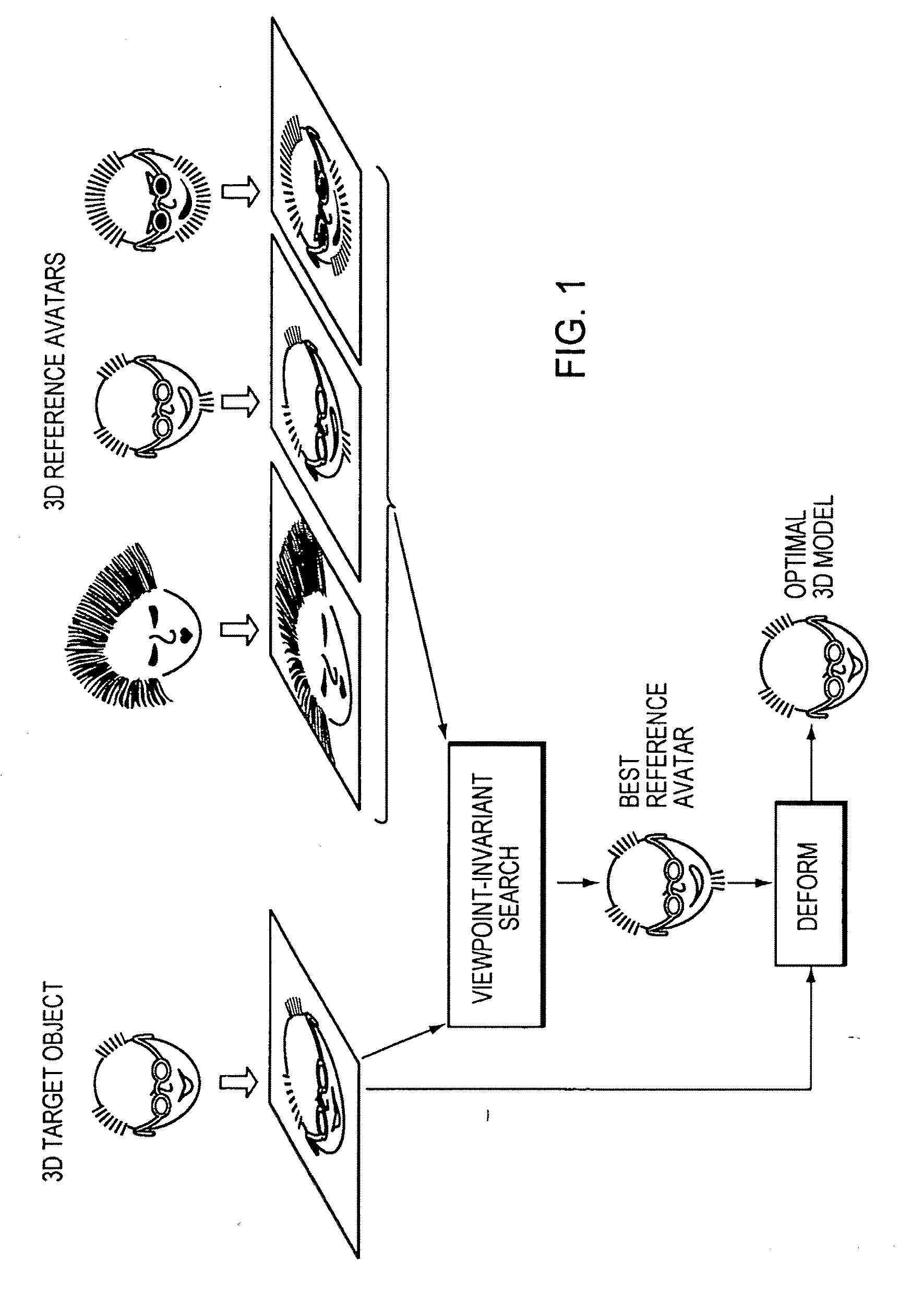
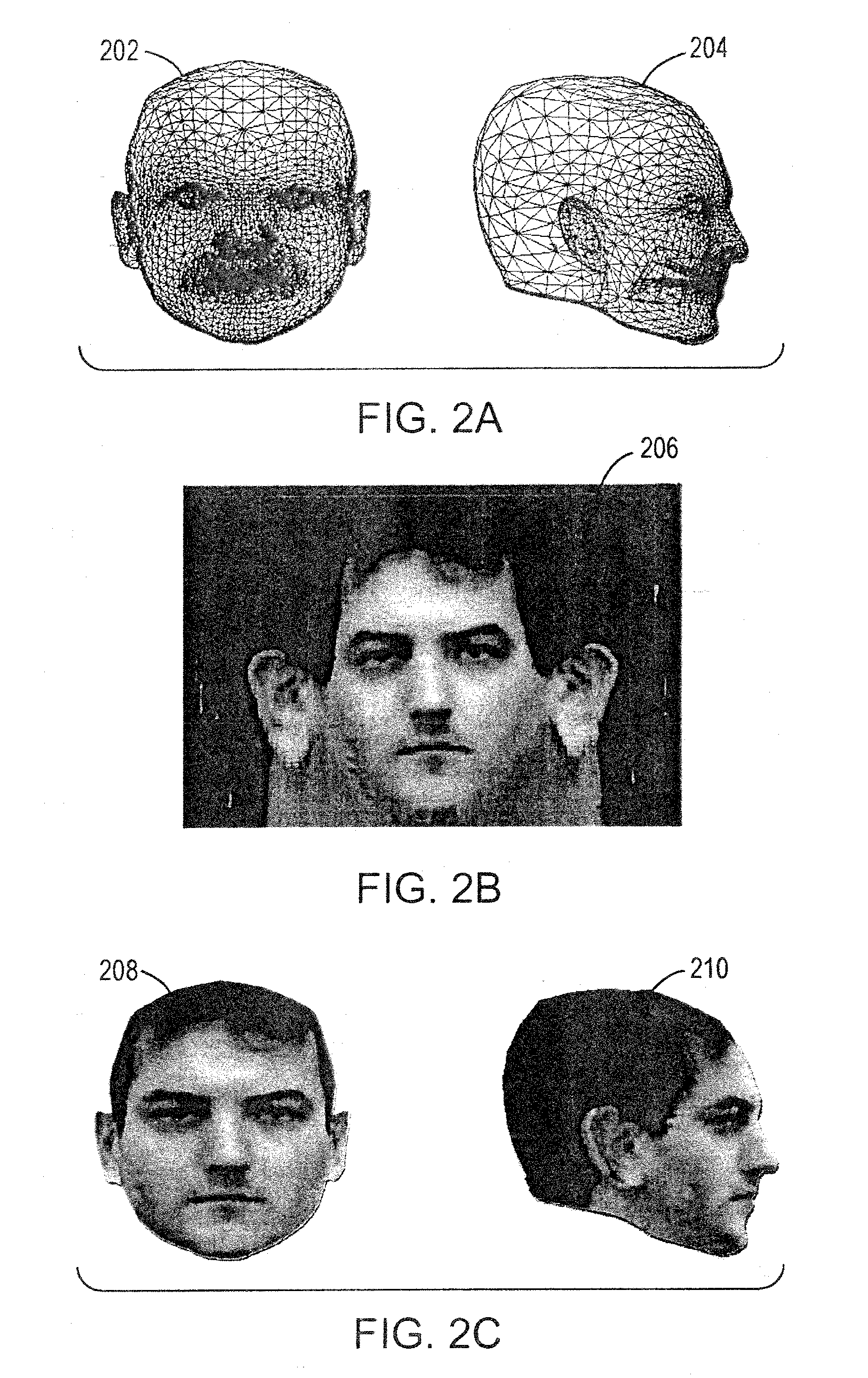
[0031]FIG. 1 illustrates the basic operation of the invention in the case where the 3D target multifeatured object is a face and the set of reference 3D representations are avatars. The matching process starts with a set of reference 3D avatars which represent, to the extent practicable, the range of different types of heads to be matched. For example, the avatars may include faces of men and women, faces with varying quantities and types of hair, faces of different ages, and faces representing different races. Typically the reference set includes numerous (e.g., several hundred or more) avatars, though the invention works with as few as one reference object, and as many for which storage space and compute time are available. In some situations, only a single reference avatar will be used. This case may arise, for example, when the best-fitting avatar has been selected manually, or by some other means, or when only one reference avatar is available. In FIG. 1, the source data of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com