Endoscopic working channel and method of making same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
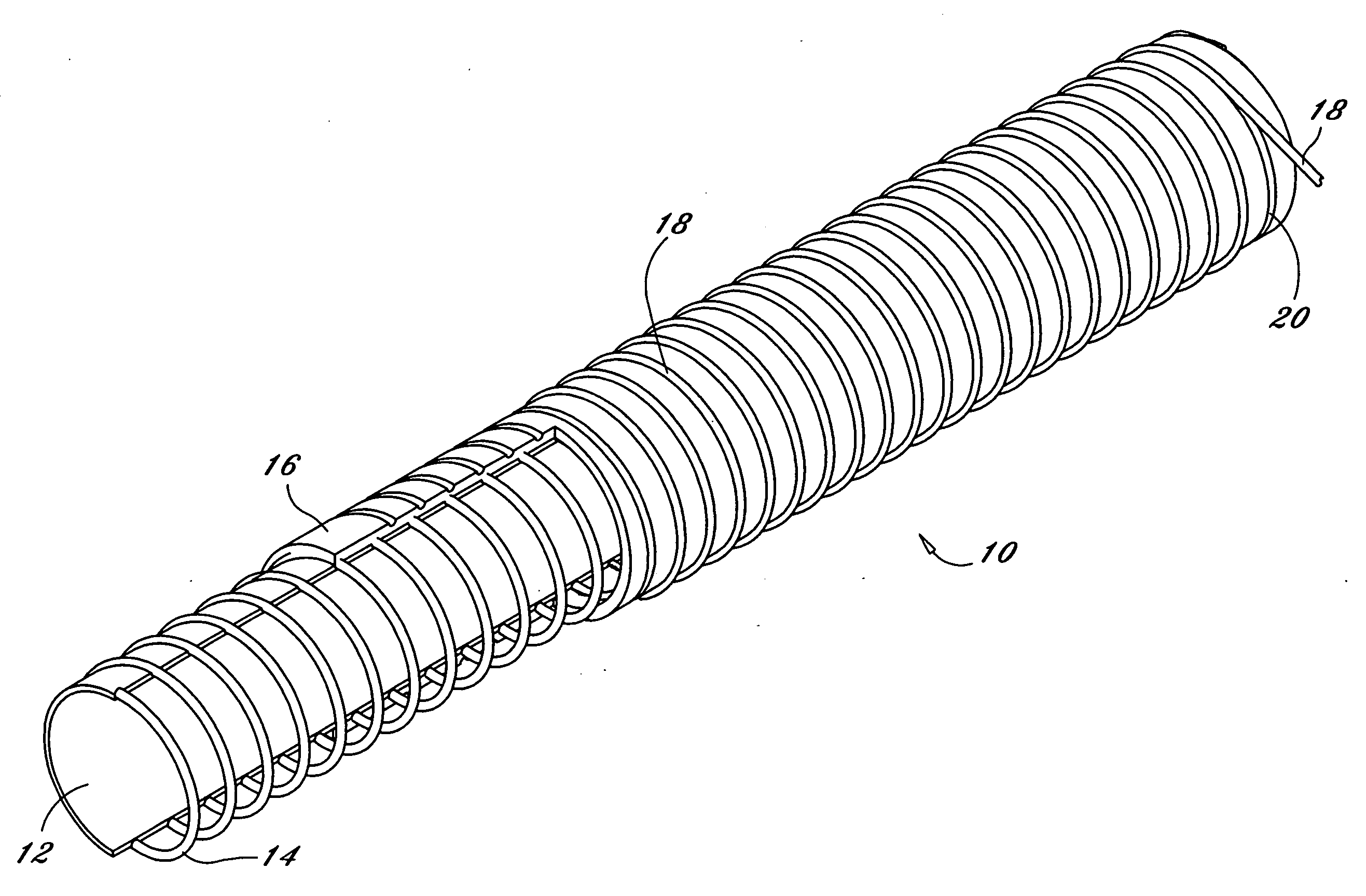
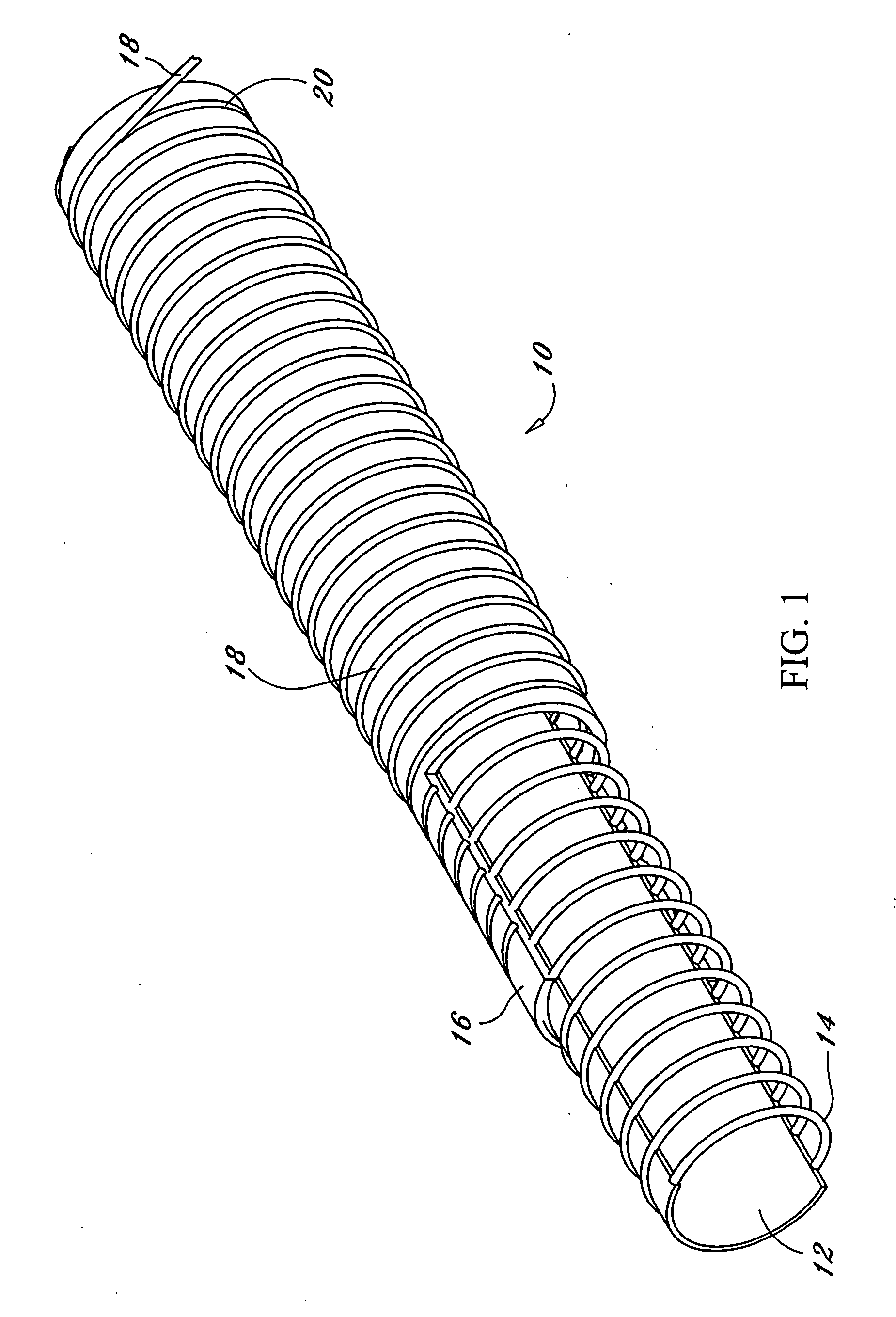
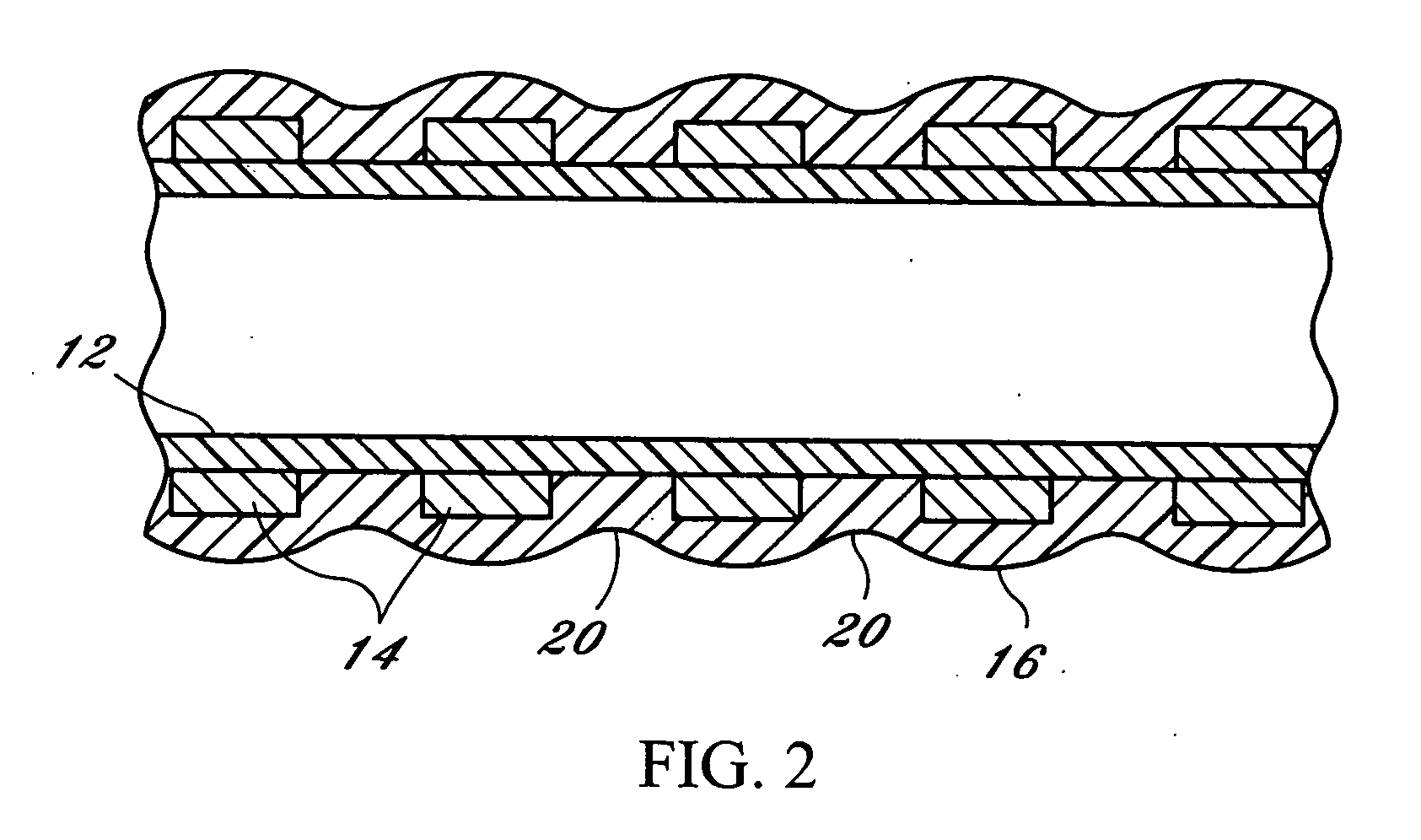
[0009]Reference now should be made to the drawings, in which the same reference numbers are used throughout the different figures to designate the same or similar components. FIGS. 1 and 2 are directed to an embodiment of an endoscopic working channel which includes an inner tubular structure or tube 12 fabricated from sintered, non-expanded or non-porous polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Typically, the density of this inner tubular structure is in the range of 1.8 to 2.2 g / cc. A typical wall thickness of the inner PTFE structure is between 0.0045 inches and 0.007 inches for use as an endoscopic working channel. Directly over this inner PTFE layer 12 is a secondary layer in the form of a flat (rectangular cross section) wire 14 which is helically wrapped around the non-porous PTFE layer in a single spiral wrap. This wire typically is made of stainless steel. The wire 14 functions as a spring and also provides radial support to the completed tubing during flexion. The wire 14 also prov...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com