Medical line securement device
a securement device and medical line technology, applied in the field of securement devices, can solve the problems of wasting valuable time and time spent by health care providers on tape application, fluid supply tube disconnection, and catheterization process often requiring relatively frequent disconnection between catheter and fluid supply tube,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
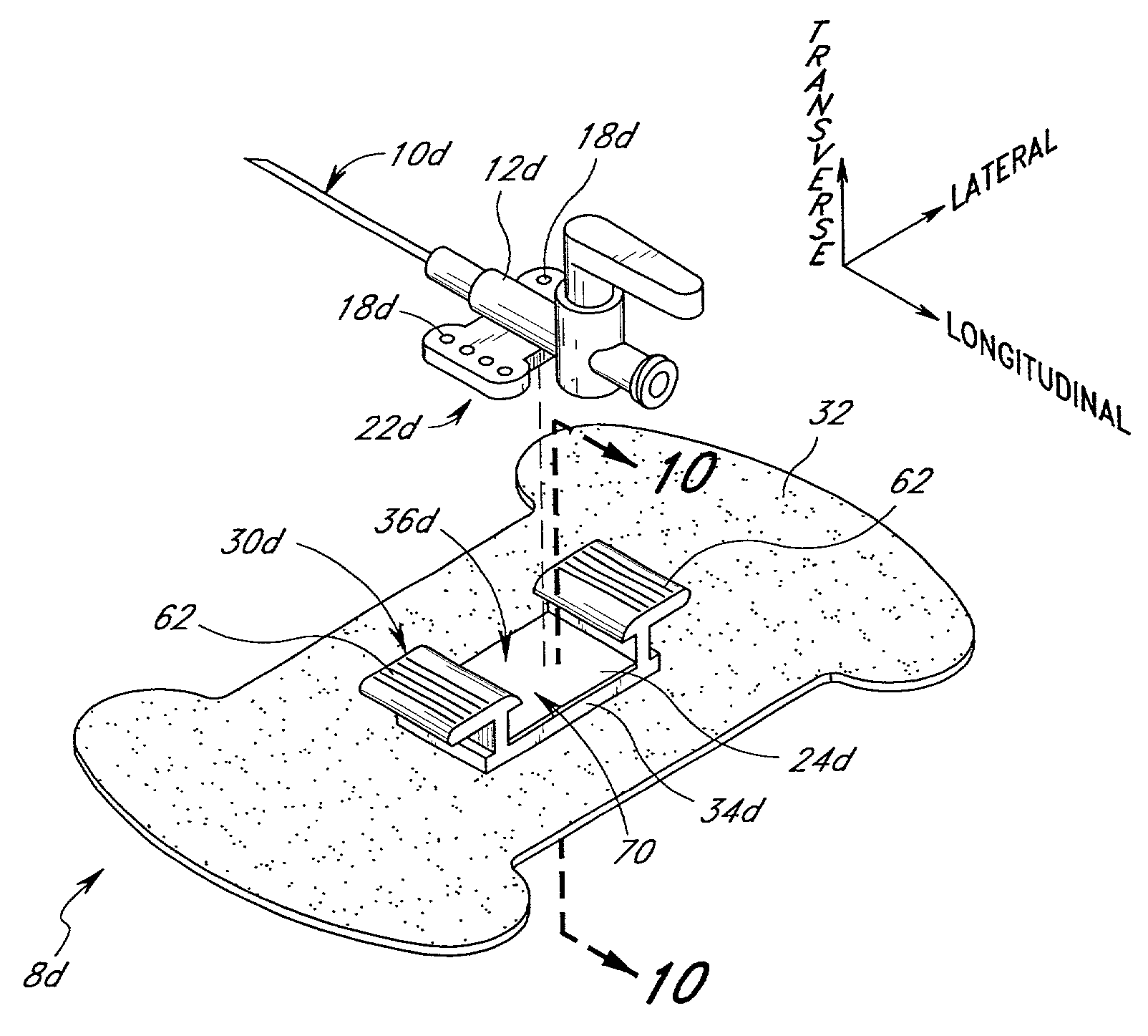
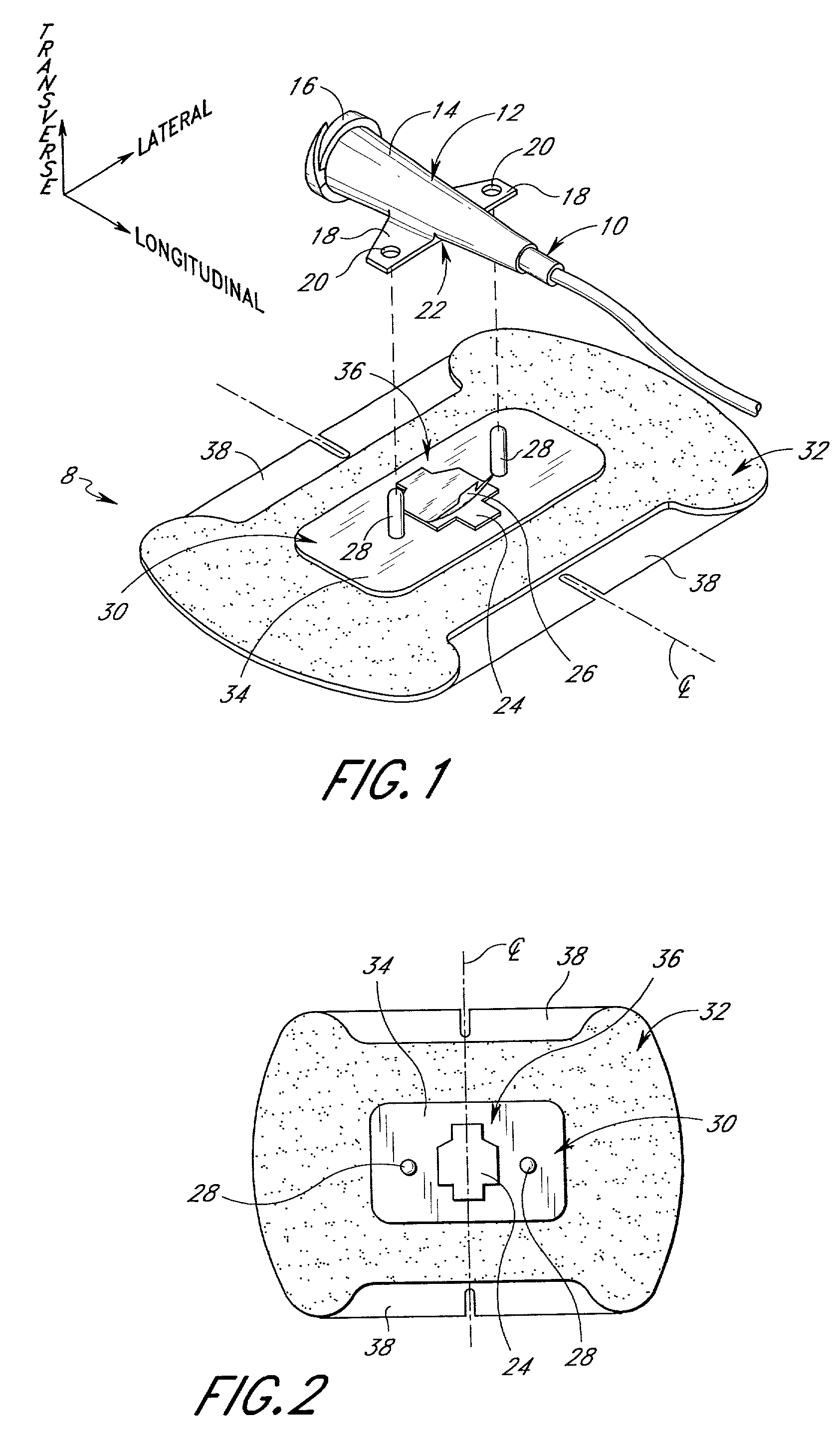
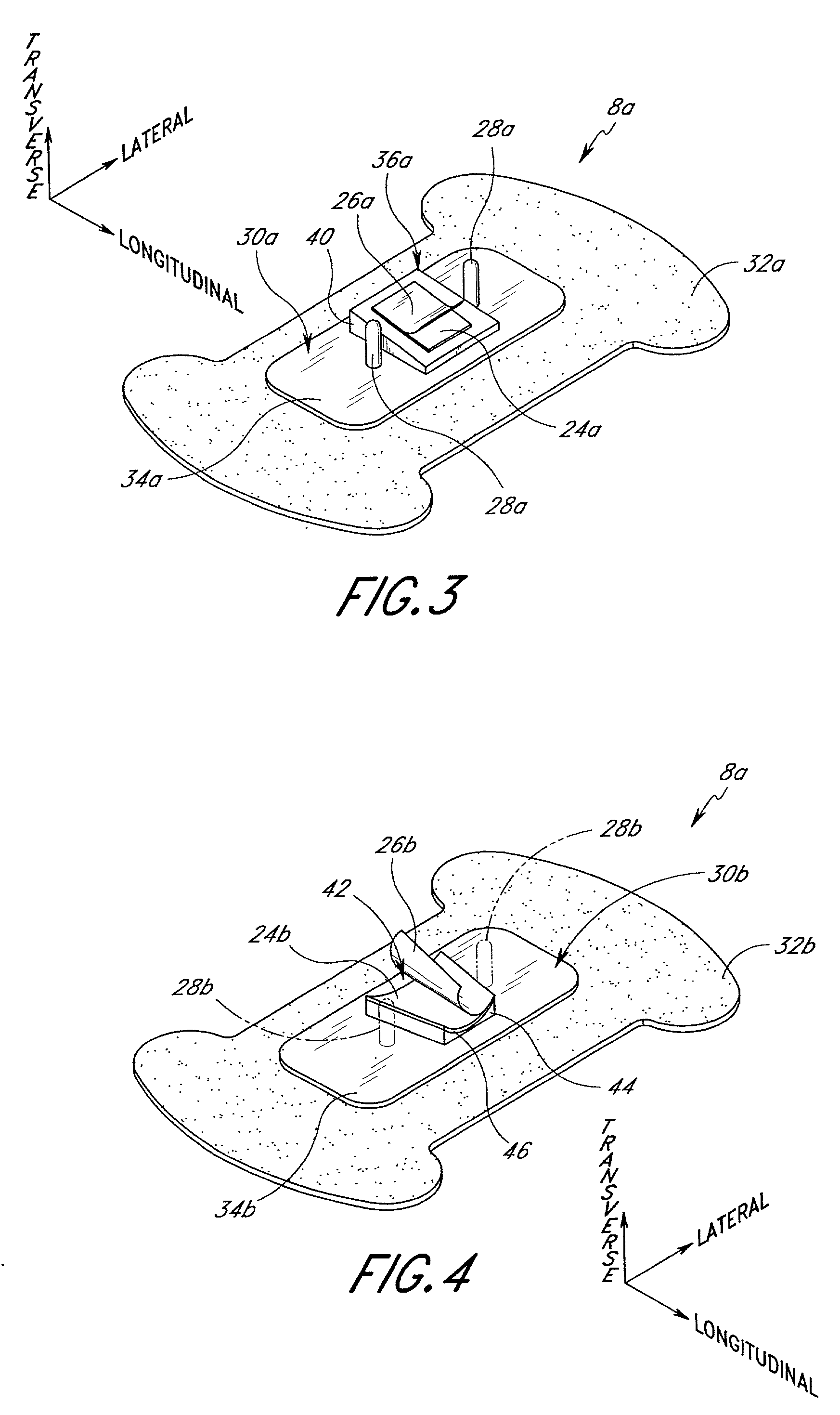
[0038] The present embodiments of the medical line securement device are disclosed in the context of an exemplary intravenous (IV) catheter. The principles of the present invention, however, are not limited to IV catheters. Instead, it will be understood by one of skill in this art, in view of the present disclosure, that the securement devices and retainers disclosed herein also can be successfully utilized in connection with other types of medical lines, including tubes for fluid communication and electrical wires. For example, but without limitation, the retainers disclosed herein can be adapted to retain CVCs, PICCs, Foley catheters, and hemodialysis catheters, surgical drainage tubes, feeding tubes, chest tubes, nasogastric tubes, scopes, as well as with electrical wires or cables connected to external or implanted electronic devices or sensors. One skilled in the art may also find additional applications for the devices and devices disclosed herein. Thus, the illustrations and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com