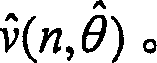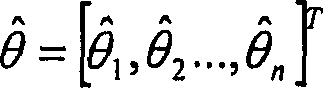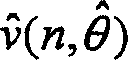Subtractive cancellation of harmonic noise
A Kalman filter, sinusoidal perturbation technology, applied in speech analysis, speech recognition, instrumentation, etc., can solve problems such as slowing down estimation, estimator unable to track changes in amplitude and phase, and not saving the content of the information-bearing spectrum
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] compensation method
[0032] The overall compensation method of the present invention is described below with reference to FIG. 1 , which proposes to eliminate noise in a disturbed signal by adding reference noise.
[0033] As can be seen from Fig. 1, the method proposed by the present invention estimates (2) and tracks the following parameters for each disturbance: in-phase amplitude, quadrature amplitude and frequency. This estimation is done recursively by an extended Kalman filter. Subsequently, based on the three estimated parameters (3), a reference signal (5) is generated (4) and subtracted (6) from the perturbed signal (1) to compensate for the Sinusoidal disturbance (9).
[0034] The reference signal used is an artificial signal (5) generated from a noise model (4) This artificial signal represents an estimate of the actual disturbance noise (9) superimposed on the information-bearing signal (8) s(n). The estimation of the reference signal (2) is done indi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com