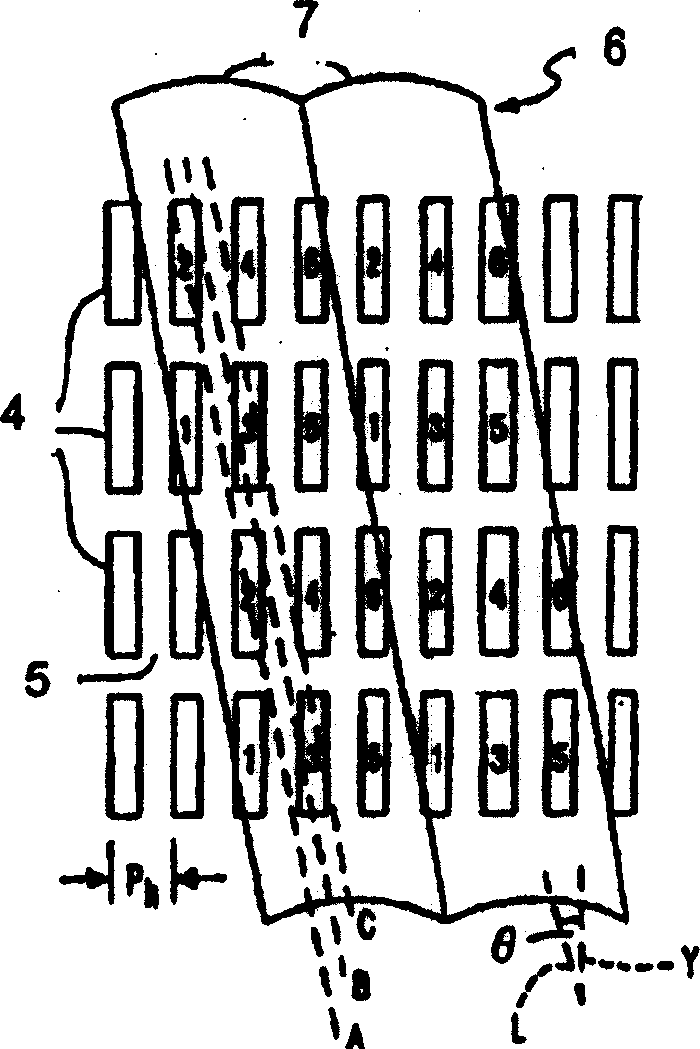Three-dimensional image display device
A technology of image display and display device, which is applied in the directions of image communication, food preservation, animal feed raw material preservation methods, etc. It can solve the problems of display obstacles, low definition, which cannot be said to have been fully improved, and achieve an improved balance of clarity , to prevent the effect of showing obstacles
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0137] In Example 1, making Figure 19 The multi-eye three-dimensional image display device shown. The two-dimensional image display device 14 is a liquid crystal display device, the light control unit 6 is provided on the front surface, and the backlight 16 is provided on the rear surface.
[0138] Specifically, in Example 1, a QUXGA-LCD panel (number of pixels 3200×2400, screen size 480 mm×360 mm) was used as a liquid crystal display device. In this liquid crystal display device 14, three sub-pixels of red, green, and blue can be independently driven. In addition, each sub-pixel of red, green, and blue has a horizontal length of 50 μm and a vertical length of 150 μm. In addition, a stripe arrangement is used for the color filter arrangement. It should be pointed out that in a common two-dimensional image display device, three sub-pixels such as red, green, and blue arranged horizontally form a pixel (a group of three), but in this example, the restriction .
[0139] The...
Embodiment 2
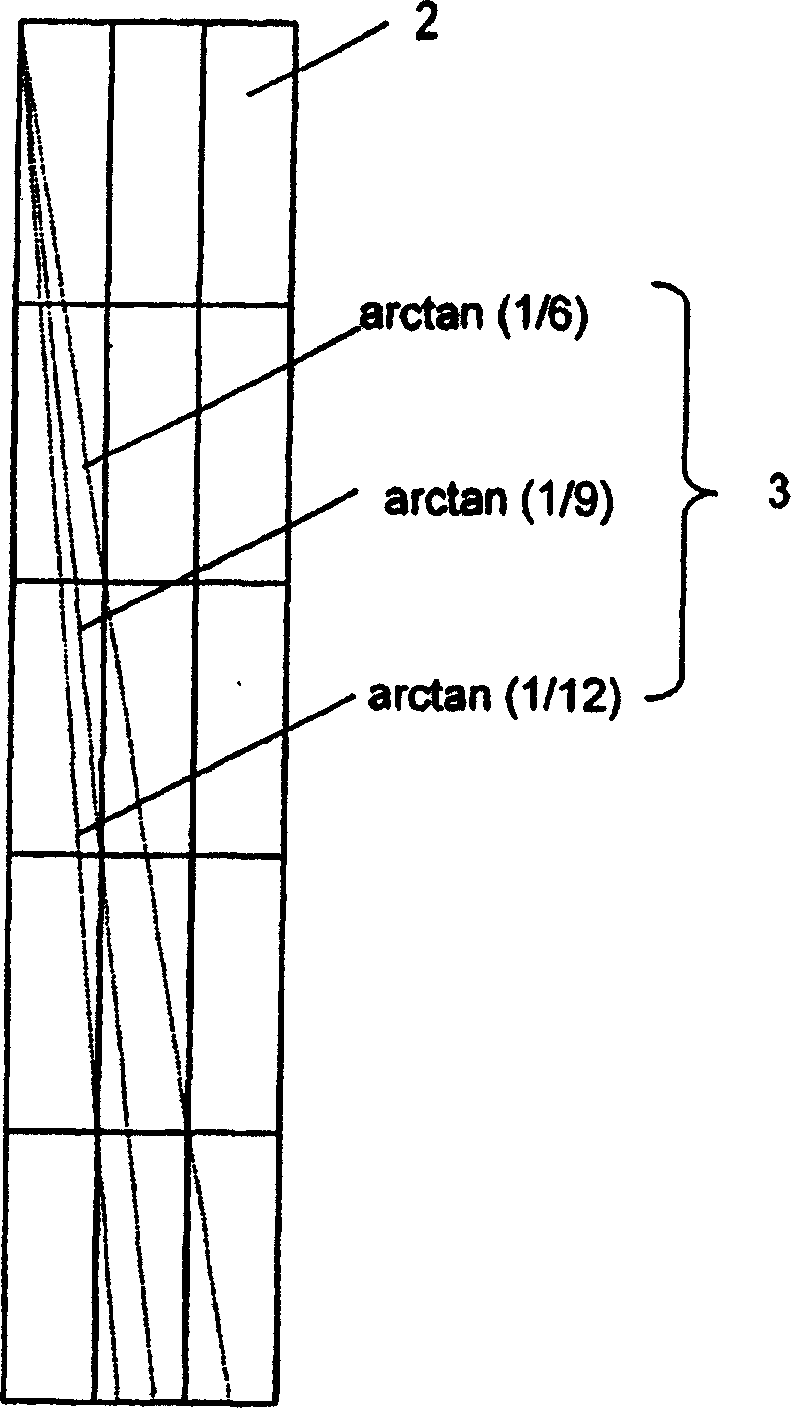
[0143] In this example 2, make Figure 19 An IP-type three-dimensional image display device of the structure shown. The exit pupil interval of the light control unit is designed to be an integer multiple of the sub-pixel interval of the image display device. Unlike the multi-eye type, there is no condensed point at the viewing distance. Differences from Embodiment 1 will be described below.
[0144] The horizontal pitch of lenses is designed to be 600 μm, which is four times the width of the sub-pixel, and the viewing distance is ±15 degrees. Accordingly, it is possible to secure a field of view equivalent to the width of the screen at a viewing distance of 1.0 m (an area where false images are not mixed and can be observed). The tilt angle of the lens is 14.0 degrees. In the viewing distance, set the gaze point in the center of the screen, (in CG, virtual) use the camera to pass through the parallel lens in the horizontal direction, and obtain 28 parallax images in the ver...
Embodiment 3
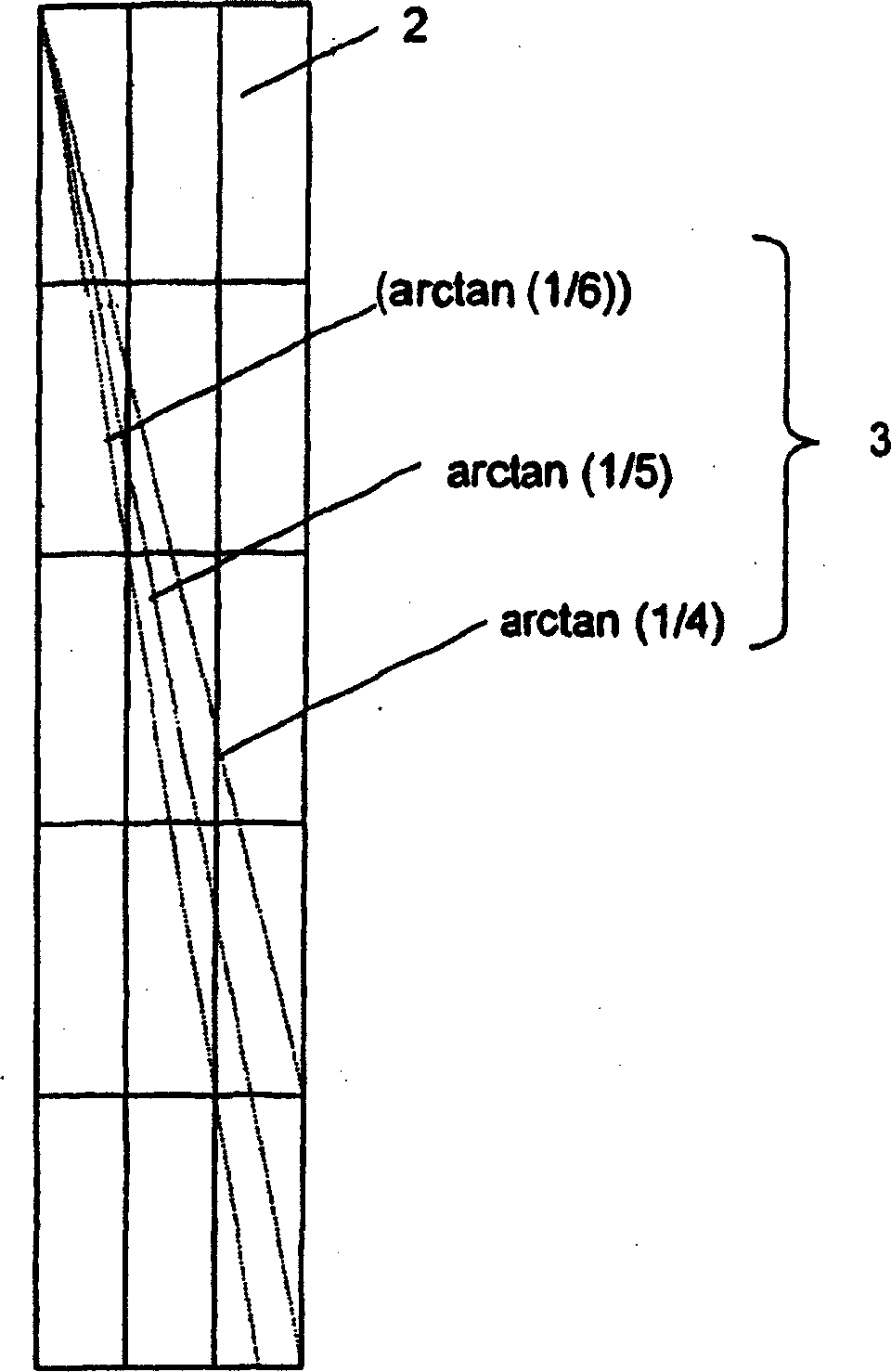
[0148] In the third embodiment, it is almost the same as the second embodiment, but adopts a design in which the number of reference parallaxes is increased to 25. The light control unit uses a lenticular lens designed so that the pixel position of the liquid crystal panel becomes the focal length. The horizontal spacing of the lenses is 750 μm, which is 15 times the sub-pixel width, and the inclination angle is 11.3 degrees.
[0149] In the viewing distance, 44 parallax images are obtained by parallel projection both vertically and horizontally with a camera whose center of the screen is set as the gaze point (virtual in CG). The resolution of the parallax image is 640(×RGB)×480. basically according to Figure 8 The mapping is to map the 640×RGB×480×25 disparity image. like Figure 12 As shown, the width of the three-dimensional image display pixels is shifted to the left in every five rows of three-dimensional image display pixels, and the column information is maintaine...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com